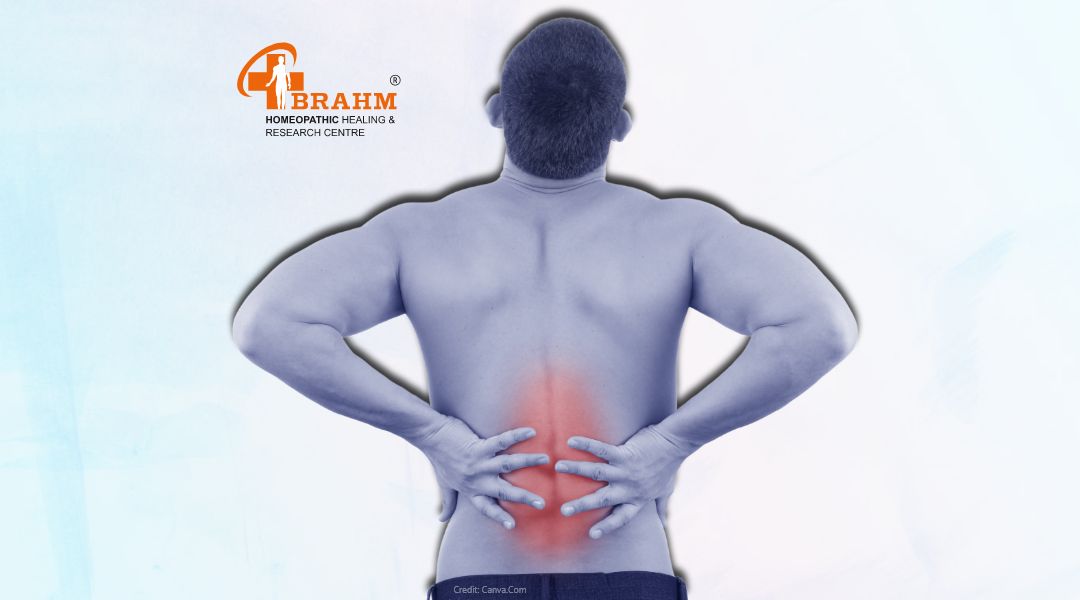
back pain
What is Back Pain?
Back pain is a common condition that affects the muscles, bones, and nerves in the back. It can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that can make it difficult to move or perform daily activities.

Causes of Back Pain:
-Back pain can be caused by various factors, including:
• Muscle or ligament strain: Repeated heavy lifting, awkward movements, or poor posture can strain back muscles and ligaments.
• Bulging or ruptured discs: Pressure on nerves from bulging or ruptured discs can cause back pain.
• Arthritis: Degeneration of spine joints can lead to back pain.
• Skeletal irregularities: Conditions like scoliosis or spinal stenosis can contribute to back pain.
• Osteoporosis: Bone weakening increases risk of vertebral fractures and back pain.
Symptoms of Back Pain:
• Muscle ache or stiffness.
• Shooting or stabbing pain
.
• Radiating pain down legs.
• Limited flexibility or range of motion.

Diagnosis of Back Pain:
• Medical history and physical examination.
• X-rays, MRI, CT scans for bone and soft tissue visualization
.
• Nerve conduction studies or EMG for nerve function evaluation.

Types of Back Pain:
• Acute: Short-term pain less than 6 weeks.
• Chronic: Persistent pain over 3 months.
• Lower: Pain in lumbar region.
• Middle: Pain in thoracic region.
• Upper: Pain in cervical and shoulder region.
Adverse Effects of Back Pain:
• Reduced mobility and quality of life.
• Depression and anxiety.
• Inability to work or perform daily activities.
• Dependence on pain medications and side effects.
• Muscle weakness and atrophy due to inactivity.

Diet in Back Pain
• Maintain a healthy weight to prevent strain on the back and worsen pain.
• Increase intake of anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3 fatty acids to reduce inflammation.
• Stay hydrated to maintain proper disc hydration and nutrient delivery to the spine.
• Limit inflammatory foods like processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats.
• Consider supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin, or turmeric, but consult a healthcare professional.
• Effective management often involves exercise, physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications.
