benign prostatic hyperplasia treatment in homeopathy
Understanding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as prostate gland enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in the size of the prostate gland. It is most common in aging men and can significantly impair quality of life because of its effect on urination. Although BPH is not cancerous and does not cause prostate cancer,
1) What is the prostate?
The prostate gland is an important organ in men, which is connected to the urinary and reproductive system. As men age, many men face prostate problems, the most common of which is BPH or enlarged prostate gland. - This condition can cause problems like difficulty in urinating, frequent urination and slow stream of urine. However, in many cases, prostate treatment is possible without surgery.
2) What are the causes and risk factors for prostate enlargement?
The exact cause of BPH is not fully known, but it is thought to be linked to hormonal changes that occur with aging. The male hormone, progesterone, decreases with age while estrogen levels may increase slightly. These hormonal changes are thought to play a role in prostate cell growth.

Risk factors for BPH include
-Age: It is rare in men under 40, but about 50% of men aged 51 to 60 have BPH,
-Family history: Having a close relative with prostate problems increases the risk.
Lifestyle factors: Obesity, lack of physical activity, and certain health conditions such as diabetes and heart disease are associated with a higher risk of BPH.

3) What are the symptoms of prostate?
BPH results from the pressure exerted on the urethra by the enlarged prostate. Common symptoms include: - Frequent urination,
- Difficulty urinating
- Weak or interrupted urination
- Weak or interrupted urination
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
4) How is prostate diagnosed?
Diagnosis of BPH begins with a physical examination. A digital rectal exam (DRE) allows the doctor to assess the size of the prostate. Other diagnostic tests may include:
- Urinalysis: To rule out infection or other conditions.
- Ultrasound: To evaluate prostate size and bladder function.
Treatment for BPH depends on the severity of symptoms and the extent to which it affects the patient's quality of life. Options include:
5) What are the treatment options for prostate?
Treatment for BPH depends on the severity of symptoms and the extent to which it affects the patient's quality of life. Options include:
- Lifestyle changes: Reducing alcohol consumption and regular exercise may help manage mild symptoms.
Stories

chronic pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियास ठीक करने के उपाय
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस एक बीमारी है जो आपके पैंक्रियास में हो सकती है। पैंक्रियास आपके पेट में एक लंबी ग्रंथि है जो भोजन को पचाने में आपकी मदद करती है। यह आपके रक्त प्रवाह में हार्मोन भी जारी करता है जो आपके शरीर को ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग करने में मदद करता है। यदि आपका पैंक्रियास क्षतिग्रस्त हो गया है, तो पाचन एंजाइम सामान्य रूप से आपकी छोटी आंत में नहीं जा सकते हैं और आपका शरीर ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग नहीं कर सकता है।
पैंक्रियास शरीर का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है जो हार्मोन इंसुलिन का उत्पादन करके रक्त शर्करा को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। यदि इस अंग को नुकसान होता है, तो इससे मानव शरीर में गंभीर समस्याएं हो सकती हैं। ऐसी ही एक समस्या है जब पैंक्रियास में सूजन हो जाती है, जिसे तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस कहा जाता है।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस पैंक्रियास की सूजन है जो लंबे समय तक रह सकती है। इससे पैंक्रियास और अन्य जटिलताओं को स्थायी नुकसान हो सकता है। इस सूजन से निशान ऊतक विकसित हो सकते हैं, जो इंसुलिन उत्पन्न करने वाली कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा सकते हैं। यह पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ वाले लगभग 45 प्रतिशत लोगों में मधुमेह का कारण बन सकता है। भारी शराब का सेवन भी वयस्कों में पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकता है। ऑटोइम्यून और आनुवंशिक रोग, जैसे सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस, कुछ लोगों में पुरानी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकते हैं।
उत्तर भारत में, ऐसे बहुत से लोग हैं जिनके पास पीने के लिए बहुत अधिक है और कभी-कभी एक छोटा सा पत्थर उनके पित्ताशय में फंस सकता है और उनके अग्न्याशय के उद्घाटन को अवरुद्ध कर सकता है। इससे उन्हें अपना खाना पचाने में मुश्किल हो सकती है। 3 हाल ही में एशिया-प्रशांत क्षेत्र के विभिन्न देशों में किए गए एक सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार दक्षिण भारत में पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ की व्यापकता प्रति 100,000 जनसंख्या पर 114-200 मामले हैं।
Chronic Pancreatitis Patient Cured Report
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण ?
-कुछ लोगों को पेट में दर्द होता है जो पीठ तक फैल सकता है। -यह दर्द मतली और उल्टी जैसी चीजों के कारण हो सकता है। -खाने के बाद दर्द और बढ़ सकता है। -कभी-कभी किसी के पेट को छूने पर दर्द महसूस हो सकता है। -व्यक्ति को बुखार और ठंड लगना भी हो सकता है। वे बहुत कमजोर और थका हुआ भी महसूस कर सकते हैं।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण ?
-पित्ताशय की पथरी -शराब
-रक्त में उच्च ट्राइग्लिसराइड का स्तर -रक्त में उच्च कैल्शियम का स्तर
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज कैसे किया जाता है?
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस नेक्रोसिस का उपचार उपचारात्मक है। आप कितने समय तक इस बीमारी से पीड़ित रहेंगे यह काफी हद तक आपकी उपचार योजना पर निर्भर करता है। ब्रह्म अनुसंधान पर आधारित चिकित्सकीय रूप से सिद्ध वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी के इलाज में अत्यधिक प्रभावी हैं। हमारे पास आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करने, सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों, रोग के पाठ्यक्रम का दस्तावेजीकरण करने, रोग के चरण, पूर्वानुमान और जटिलताओं को समझने की क्षमता है, हमारे पास अत्यधिक योग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है। फिर वे आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताएंगे, आपको एक उचित आहार योजना (क्या खाएं और क्या नहीं खाएं), व्यायाम योजना, जीवनशैली योजना और कई अन्य कारक प्रदान करेंगे जो आपके समग्र स्वास्थ्य में सुधार कर सकते हैं। पढ़ाना। व्यवस्थित उपचार रोग ठीक होने तक होम्योपैथिक औषधियों से उपचार करें। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, चाहे वह थोड़े समय के लिए हो या कई सालों से। हम सभी ठीक हो सकते हैं, लेकिन बीमारी के प्रारंभिक चरण में हम तेजी से ठीक हो जाते हैं। पुरानी या देर से आने वाली या लंबे समय तक चलने वाली बीमारियों को ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगता है। समझदार लोग इस बीमारी के लक्षण दिखते ही इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं। इसलिए, यदि आपको कोई असामान्यता नज़र आती है, तो कृपया तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।