Stories

chronic pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियास ठीक करने के उपाय
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस एक बीमारी है जो आपके पैंक्रियास में हो सकती है। पैंक्रियास आपके पेट में एक लंबी ग्रंथि है जो भोजन को पचाने में आपकी मदद करती है। यह आपके रक्त प्रवाह में हार्मोन भी जारी करता है जो आपके शरीर को ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग करने में मदद करता है। यदि आपका पैंक्रियास क्षतिग्रस्त हो गया है, तो पाचन एंजाइम सामान्य रूप से आपकी छोटी आंत में नहीं जा सकते हैं और आपका शरीर ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग नहीं कर सकता है।
पैंक्रियास शरीर का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है जो हार्मोन इंसुलिन का उत्पादन करके रक्त शर्करा को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। यदि इस अंग को नुकसान होता है, तो इससे मानव शरीर में गंभीर समस्याएं हो सकती हैं। ऐसी ही एक समस्या है जब पैंक्रियास में सूजन हो जाती है, जिसे तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस कहा जाता है।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस पैंक्रियास की सूजन है जो लंबे समय तक रह सकती है। इससे पैंक्रियास और अन्य जटिलताओं को स्थायी नुकसान हो सकता है। इस सूजन से निशान ऊतक विकसित हो सकते हैं, जो इंसुलिन उत्पन्न करने वाली कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा सकते हैं। यह पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ वाले लगभग 45 प्रतिशत लोगों में मधुमेह का कारण बन सकता है। भारी शराब का सेवन भी वयस्कों में पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकता है। ऑटोइम्यून और आनुवंशिक रोग, जैसे सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस, कुछ लोगों में पुरानी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकते हैं।
उत्तर भारत में, ऐसे बहुत से लोग हैं जिनके पास पीने के लिए बहुत अधिक है और कभी-कभी एक छोटा सा पत्थर उनके पित्ताशय में फंस सकता है और उनके अग्न्याशय के उद्घाटन को अवरुद्ध कर सकता है। इससे उन्हें अपना खाना पचाने में मुश्किल हो सकती है। 3 हाल ही में एशिया-प्रशांत क्षेत्र के विभिन्न देशों में किए गए एक सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार दक्षिण भारत में पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ की व्यापकता प्रति 100,000 जनसंख्या पर 114-200 मामले हैं।
Chronic Pancreatitis Patient Cured Report
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण ?
-कुछ लोगों को पेट में दर्द होता है जो पीठ तक फैल सकता है। -यह दर्द मतली और उल्टी जैसी चीजों के कारण हो सकता है। -खाने के बाद दर्द और बढ़ सकता है। -कभी-कभी किसी के पेट को छूने पर दर्द महसूस हो सकता है। -व्यक्ति को बुखार और ठंड लगना भी हो सकता है। वे बहुत कमजोर और थका हुआ भी महसूस कर सकते हैं।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण ?
-पित्ताशय की पथरी -शराब
-रक्त में उच्च ट्राइग्लिसराइड का स्तर -रक्त में उच्च कैल्शियम का स्तर
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज कैसे किया जाता है?
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस नेक्रोसिस का उपचार उपचारात्मक है। आप कितने समय तक इस बीमारी से पीड़ित रहेंगे यह काफी हद तक आपकी उपचार योजना पर निर्भर करता है। ब्रह्म अनुसंधान पर आधारित चिकित्सकीय रूप से सिद्ध वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी के इलाज में अत्यधिक प्रभावी हैं। हमारे पास आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करने, सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों, रोग के पाठ्यक्रम का दस्तावेजीकरण करने, रोग के चरण, पूर्वानुमान और जटिलताओं को समझने की क्षमता है, हमारे पास अत्यधिक योग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है। फिर वे आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताएंगे, आपको एक उचित आहार योजना (क्या खाएं और क्या नहीं खाएं), व्यायाम योजना, जीवनशैली योजना और कई अन्य कारक प्रदान करेंगे जो आपके समग्र स्वास्थ्य में सुधार कर सकते हैं। पढ़ाना। व्यवस्थित उपचार रोग ठीक होने तक होम्योपैथिक औषधियों से उपचार करें। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, चाहे वह थोड़े समय के लिए हो या कई सालों से। हम सभी ठीक हो सकते हैं, लेकिन बीमारी के प्रारंभिक चरण में हम तेजी से ठीक हो जाते हैं। पुरानी या देर से आने वाली या लंबे समय तक चलने वाली बीमारियों को ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगता है। समझदार लोग इस बीमारी के लक्षण दिखते ही इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं। इसलिए, यदि आपको कोई असामान्यता नज़र आती है, तो कृपया तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।

Acute Necrotizing pancreas treatment in hindi
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ ?
आक्रामक अंतःशिरा द्रव पुनर्जीवन, दर्द प्रबंधन, और आंत्र भोजन की जल्द से जल्द संभव शुरुआत उपचार के मुख्य घटक हैं। जबकि उपरोक्त सावधानियों से बाँझ परिगलन में सुधार हो सकता है, संक्रमित परिगलन के लिए अतिरिक्त उपचार की आवश्यकता होती है।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लक्षण ? - बुखार - फूला हुआ पेट - मतली और दस्त तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण ?
- अग्न्याशय में चोट - उच्च रक्त कैल्शियम स्तर और रक्त वसा सांद्रता
ऐसी स्थितियाँ जो अग्न्याशय को प्रभावित करती हैं और आपके परिवार में चलती रहती हैं, उनमें सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस और अन्य आनुवंशिक विकार शामिल हैं जिनके परिणामस्वरूप बार-बार अग्नाशयशोथ होता है|
क्या एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रिएटाइटिस का इलाज होम्योपैथी से संभव है ?
हां, होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनकर एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज संभव है। होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनने से आपको इन दवाओं का कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं होगा और यह समस्या को जड़ से खत्म कर देता है, इसीलिए आपको अपने एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के इलाज के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार का ही चयन करना चाहिए।
आप तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ से कैसे छुटकारा पा सकते हैं ?
शुरुआती चरण में सर्वोत्तम उपचार चुनने से आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस से छुटकारा मिल जाएगा। होम्योपैथिक उपचार का चयन करके, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे विश्वसनीय उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करता है। एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार सबसे अच्छा इलाज है। जैसे ही आप एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक करने के लिए अपना उपचार शुरू करेंगे, आपको निश्चित परिणाम मिलेंगे।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार से तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ का इलाज संभव है। आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, इसका उपचार योजना पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ता है। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कब से अपनी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, या तो हाल ही में या कई वर्षों से - हमारे पास सब कुछ ठीक है, लेकिन बीमारी के शुरुआती चरण में, आप तेजी से ठीक हो जाएंगे। पुरानी स्थितियों के लिए या बाद के चरण में या कई वर्षों की पीड़ा के मामले में, इसे ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगेगा। बुद्धिमान व्यक्ति हमेशा इस बीमारी के किसी भी लक्षण को देखते ही तुरंत इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं, इसलिए जैसे ही आपमें कोई असामान्यता दिखे तो तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एवं रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
ब्रह्म अनुसंधान आधारित, चिकित्सकीय रूप से प्रमाणित, वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी को ठीक करने में बहुत प्रभावी है। हमारे पास सुयोग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है जो आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करती है, रोग की प्रगति के साथ-साथ सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों को रिकॉर्ड करती है, इसकी प्रगति के चरणों, पूर्वानुमान और इसकी जटिलताओं को समझती है। उसके बाद वे आपको आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताते हैं, आपको उचित आहार चार्ट [क्या खाएं या क्या न खाएं], व्यायाम योजना, जीवन शैली योजना प्रदान करते हैं और कई अन्य कारकों के बारे में मार्गदर्शन करते हैं जो व्यवस्थित प्रबंधन के साथ आपकी सामान्य स्वास्थ्य स्थिति में सुधार कर सकते हैं। जब तक यह ठीक न हो जाए तब तक होम्योपैथिक दवाओं से अपनी बीमारी का इलाज करें।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लिए आहार ?
कुपोषण और पोषण संबंधी कमियों को रोकने के लिए, सामान्य रक्त शर्करा के स्तर को बनाए रखने और मधुमेह, गुर्दे की समस्याओं और पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ से जुड़ी अन्य स्थितियों को रोकने या बेहतर ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए, अग्नाशयशोथ की तीव्र घटना से बचना महत्वपूर्ण है।
यदि आप एक स्वस्थ आहार योजना की तलाश में हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। हमारे विशेषज्ञ आपकी व्यक्तिगत आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप एक योजना बनाने में आपकी सहायता कर सकते हैं

Pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ?