Acute Necrotizing pancreas treatment in hindi
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ ?
आक्रामक अंतःशिरा द्रव पुनर्जीवन, दर्द प्रबंधन, और आंत्र भोजन की जल्द से जल्द संभव शुरुआत उपचार के मुख्य घटक हैं। जबकि उपरोक्त सावधानियों से बाँझ परिगलन में सुधार हो सकता है, संक्रमित परिगलन के लिए अतिरिक्त उपचार की आवश्यकता होती है।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लक्षण ? - बुखार - फूला हुआ पेट - मतली और दस्त तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण ?
- अग्न्याशय में चोट - उच्च रक्त कैल्शियम स्तर और रक्त वसा सांद्रता
ऐसी स्थितियाँ जो अग्न्याशय को प्रभावित करती हैं और आपके परिवार में चलती रहती हैं, उनमें सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस और अन्य आनुवंशिक विकार शामिल हैं जिनके परिणामस्वरूप बार-बार अग्नाशयशोथ होता है|
क्या एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रिएटाइटिस का इलाज होम्योपैथी से संभव है ?
हां, होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनकर एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज संभव है। होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनने से आपको इन दवाओं का कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं होगा और यह समस्या को जड़ से खत्म कर देता है, इसीलिए आपको अपने एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के इलाज के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार का ही चयन करना चाहिए।
आप तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ से कैसे छुटकारा पा सकते हैं ?
शुरुआती चरण में सर्वोत्तम उपचार चुनने से आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस से छुटकारा मिल जाएगा। होम्योपैथिक उपचार का चयन करके, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे विश्वसनीय उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करता है। एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार सबसे अच्छा इलाज है। जैसे ही आप एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक करने के लिए अपना उपचार शुरू करेंगे, आपको निश्चित परिणाम मिलेंगे।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार से तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ का इलाज संभव है। आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, इसका उपचार योजना पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ता है। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कब से अपनी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, या तो हाल ही में या कई वर्षों से - हमारे पास सब कुछ ठीक है, लेकिन बीमारी के शुरुआती चरण में, आप तेजी से ठीक हो जाएंगे। पुरानी स्थितियों के लिए या बाद के चरण में या कई वर्षों की पीड़ा के मामले में, इसे ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगेगा। बुद्धिमान व्यक्ति हमेशा इस बीमारी के किसी भी लक्षण को देखते ही तुरंत इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं, इसलिए जैसे ही आपमें कोई असामान्यता दिखे तो तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एवं रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
ब्रह्म अनुसंधान आधारित, चिकित्सकीय रूप से प्रमाणित, वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी को ठीक करने में बहुत प्रभावी है। हमारे पास सुयोग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है जो आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करती है, रोग की प्रगति के साथ-साथ सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों को रिकॉर्ड करती है, इसकी प्रगति के चरणों, पूर्वानुमान और इसकी जटिलताओं को समझती है। उसके बाद वे आपको आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताते हैं, आपको उचित आहार चार्ट [क्या खाएं या क्या न खाएं], व्यायाम योजना, जीवन शैली योजना प्रदान करते हैं और कई अन्य कारकों के बारे में मार्गदर्शन करते हैं जो व्यवस्थित प्रबंधन के साथ आपकी सामान्य स्वास्थ्य स्थिति में सुधार कर सकते हैं। जब तक यह ठीक न हो जाए तब तक होम्योपैथिक दवाओं से अपनी बीमारी का इलाज करें।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लिए आहार ?
कुपोषण और पोषण संबंधी कमियों को रोकने के लिए, सामान्य रक्त शर्करा के स्तर को बनाए रखने और मधुमेह, गुर्दे की समस्याओं और पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ से जुड़ी अन्य स्थितियों को रोकने या बेहतर ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए, अग्नाशयशोथ की तीव्र घटना से बचना महत्वपूर्ण है।
यदि आप एक स्वस्थ आहार योजना की तलाश में हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। हमारे विशेषज्ञ आपकी व्यक्तिगत आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप एक योजना बनाने में आपकी सहायता कर सकते हैं

Pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ?
जब पैंक्रियाटाइटिसमें सूजन और संक्रमण हो जाता है तो इससे पैंक्रिअटिटिस नामक रोग हो जाता है। पैंक्रियास एक लंबा, चपटा अंग है जो पेट के पीछे पेट के शीर्ष पर छिपा होता है। पैंक्रिअटिटिस उत्तेजनाओं और हार्मोन का उत्पादन करके पाचन में मदद करता है जो आपके शरीर में ग्लूकोज के प्रसंस्करण को विनियमित करने में मदद करते हैं।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण:
-पेट के ऊपरी भाग में दर्द होना। -बेकार वजन घटाना. -पेट का ख़राब होना.
-शरीर का असामान्य रूप से उच्च तापमान। -पेट को छूने पर दर्द होना। -तेज़ दिल की धड़कन. -हाइपरटोनिक निर्जलीकरण.
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण:
-पित्ताशय में पथरी. -भारी शराब का सेवन.
-भारी खुराक वाली दवाएँ। -हार्मोन का असंतुलन. -रक्त में वसा जो ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स का कारण बनता है। -आनुवंशिकता की स्थितियाँ. -पेट में सूजन ।
क्या होम्योपैथी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक कर सकती है?
हाँ, होम्योपैथीपैंक्रियाटाइटिसको ठीक कर सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको पैंक्रिअटिटिस के लिए सबसे भरोसेमंद उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करती है।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा उपचार क्या है?
यदि पैंक्रियाज अच्छी तरह से काम नहीं कर रहा है तो होम्योपैथिक उपचार वास्तव में बेहतर होने में मदद करने का एक अच्छा तरीका है। जब आप उपचार शुरू करते हैं, तो आप जल्दी परिणाम देखेंगे। बहुत सारे लोग इस इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जा रहे हैं और वे वास्तव में अच्छा कर रहे हैं। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपके पैंक्रियाज के को बेहतर बनाने में मदद करने के लिए आपको सबसे तेज़ और सुरक्षित तरीका प्रदान करना सुनिश्चित करती है।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
बीमार होने पर लोगों को बेहतर महसूस कराने में मदद करने के लिए हमारे पास एक विशेष तरीका है। हमारे पास वास्तव में स्मार्ट डॉक्टर हैं जो ध्यान से देखते हैं और नोट करते हैं कि बीमारी व्यक्ति को कैसे प्रभावित कर रही है। फिर, वे सलाह देते हैं कि क्या खाना चाहिए, व्यायाम करना चाहिए और स्वस्थ जीवन कैसे जीना चाहिए। वे व्यक्ति को ठीक होने में मदद करने के लिए विशेष दवा भी देते हैं। यह तरीका कारगर साबित हुआ है!
Tips

dehydration treatment in homeopathy
1. Dehydration treatment
When the body loses more fluid than it takes in, it causes an imbalance in electrolytes and fluids needed for normal body function. This can be due to excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, or not drinking enough water.
While severe dehydration requires medical attention, mild to moderate dehydration can often be treated effectively at home without the use of drugs or medication. Natural remedies and lifestyle changes can help restore hydration and balance in a safe and gentle way.
1. Replenish water
The most important step in treating dehydration is to drink water. Clean water is the best way to rehydrate the body. Drink water slowly and in small sips rather than drinking large amounts at once, especially if nausea occurs. -Drinking small amounts at regular intervals allows the body to absorb fluids more effectively.
2. Consume natural electrolytes
When we sweat due to illness, we also lose essential electrolytes like sodium, potassium and magnesium. Without these, just drinking water is not enough. You can make an electrolyte drink at home by mixing the following:
- 1 liter of clean water - 6 teaspoons of sugar
- 1/2 teaspoon of salt This solution helps a lot in balancing electrolytes and can be more effective than plain water.
- Coconut water is a natural alternative as it has a good balance of sodium, potassium and other electrolytes.
3. Eat hydrating foods
Some foods are high in water and can help restore hydration naturally. For example,
watermelon, cucumber, oranges, lettuce - Some foods in your diet can provide both fluids and essential nutrients.
4. Avoid dehydrating substances
- Coffee, energy drinks
- Alcohol
- Salty snacks
These can worsen fluid loss. Sticking to water and natural fluids is the best option until hydration is restored.
5. Rest
If the dehydration is caused by heat or strenuous physical activity, resting in a cool, shady area is a must. - Avoiding excessive sweating or exertion helps the body recover more easily. - Using a fan, cool cloth or taking a warm bath also helps regulate body temperature
6. Monitor symptoms
It is important to monitor your condition. Signs of dehydration include: - Increased urine with a light color
- Decreased thirst
If symptoms persist or worsen - such as dizziness, very dark urine, it is important to seek medical help immediately.
Final Thoughts
Dehydration can often be treated effectively without medication or drugs, especially when it's caught early.
-While natural remedies are helpful, it's important to see a doctor if symptoms become severe or don't respond to home remedies

hamare sarir ke liye sabji ke labh
सब्जियाँ हमारे आहार का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा हैं। इनमें कई प्रकार के विटामिन, खनिज, एंटीऑक्सीडेंट और फाइबर होते हैं, जो शरीर को स्वस्थ बनाए रखते हैं। सब्जियों का सेवन न केवल रोगों से बचाव करता है बल्कि संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य को भी बनाए रखता है।
सब्जियों के प्रकार और उनके लाभ
1. हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ (Leafy Green Vegetables)
हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ पोषण से भरपूर होती हैं और शरीर को कई तरह के आवश्यक तत्व प्रदान करती हैं।
-1. पालक (Spinach) लाभ: आयरन, कैल्शियम और फाइबर से भरपूर। हड्डियों और मांसपेशियों को मजबूत बनाता है। एनीमिया और कब्ज से बचाव करता है।
2. सरसों के पत्ते (Mustard Greens)
-लाभ: -हड्डियों के लिए फायदेमंद। -इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है। -त्वचा और बालों को स्वस्थ रखता है।
3. मेथी (Fenugreek Leaves)
-लाभ: -डायबिटीज को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। -पाचन को सुधारता है और भूख बढ़ाता है।
4. धनिया और पुदीना (Coriander & Mint Leaves)
-लाभ: -पाचन को सुधारते हैं। -विषाक्त पदार्थों को बाहर निकालते हैं। -त्वचा को चमकदार बनाते हैं।
2. जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ (Root Vegetables)
जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ फाइबर और आवश्यक खनिजों से भरपूर होती हैं।
5. गाजर (Carrot)