जब पैंक्रियाटाइटिसमें सूजन और संक्रमण हो जाता है तो इससे पैंक्रिअटिटिस नामक रोग हो जाता है। पैंक्रियास एक लंबा, चपटा अंग है जो पेट के पीछे पेट के शीर्ष पर छिपा होता है। पैंक्रिअटिटिस उत्तेजनाओं और हार्मोन का उत्पादन करके पाचन में मदद करता है जो आपके शरीर में ग्लूकोज के प्रसंस्करण को विनियमित करने में मदद करते हैं।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण:
-पेट के ऊपरी भाग में दर्द होना। -बेकार वजन घटाना. -पेट का ख़राब होना.
-शरीर का असामान्य रूप से उच्च तापमान। -पेट को छूने पर दर्द होना। -तेज़ दिल की धड़कन. -हाइपरटोनिक निर्जलीकरण.
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण:
-पित्ताशय में पथरी. -भारी शराब का सेवन.
-भारी खुराक वाली दवाएँ। -हार्मोन का असंतुलन. -रक्त में वसा जो ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स का कारण बनता है। -आनुवंशिकता की स्थितियाँ. -पेट में सूजन ।
क्या होम्योपैथी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक कर सकती है?
हाँ, होम्योपैथीपैंक्रियाटाइटिसको ठीक कर सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको पैंक्रिअटिटिस के लिए सबसे भरोसेमंद उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करती है।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा उपचार क्या है?
यदि पैंक्रियाज अच्छी तरह से काम नहीं कर रहा है तो होम्योपैथिक उपचार वास्तव में बेहतर होने में मदद करने का एक अच्छा तरीका है। जब आप उपचार शुरू करते हैं, तो आप जल्दी परिणाम देखेंगे। बहुत सारे लोग इस इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जा रहे हैं और वे वास्तव में अच्छा कर रहे हैं। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपके पैंक्रियाज के को बेहतर बनाने में मदद करने के लिए आपको सबसे तेज़ और सुरक्षित तरीका प्रदान करना सुनिश्चित करती है।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
बीमार होने पर लोगों को बेहतर महसूस कराने में मदद करने के लिए हमारे पास एक विशेष तरीका है। हमारे पास वास्तव में स्मार्ट डॉक्टर हैं जो ध्यान से देखते हैं और नोट करते हैं कि बीमारी व्यक्ति को कैसे प्रभावित कर रही है। फिर, वे सलाह देते हैं कि क्या खाना चाहिए, व्यायाम करना चाहिए और स्वस्थ जीवन कैसे जीना चाहिए। वे व्यक्ति को ठीक होने में मदद करने के लिए विशेष दवा भी देते हैं। यह तरीका कारगर साबित हुआ है!
Tips

hamare sarir ke liye sabji ke labh
सब्जियाँ हमारे आहार का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा हैं। इनमें कई प्रकार के विटामिन, खनिज, एंटीऑक्सीडेंट और फाइबर होते हैं, जो शरीर को स्वस्थ बनाए रखते हैं। सब्जियों का सेवन न केवल रोगों से बचाव करता है बल्कि संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य को भी बनाए रखता है।
सब्जियों के प्रकार और उनके लाभ
1. हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ (Leafy Green Vegetables)
हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ पोषण से भरपूर होती हैं और शरीर को कई तरह के आवश्यक तत्व प्रदान करती हैं।
-1. पालक (Spinach) लाभ: आयरन, कैल्शियम और फाइबर से भरपूर। हड्डियों और मांसपेशियों को मजबूत बनाता है। एनीमिया और कब्ज से बचाव करता है।
2. सरसों के पत्ते (Mustard Greens)
-लाभ: -हड्डियों के लिए फायदेमंद। -इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है। -त्वचा और बालों को स्वस्थ रखता है।
3. मेथी (Fenugreek Leaves)
-लाभ: -डायबिटीज को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। -पाचन को सुधारता है और भूख बढ़ाता है।
4. धनिया और पुदीना (Coriander & Mint Leaves)
-लाभ: -पाचन को सुधारते हैं। -विषाक्त पदार्थों को बाहर निकालते हैं। -त्वचा को चमकदार बनाते हैं।
2. जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ (Root Vegetables)
जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ फाइबर और आवश्यक खनिजों से भरपूर होती हैं।
5. गाजर (Carrot)

sarir ke liye vitamin or unke labh
हमारे शरीर के लिए सभी विटामिन और उनके लाभ
विटामिन हमारे शरीर के लिए आवश्यक पोषक तत्व हैं, जो शरीर के विभिन्न कार्यों को सुचारू रूप से चलाने में मदद करते हैं। ये सूक्ष्म पोषक तत्व होते हैं, लेकिन शरीर में इनकी भूमिका बहुत महत्वपूर्ण होती है। विटामिन की कमी से कई स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ हो सकती हैं, इसलिए संतुलित आहार लेना जरूरी है।
विटामिन कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
-विटामिन दो प्रकार के होते हैं: -1. वसा में घुलनशील विटामिन (Fat-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में वसा में संग्रहित होते हैं और जरूरत पड़ने पर उपयोग किए जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन A, D, E और K आते हैं।
-2. जल में घुलनशील विटामिन (Water-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में जमा नहीं होते और मूत्र के माध्यम से बाहर निकल जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन C और सभी B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन आते हैं।
विटामिन और उनके लाभ
1. विटामिन A (रेटिनॉल, बीटा-कैरोटीन)
भूमिका:
आँखों की रोशनी को बनाए रखता है।
त्वचा और इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है।
हड्डियों और दांतों के विकास में सहायक है।
स्रोत:
गाजर पालकआम, शकरकंद, डेयरी उत्पाद, अंडे, मछली का तेल।
कमी के प्रभाव:
रतौंधी (नाइट ब्लाइंडनेस)
त्वचा में रूखापन
रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी
---
2. विटामिन B-कॉम्प्लेक्स (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12)
B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र और रक्त निर्माण में मदद करते हैं। B1 (थायमिन)
भूमिका: ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र के कार्यों में सहायक।
स्रोत: साबुत अनाज, बीन्स, सूरजमुखी के बीज, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: कमजोरी, भूख न लगना, तंत्रिका तंत्र की समस्या।
B2 (राइबोफ्लेविन)
भूमिका: त्वचा, आँखों और ऊर्जा उत्पादन के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: दूध, दही, अंडे, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: होंठों में दरारें, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B3 (नियासिन)
भूमिका: कोलेस्ट्रॉल को नियंत्रित करता है और पाचन में सहायक होता है।
स्रोत: मूंगफली, मशरूम, टमाटर, चिकन, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा रोग, मानसिक कमजोरी। B5 (पैंटोथेनिक एसिड)
भूमिका: हार्मोन उत्पादन और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: मशरूम, एवोकाडो, दूध, ब्रोकली।
कमी के प्रभाव: थकान, सिरदर्द।
B6 (पाइरिडोक्सिन)
भूमिका: तंत्रिका तंत्र और प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को मजबूत करता है।
स्रोत: केला, चिकन, सोयाबीन, आलू।
कमी के प्रभाव: अवसाद, त्वचा रोग।
B7 (बायोटिन)
भूमिका: बालों और त्वचा के स्वास्थ्य को बनाए रखता है।
स्रोत: अंडे, मूंगफली, फूलगोभी।
कमी के प्रभाव: बाल झड़ना, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B9 (फोलिक एसिड)
भूमिका: डीएनए निर्माण और गर्भावस्था में जरूरी।
स्रोत: दालें, हरी सब्जियाँ, बीन्स। कमी के प्रभाव: एनीमिया, जन्म दोष।
B12 (कोबालामिन)
भूमिका: लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं और तंत्रिका तंत्र के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: मांस, अंडे, डेयरी उत्पाद। कमी के प्रभाव: स्मरण शक्ति की कमजोरी, एनीमिया।
---
3. विटामिन C (एस्कॉर्बिक एसिड)
भूमिका: इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है, त्वचा को चमकदार बनाता है, और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: संतरा, नींबू, स्ट्रॉबेरी, टमाटर, हरी मिर्च।
कमी के प्रभाव: स्कर्वी, मसूड़ों से खून आना, रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी।
---
4. विटामिन D (कोलेकल्सीफेरोल)
भूमिका: हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाता है और कैल्शियम के अवशोषण में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: सूर्य का प्रकाश, मछली, अंडे, दूध।
कमी के प्रभाव: हड्डियों में कमजोरी, रिकेट्स।
---
5. विटामिन E (टोकोफेरॉल)
भूमिका: एंटीऑक्सीडेंट के रूप में कार्य करता है और त्वचा तथा बालों के लिए लाभदायक है। स्रोत: बादाम, सूरजमुखी के बीज, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा की समस्याएँ, कमजोरी।
---
6. विटामिन K (फायलोक्विनोन)
भूमिका: रक्त को थक्का जमाने (ब्लड क्लॉटिंग) में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: पालक, ब्रोकोली, हरी सब्जियाँ।
कमी के प्रभाव: चोट लगने पर खून न रुकना। ---
निष्कर्ष