sarir ke liye vitamin or unke labh
हमारे शरीर के लिए सभी विटामिन और उनके लाभ
विटामिन हमारे शरीर के लिए आवश्यक पोषक तत्व हैं, जो शरीर के विभिन्न कार्यों को सुचारू रूप से चलाने में मदद करते हैं। ये सूक्ष्म पोषक तत्व होते हैं, लेकिन शरीर में इनकी भूमिका बहुत महत्वपूर्ण होती है। विटामिन की कमी से कई स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ हो सकती हैं, इसलिए संतुलित आहार लेना जरूरी है।
विटामिन कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
-विटामिन दो प्रकार के होते हैं: -1. वसा में घुलनशील विटामिन (Fat-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में वसा में संग्रहित होते हैं और जरूरत पड़ने पर उपयोग किए जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन A, D, E और K आते हैं।
-2. जल में घुलनशील विटामिन (Water-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में जमा नहीं होते और मूत्र के माध्यम से बाहर निकल जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन C और सभी B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन आते हैं।
विटामिन और उनके लाभ
1. विटामिन A (रेटिनॉल, बीटा-कैरोटीन)
भूमिका:
आँखों की रोशनी को बनाए रखता है।
त्वचा और इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है।
हड्डियों और दांतों के विकास में सहायक है।
स्रोत:
गाजर पालकआम, शकरकंद, डेयरी उत्पाद, अंडे, मछली का तेल।
कमी के प्रभाव:
रतौंधी (नाइट ब्लाइंडनेस)
त्वचा में रूखापन
रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी
---
2. विटामिन B-कॉम्प्लेक्स (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12)
B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र और रक्त निर्माण में मदद करते हैं। B1 (थायमिन)
भूमिका: ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र के कार्यों में सहायक।
स्रोत: साबुत अनाज, बीन्स, सूरजमुखी के बीज, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: कमजोरी, भूख न लगना, तंत्रिका तंत्र की समस्या।
B2 (राइबोफ्लेविन)
भूमिका: त्वचा, आँखों और ऊर्जा उत्पादन के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: दूध, दही, अंडे, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: होंठों में दरारें, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B3 (नियासिन)
भूमिका: कोलेस्ट्रॉल को नियंत्रित करता है और पाचन में सहायक होता है।
स्रोत: मूंगफली, मशरूम, टमाटर, चिकन, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा रोग, मानसिक कमजोरी। B5 (पैंटोथेनिक एसिड)
भूमिका: हार्मोन उत्पादन और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: मशरूम, एवोकाडो, दूध, ब्रोकली।
कमी के प्रभाव: थकान, सिरदर्द।
B6 (पाइरिडोक्सिन)
भूमिका: तंत्रिका तंत्र और प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को मजबूत करता है।
स्रोत: केला, चिकन, सोयाबीन, आलू।
कमी के प्रभाव: अवसाद, त्वचा रोग।
B7 (बायोटिन)
भूमिका: बालों और त्वचा के स्वास्थ्य को बनाए रखता है।
स्रोत: अंडे, मूंगफली, फूलगोभी।
कमी के प्रभाव: बाल झड़ना, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B9 (फोलिक एसिड)
भूमिका: डीएनए निर्माण और गर्भावस्था में जरूरी।
स्रोत: दालें, हरी सब्जियाँ, बीन्स। कमी के प्रभाव: एनीमिया, जन्म दोष।
B12 (कोबालामिन)
भूमिका: लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं और तंत्रिका तंत्र के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: मांस, अंडे, डेयरी उत्पाद। कमी के प्रभाव: स्मरण शक्ति की कमजोरी, एनीमिया।
---
3. विटामिन C (एस्कॉर्बिक एसिड)
भूमिका: इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है, त्वचा को चमकदार बनाता है, और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: संतरा, नींबू, स्ट्रॉबेरी, टमाटर, हरी मिर्च।
कमी के प्रभाव: स्कर्वी, मसूड़ों से खून आना, रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी।
---
4. विटामिन D (कोलेकल्सीफेरोल)
भूमिका: हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाता है और कैल्शियम के अवशोषण में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: सूर्य का प्रकाश, मछली, अंडे, दूध।
कमी के प्रभाव: हड्डियों में कमजोरी, रिकेट्स।
---
5. विटामिन E (टोकोफेरॉल)
भूमिका: एंटीऑक्सीडेंट के रूप में कार्य करता है और त्वचा तथा बालों के लिए लाभदायक है। स्रोत: बादाम, सूरजमुखी के बीज, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा की समस्याएँ, कमजोरी।
---
6. विटामिन K (फायलोक्विनोन)
भूमिका: रक्त को थक्का जमाने (ब्लड क्लॉटिंग) में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: पालक, ब्रोकोली, हरी सब्जियाँ।
कमी के प्रभाव: चोट लगने पर खून न रुकना। ---
निष्कर्ष
शरीर को सभी विटामिनों की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि सभी अंग सही से काम कर सकें। इनके लिए संतुलित आहार लेना बहुत जरूरी है। यदि विटामिन की कमी हो, तो डॉक्टर से परामर्श लेकर सप्लीमेंट्स भी लिए जा सकते हैं। लेकिन, प्राकृतिक स्रोतों से विटामिन प्राप्त करना हमेशा सबसे अच्छा होता है।
-आपके शरीर की जरूरतों के अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक सेंटर में भी विटामिन डेफिशिएंसी का होम्योपैथिक उपचार उपलब्ध है। यदि आपको कोई लक्षण महसूस हो रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक से संपर्क करें और स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर बनाएँ।
Testimonials