शरीर को सभी विटामिनों की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि सभी अंग सही से काम कर सकें। इनके लिए संतुलित आहार लेना बहुत जरूरी है। यदि विटामिन की कमी हो, तो डॉक्टर से परामर्श लेकर सप्लीमेंट्स भी लिए जा सकते हैं। लेकिन, प्राकृतिक स्रोतों से विटामिन प्राप्त करना हमेशा सबसे अच्छा होता है।
-आपके शरीर की जरूरतों के अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक सेंटर में भी विटामिन डेफिशिएंसी का होम्योपैथिक उपचार उपलब्ध है। यदि आपको कोई लक्षण महसूस हो रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक से संपर्क करें और स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर बनाएँ।

best 5 winter food to keep you warm and strong
1.Root Vegetables
Ingredients: Carrots, Beets, and Sweet Potatoes are rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Nutrients:
Carrots: High in beta-carotene (vitamin A), fiber, and potassium. Beets: Contain folate, manganese, and antioxidants. Sweet Potatoes: Rich in vitamins A, C, and B6, as well as fiber and manganese.
Benefits: Vitamin A supports eye health and enhances immunity, while fiber aids digestion.Folate plays a key role in red blood cell formation and helps maintain brain health. Beets also have anti-inflammatory properties that can improve cardiovascular function.Sweet potatioes also packed with antioxidants, they protect against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Their high fiber content promotes digestive health and stabilizes blood sugar levels.
2. Citrus Fruits
Ingredients: Oranges, grapefruits, and lemons provide a refreshing addition to winter diets. Nutrients: All three are excellent sources of vitamin C, flavonoids, and fiber.
Benefits: Vitamin C strengthens the immune system, helping the body fend off winter colds and infections. Flavonoids have antioxidant properties that combat inflammation and support heart health. The fiber content aids in digestion, enhancing gut health, which is crucial during the winter months when digestive issues can be more prevalent.
3. Nuts and Seeds
Ingredients: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds are nutrient-packed options for winter snacks. Nutrients:
Almonds: Main source of vitamin E, magnesium, and healthy fats. Walnuts: High in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins.
Chia Seeds: Loaded with fiber, protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential minerals such as calcium and iron. Benefits:
Vitamin E acts as a potent antioxidant, promoting skin health and maintaining immune function. Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function, which can be especially important during colder months when exercises might decrease.Walnuts are Rich in omega-3s, they support brain health and it also help to alleviate symptoms like depression, which can be exacerbated in winter. Their antioxidant content contributes to heart health.Chia Seed is also Known to maintain hydration and provide long-lasting energy, benefiting those who may engage in winter sports or outdoor activities. Their fiber can also promote gut health, helping to alleviate any tendency towards constipation during winter.
4. Whole Grains
Ingredients: Quinoa, oats, and brown rice are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates.
Nutrients:
Quinoa: Contains complete protein, fiber, magnesium, and iron.
Oats: High in beta-glucan fiber, vitamins B1 and B5, and manganese. Brown Rice: Rich in fiber, B vitamins, and essential minerals.
Benefits:
Quinoa is a complete protein, it supports muscle health and provides sustained energy throughout the day. Its iron content helps in the formation of red blood cells, especially important during winter.You should obtained beta-glucan in oats aids in cholesterol reduction, supporting heart health, while their fiber content keeps one feeling full and satisfied, promoting weight management.Unlike white rice, Brown Rice provides more fiber and nutrients, stabilizing blood sugar levels, which is crucial during winter when metabolism may slow.