body weakness treatment
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से 10 महीने में चमत्कारी इलाज: एक मरीज की कहानी
आज के समय में जब लोग तरह-तरह की बीमारियों से जूझ रहे हैं, तब होम्योपैथी चिकित्सा कई मरीजों के लिए आशा की किरण बन रही है। ऐसी ही एक प्रेरणादायक कहानी है एक मरीज की, जिसने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के माध्यम से 10 महीने में अपनी बीमारी से निजात पाई।
शुरुआत में थी थकान और शरीर में भारीपन
मरीज ने बताया, "मुझे कई दिनों से शरीर में थकान, भारीपन और बेचैनी महसूस हो रही थी। यह परेशानी धीरे-धीरे इतनी बढ़ गई कि रोजमर्रा के काम भी कठिन लगने लगे। मेरी माँ पहले से ही ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी क्लीनिक में इलाज करा रही थीं। उन्होंने बताया कि उन्हें वेरीकोज वेन्स की समस्या थी और यहाँ के इलाज से उन्हें बहुत लाभ हुआ था। उनकी सलाह पर मैं भी यहाँ आया।"
होम्योपैथी इलाज का असर मात्र एक सप्ताह में
मरीज के अनुसार, "जब मैंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा से परामर्श लिया और उनकी सलाह के अनुसार दवाएं लेना शुरू किया, तो सिर्फ एक हफ्ते के भीतर ही मुझे सुधार महसूस होने लगा। मेरी थकान कम हो गई, शरीर की ऊर्जा बढ़ने लगी और पहले की तुलना में मैं ज्यादा सक्रिय महसूस करने लगा।"
लगातार 10 महीने तक किया उपचार, मिली पूरी राहत
मरीज ने लगातार 10 महीने तक ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाएं लीं और सभी निर्देशों का पालन किया। उन्होंने कहा, "लगभग 15 दिनों के अंदर ही मेरी स्थिति में काफी सुधार हुआ और अब 10 महीने बाद मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ महसूस कर रहा हूँ। यह सब डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा और ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाओं की वजह से संभव हुआ।"
होम्योपैथी: सभी बीमारियों के लिए वरदान
मरीज ने आगे कहा, "इस क्लिनिक का माहौल बहुत अच्छा है और इलाज का तरीका बेहद प्रभावी है। यहाँ की दवाएँ बहुत असरदार हैं और मुझे इनके इस्तेमाल से कोई साइड इफेक्ट भी नहीं हुआ। यह सच में होम्योपैथी का सबसे बेहतरीन केंद्र है। मैं सभी मरीजों से अनुरोध करूंगा कि अगर वे किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान हैं, तो एक बार ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी का इलाज जरूर लें। यह एक बीमार मरीजों के लिए किसी स्वर्ग से कम नहीं है।"
निष्कर्ष
इस मरीज की कहानी यह साबित करती है कि सही चिकित्सा और सही मार्गदर्शन से कोई भी बीमारी ठीक हो सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में न केवल आधुनिक चिकित्सा पद्धति का समावेश है, बल्कि यहाँ मरीजों की समस्याओं को गहराई से समझकर उनका संपूर्ण इलाज किया जाता है। यदि आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी एक बेहतरीन विकल्प हो सकता है।

acute pancreatitis ka ilaaj
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: एक मरीज की जीवन बदलने वाली कहानी
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस: एक गंभीर समस्या
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में तीव्र सूजन हो जाती है। जब यह समस्या उत्पन्न होती है, तो मरीज को शुरुआत में इसकी जानकारी नहीं होती, लेकिन दर्द इतना असहनीय होता है कि उसे तुरंत अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की आवश्यकता पड़ती है। इस स्थिति का मुख्य कारण अनुचित जीवनशैली, जंक फूड, शराब का सेवन, ऑटोइम्यून बीमारियां, कुछ रसायन और विकिरण हो सकते हैं। यदि समय रहते सही इलाज नहीं किया गया, तो यह स्थिति क्रॉनिक पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस में बदल सकती है।
अमन बाजपेई की प्रेरणादायक यात्रा
मैं, अमन बाजपेई, पिछले 1.5 वर्षों से एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का मरीज था। यह समय मेरे लिए बेहद कठिन था। मैं बहुत परेशान था, खाना खाने तक के लिए तरस गया था। पिछले 7-8 महीनों में मैंने रोटी तक नहीं खाई, केवल खिचड़ी और फल खाकर गुजारा कर रहा था। बार-बार मुझे इस बीमारी के हमले झेलने पड़ रहे थे। हर 5-10 दिनों में दवा लेनी पड़ती थी, लेकिन कोई लाभ नहीं हो रहा था।
इस बीमारी के इलाज में मैंने 6-7 लाख रुपये खर्च कर दिए। दिल्ली और झांसी समेत कई बड़े अस्पतालों में इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई राहत नहीं मिली। मेरा वजन 95 किलो से घटकर 55 किलो हो गया और मैं बहुत कमजोर हो गया था। तभी मुझे सोशल मीडिया के माध्यम से ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के बारे में पता चला।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: उम्मीद की एक नई किरण
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी वह जगह है जहां कम खर्च में उत्कृष्ट इलाज संभव है। मैंने आज तक किसी भी डॉक्टर या अस्पताल में इतना अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं देखा। डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा सर ने मुझे एक नई जिंदगी दी। पहले मुझे लगा था कि मैं शायद कभी ठीक नहीं हो पाऊंगा, लेकिन आज मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ हूं।
मैं सभी मरीजों को यही सलाह दूंगा कि वे पैसे की बर्बादी न करें और सही इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जाएं। यह भारत में एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा अस्पताल है। मेरे लिए डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा किसी देवता से कम नहीं हैं।
वैज्ञानिक रूप से प्रमाणित उपचार पद्धति
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के विशेषज्ञों ने शोध आधारित एक विशेष उपचार पद्धति विकसित की है, जिससे न केवल लक्षणों में सुधार होता है बल्कि बीमारी को जड़ से ठीक किया जाता है। हजारों मरीज इस उपचार का लाभ ले रहे हैं और उनकी मेडिकल रिपोर्ट में भी उल्लेखनीय सुधार देखा गया है।
यदि आप भी इस बीमारी से जूझ रहे हैं और सही इलाज की तलाश कर रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। यह न केवल बीमारी को बढ़ने से रोकता है बल्कि इसे जड़ से ठीक भी करता है।

urticaria ka ilaaj
रेणुका बहन श्रीमाली की प्रेरणादायक कहानी: 10 साल की तकलीफ से छुटकारारेणुका बहन श्रीमाली पिछले 10 वर्षों से एक गंभीर समस्या से जूझ रही थीं। उन्हें जब भी कुछ खाने की कोशिश करतीं, उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और अत्यधिक खुजली होने लगती थी। इस समस्या के कारण वे बहुत परेशान थीं और 10 वर्षों तक कुछ भी सही तरीके से नहीं खा पाती थीं। उन्होंने कई जगहों पर इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई भी उपचार कारगर नहीं हुआ।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर से नई उम्मीदआखिरकार, 17 मई 2021 को उन्होंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में अपना ट्रीटमेंट शुरू किया। पहले से निराश हो चुकीं रेणुका बहन के लिए यह एक नई उम्मीद की किरण थी।एक साल में चमत्कारी सुधारट्रीटमेंट शुरू करने के बाद, धीरे-धीरे उनके स्वास्थ्य में सुधार होने लगा। एक साल के भीतर उन्होंने अपने आहार में वे सभी चीजें फिर से शुरू कर दीं, जिन्हें वे पहले नहीं खा पाती थीं। पहले जहाँ कोई भी चीज खाने से उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और खुजली होती थी, वहीं अब वे बिना किसी परेशानी के सामान्य जीवन जी रही हैं।ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर का योगदान
रेणुका बहन का कहना है कि यह इलाज उनके लिए किसी चमत्कार से कम नहीं था। उन्होंने अपनी पुरानी जीवनशैली को फिर से अपनाया और अब वे पूरी तरह से स्वस्थ महसूस कर रही हैं। उनके अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में इलाज का असर तुरंत दिखने लगता है और दवाइयाँ भी पूरी तरह से प्रभावी होती हैं।
अन्य समस्याओं के लिए भी कारगर
इस रिसर्च सेंटर में सिर्फ एलर्जी ही नहीं, बल्कि स्पॉन्डिलाइटिस, पीसीओडी जैसी कई अन्य बीमारियों का भी सफलतापूर्वक इलाज किया जाता है। रेणुका बहन जैसी कई अन्य मरीजों को भी यहाँ से सकारात्मक परिणाम मिले हैं।
रेणुका बहन का संदेश
रेणुका बहन उन सभी लोगों को धन्यवाद देती हैं जिन्होंने उनके इलाज में मदद की। वे यह संदेश देना चाहती हैं कि यदि कोई भी व्यक्ति किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान है और अब तक उसे कोई समाधान नहीं मिला है, तो उन्हें ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में एक बार अवश्य आना चाहिए।
"यहाँ इलाज प्रभावी, सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक तरीके से किया जाता है। मैं इस सेंटर के प्रति आभार व्यक्त करती हूँ, जिसने मुझे 10 साल पुरानी तकलीफ से राहत दिलाई।"
अगर आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं और समाधान की तलाश में हैं, तो इस होम्योपैथिक उपचार को आज़मा सकते हैं।
Departments
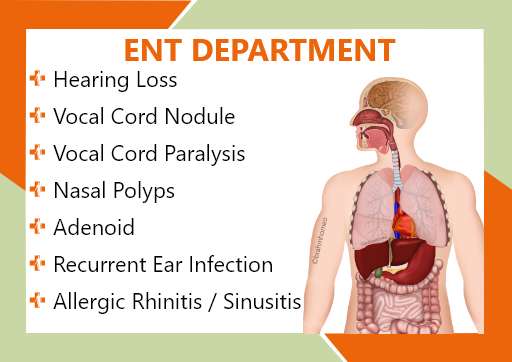
ENT DEPARTMENT
Hearing Loss, Vocal Cord Nodule, Vocal Cord Paralysis, Nasal Polip, Adenoid, Recurrent ear infection, Allergic Rhinitis/Sinusitis

GENERAL MEDICINE
Diabetes
Hypertension
Thyroid Disorders
Cholesterol problem (Dislipimidia)
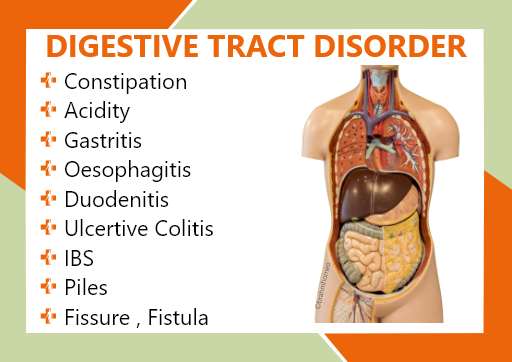
DIGESTIVE TRACT DISORDER
Constipation
Acidity
Gastritis
Oesophagitis
Duodenitis
Ulcertive Colitis
IBS
Piles
Fissure
Fistula
Diseases

piliya kya hota hai
१) पीलिया क्या होता है?
पीलिया ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें हमारी त्वचा और आंखों का सफेद भाग पीला होने लग जाता है। यह बिलीरुबिन नामक पीला पदार्थ के शरीर में जमा होने से होता है,यह लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं के टूटने पर होता है
2) पीलिया के लक्षण क्या हैं?
-पीलिया के सामान्य लक्षण हैं जो की इस प्रकार है - आंखों के सफेद भाग का पीला पड़ना - गहरे रंग का पेशाब
- त्वचा में खुजली - वजन कम होना - उल्टी - जी मिचलाना - भूख न लगना - पेट में दर्द और कोमलता
3) पीलिया के जोखिम कारक क्या हैं?
जोखिम कारक पीलिया की संभावना को और बढ़ा सकते हैं, वे यकृत और पित्ताशय की थैली विकारों के समान हैं। - ऐसी दवाओं का अत्यधिक उपयोग जो यकृत को नुकसान पहुंचा सकती हैं - हेपेटाइटिस ए, हेपेटाइटिस बी या हेपेटाइटिस सी जैसे संक्रमण होना - रसायनों के संपर्क में आना - यकृत को नुकसान - पित्त नलिकाओं में रुकावट - कुछ विटामिन और एंजाइम की कमी - अत्यधिक शराब का सेवन
4) पीलिया रोकथाम के उपाय क्या है ?
पीलिया यकृत के कार्य से जुड़ा है। चूंकि पीलिया के कई कारण हैं, इसलिए कोई सटीक रोकथाम नहीं हैं। कुछ उपाय बताये गए है जो की इस प्रकार से है। -हेपेटाइटिस संक्रमण से बचना -अधिक वजन को नियंत्रित रखें
-कोलेस्ट्रॉल के स्तर की जाँच करें -संतुलित आहार लें -नियमित व्यायाम करें
-शराब के सेवन को नियंत्रित करें -किसी भी हर्बल थेरेपी को करने से पहले डॉक्टर से पूछे - पारिवारिक इतिहास है, तो पूरे शरीर की जाँच करवाएँ
gallstones treatment in homeopathy
1) What causes gallstones?
Gallstones form when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile – a digestive fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
-When bile contains too much cholesterol, bilirubin, when the gallbladder does not empty properly, stones can form.
- Risk factors for gallstones include rapid weight loss, obesity, age, and certain medical conditions.
2) What are the symptoms of gallstones?
While many people with gallstones may have no symptoms, others may have symptoms such as: - Nausea
- Vomiting - Bloating
- Indigestion
3) What are the nonsurgical treatments for gallstones?
For patients who do not have severe symptoms or complications, nonsurgical methods are considered. 1. Dietary changes The first step in managing gallstones is to adopt a healthy diet. A diet rich in fiber, fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is recommended. Eating more frequent meals may help the gallbladder work more efficiently.
2. Watchful waiting If gallstones are not causing any symptoms, the doctor may suggest waiting. Regular monitoring ensures that any changes or developments are addressed promptly, while avoiding unnecessary treatment in asymptomatic cases.
3) What is the surgical treatment for gallstones?
When gallstones cause frequent or severe symptoms, surgery is required. - Gallbladder removal
The most common surgical treatment for gallstones is the removal of the gallbladder. This procedure is known as cholecystectomy.
- It can be performed in two ways: 1) Laparoscopic surgery 2) Open surgery
Laparoscopic surgery: This procedure involves making small incisions in the abdomen to remove the gallbladder. It is usually less painful and requires a shorter hospital stay . Open surgery: Open surgery is performed when laparoscopic surgery is not possible. It involves a larger incision and a longer recovery period.
- Only after the gallbladder is removed can bile flow directly from the liver to the small intestine. Most people can live healthy lives without a gallbladder.
Conclusion
Gallstones are digestive problems that can range from harmless to extremely painful. While dietary changes and careful monitoring may be effective in mild cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder is the most definitive treatment for symptomatic gallstones.
homeopathy fatty liver treatment
1. What is fatty liver disease?
-The largest organ in the body is the liver. The main function of the liver is to remove toxins and process nutrients from food.
-It is normal to have some fat in the liver, but if more than 10% of the liver's weight is fat, you may have fatty liver. This can lead to other complications. Fatty liver is harmless, but sometimes excess fat can cause inflammation in the liver. 2. What are the symptoms of fatty liver?
The symptoms of fatty liver can be as follows, - Feeling tired
- Weight loss- Loss of appetite - Nausea - Pain in the middle or right upper abdomen.
3. What are the main causes of fatty liver?
When fat starts accumulating in the liver due to eating too many calories, the liver is unable to break down the fat normally, so too much fat gets accumulated. Due to which people suffering from certain conditions like obesity, diabetes are more likely to have fatty liver.
4. Treatment of fatty liver in homeopathy?
Fatty liver is a very common problem in today's time. People who eat outside food, eat a lot of fried food, consume a lot of alcohol, do not maintain the time and schedule of eating, gradually develop the problem of fatty liver. -At the primary level, grade 1 fatty liver does not cause much problem, but as the grade increases, there is grade 2, grade 3, fibrosis occurs and after a time your liver may fail, cirrhosis can also be seen in the liver.
Videos

kabj gas acidity ka ilaaj
१) कब्ज, गैस और एसिडिटी का इलाज?
वर्त्तमान समय के बदलते जीवनशैली, अनियमित खान-पान, और शारीरिक गतिविधियों की कमी के कारण से कब्ज, गैस और एसिडिटी जैसी पेट की समस्याएं आम बात हो गई हैं। ये समस्याएं छोटी लगती हैं, पर समय रहते इलाज न किया जाए, तो यह गंभीर रोगों का रूप ले सकती हैं। -आज का आर्टिकल में हम जानेंगे कि इन समस्याओं के क्या कारण हैं, इनके लक्षण क्या हैं और घरेलू उपायों से कैसे इनका इलाज किया जा सकता है।
2) कब्ज क्या है?
जब व्यक्ति को नियमित रूप से मल त्यागने में परेशानी होती है या मल पूरी तरह से बाहर नहीं निकलता है । आमतौर पर सप्ताह में तीन बार से कम शौच जाना कब्ज है।
कब्ज के कारण क्या है ?
-फाइबर रहित भोजन -पानी की कमी से -ज्यादा जंक फ़ूड खाना -शारीरिक गतिविधि की कमी - चाय या कॉफी का सेवन
कब्ज के लक्षण क्या होते है ?
- पेट में गैस बनना - सिर में दर्द का होना - मुह का स्वाद खराब हो जानाघरेलू उपाय ?
-सुबह खाली पेट गुनगुना नींबू पानी पीना - फल, सब्जियां, ओट्स खाने में उपयोग करना -खूब पानी पिएं
2. गैस बनने के क्या कारण है?
गैस बनने के कारण निचे अनुसार हो सकते है ,जैसे की , - मसालेदार भोजन खाना -भोजन को चबाए बिना ही जल्दी-जल्दी खा जाना -कब्ज की स्थिति
-कार्बोनेटेड ड्रिंक का सेवन
गैस के लक्षण क्या है ?
-पेट में सूजन और पेट फूलना -डकार आना
- उल्टी जैसा मन का होना
३) एसिडिटी क्या है?
जब पेट में एसिड का ज्यादा स्राव होता है और वह ऊपर की ओर अन्ननली में आने लगता है, तो उसे एसिडिटी कहते हैं।एसिडिटी के कारण
-अधिक चाय या कॉफी पीना - मसालेदार भोजन - भोजन करने के बाद लेटनाएसिडिटी के लक्षण क्या है ?
-सीने में जलन -खट्टी डकारें -गले में जलन -पेट में जलन या दर्द

homeopathy me bina operation pancreas ka ilaaj
१)पैंक्रियास का होमियोपैथी में बिना सर्जरी इलाज क्या है ?
अग्न्याशय हमारे शरीर का मुख्या अंग है, जो की दो तरह से कार्य करता है : पाचन एंजाइम बनाना और इंसुलिन जैसे हार्मोन का निर्माण करना - जब पैंक्रियास में कोई समस्या आती है, जैसे कि पैंक्रियास की पथरी, या ट्यूमर, तो इसका असर हमारे पूरे पाचन तंत्र और शुगर कण्ट्रोल प्रणाली पर होता है
२) होमियोपैथी और पैंक्रियास?
होमियोपैथी वैकल्पिक चिकित्सा प्रणाली है, जो "समान को समान से ठीक किया जा सकता है" होमियोपैथी के सिद्धांत पर कार्य करती है। इसका उद्देश्य बीमारी के लक्षणों को जड़ से ठीक करना है। पैंक्रियास से संबंधित रोगों के लिए भी होमियोपैथी में कई औषधियाँ हैं, जो बिना सर्जरी के इलाज में मदद हो सकती हैं।
1. पैंक्रियाटाइटिस (Pancreatitis)
जब पैंक्रियास में सूजन आ जाती है। इसके कारणों में शराब का सेवन, गॉलब्लैडर की पथरी, संक्रमण, शामिल हैं।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस होने पर कैसे लक्षण देखने को मिलते है ? पैंक्रियाटाइटिस होने पर निचे बताये अनुसार लक्षण देखने को मिलते है जैसे की -मतली और उल्टी -भूख में कमी होना -वजन घट जाना -बुखार -दस्त -मधुमेह -थकान या कमज़ोरी
अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण क्या है ? अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण नीचे बताये गए है जैसे की ,
-पित्त की पथरी -तंबाकू का ज्यादा सेवन करना -शराब का अत्यधिक सेवन - पारिवारिक इतिहास
2. क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ?
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस लंबे समय तक बनी रहने वाली सूजन है, जिससे पैंक्रियास की काम करने में धीरे-धीरे कम हो जाता है - Chronic pancreatitis के मुख्य लक्षणों में बार-बार पेट में होने वाला दर्द, वजन कम होना और पाचन में समस्या है.
३) पैंक्रियाज को मजबूत कैसे करें?
* आहार * - हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियां : पालक, मेथी, जैसे हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियां पैंक्रियाज के लिए फायदेमंद हैं। - फल : अनार, अमरूद, सेब, और पपीता जैसे फल और सब्जियां फाइबर और विटामिन से भरपूर होते हैं, -प्रोटीन : लीन मीट, सोयाबीन, दही, और नट्स में प्रोटीन होता है, -नारियल पानी : नारियल पानी पैंक्रियाज के स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर बनाने में मदद कर सकता है। -पानी : हर दिन 8-10 गिलास पानी पीना चाहिए, - व्यायाम : नियमित व्यायाम से ब्लड सर्कुलेशन होता है, जो पैंक्रियाज के लिए भी फायदेमंद होता है।

ibs ka homeopathy me ilaaj
१) आईबीएस का इलाज क्या है?
- IBS आम बीमारी है ,जो की बड़ी आंत को असर करती है, जब हम भोजन करते हैं तब भोजन को पाचन तंत्र में पहुंचाने की क्रिया के दौरान ये मांसपेशियां सिकुड़ने लगती हैं, लेकिन जब मांसपेशियां अधिक सिकुड़ जाती हैं ,तो पेट में गैस बनने लग जाती है और आंत में भी सूजन आती है जिसके कारण हमारी आंत कमजोर हो जाती है ,इसको IBS कहते है।
२) IBS के कारण क्या क्या हो सकते है?
IBS के कई कारण हो सकते है जैसे की , -तनाव और चिंता -गलत तरह का खान-पान -हार्मोनल असंतुलन
-आनुवंशिकता
३) IBS होने के क्या-क्या लक्षण हो सकते है?
IBS दुनिया भर के २०% लोगो को असर करती है। इसके लक्षण निचे अनुसार हो है,जैसे की - पेट में ऐंठन का होना - कब्ज़ या दस्त - पेट फूल जाना -भूख में कमी लगना - वजन भी कम होना
४ ) IBS होने पर क्या खाने से दूर रहना चाहिए ?
IBS में इन खाने वाली चीज़ों से बचना चाहिए जैसे की , - बीन्स, और मटर जैसे प्रोटीन और फ़ाइबर से भरपूर पदार्थ
- कार्बोहाइड्रेट -मूली, और टमाटर जैसी कच्ची सब्ज़ियां
-डेयरी उत्पाद में पनीर, क्रीम