5. Spices and Herbs
Ingredients:The main spices and Herbs like Ginger, turmeric, cinnamon, and garlic.
Nutrients: Antioxidants: Combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Anti-inflammatory compounds: Reduce inflammation and pain.
Vitamins and Minerals: Many spices offer small amounts of essential vitamins and minerals.
Benefits:
Ginger and garlic boost the immune system and can help reduce symptoms of cold and flu.Turmeric has powerful anti-inflammatory properties, ideal for joint health during cold months.Enhance flavor of foods without added calories, making dishes more enjoyable. Homeopathic treatment stands as a beacon of holistic healing, emphasizing the body’s innate capacity to restore balance and health. Under the expert guidance of a dedicated homeopath, patients receive personalized remedies tailored to their unique symptoms and underlying causes, rather than merely treating superficial manifestations. This philosophy fosters a profound understanding of individual health, where the doctor and patient collaborate closely to explore not only the physical ailments but also emotional and mental well-being. By utilizing highly diluted natural substances that trigger the body’s self-healing processes, homeopathy aims to stimulate vitality and resilience, paving the way for sustainable health and preventing future ailments. This gentle yet effective approach not only alleviates symptoms but also empowers individuals to achieve optimal well-being and harmony in their lives.
Testimonials

body weakness treatment
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से 10 महीने में चमत्कारी इलाज: एक मरीज की कहानी
आज के समय में जब लोग तरह-तरह की बीमारियों से जूझ रहे हैं, तब होम्योपैथी चिकित्सा कई मरीजों के लिए आशा की किरण बन रही है। ऐसी ही एक प्रेरणादायक कहानी है एक मरीज की, जिसने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के माध्यम से 10 महीने में अपनी बीमारी से निजात पाई।
शुरुआत में थी थकान और शरीर में भारीपन
मरीज ने बताया, "मुझे कई दिनों से शरीर में थकान, भारीपन और बेचैनी महसूस हो रही थी। यह परेशानी धीरे-धीरे इतनी बढ़ गई कि रोजमर्रा के काम भी कठिन लगने लगे। मेरी माँ पहले से ही ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी क्लीनिक में इलाज करा रही थीं। उन्होंने बताया कि उन्हें वेरीकोज वेन्स की समस्या थी और यहाँ के इलाज से उन्हें बहुत लाभ हुआ था। उनकी सलाह पर मैं भी यहाँ आया।"
होम्योपैथी इलाज का असर मात्र एक सप्ताह में
मरीज के अनुसार, "जब मैंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा से परामर्श लिया और उनकी सलाह के अनुसार दवाएं लेना शुरू किया, तो सिर्फ एक हफ्ते के भीतर ही मुझे सुधार महसूस होने लगा। मेरी थकान कम हो गई, शरीर की ऊर्जा बढ़ने लगी और पहले की तुलना में मैं ज्यादा सक्रिय महसूस करने लगा।"
लगातार 10 महीने तक किया उपचार, मिली पूरी राहत
मरीज ने लगातार 10 महीने तक ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाएं लीं और सभी निर्देशों का पालन किया। उन्होंने कहा, "लगभग 15 दिनों के अंदर ही मेरी स्थिति में काफी सुधार हुआ और अब 10 महीने बाद मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ महसूस कर रहा हूँ। यह सब डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा और ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाओं की वजह से संभव हुआ।"
होम्योपैथी: सभी बीमारियों के लिए वरदान
मरीज ने आगे कहा, "इस क्लिनिक का माहौल बहुत अच्छा है और इलाज का तरीका बेहद प्रभावी है। यहाँ की दवाएँ बहुत असरदार हैं और मुझे इनके इस्तेमाल से कोई साइड इफेक्ट भी नहीं हुआ। यह सच में होम्योपैथी का सबसे बेहतरीन केंद्र है। मैं सभी मरीजों से अनुरोध करूंगा कि अगर वे किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान हैं, तो एक बार ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी का इलाज जरूर लें। यह एक बीमार मरीजों के लिए किसी स्वर्ग से कम नहीं है।"
निष्कर्ष
इस मरीज की कहानी यह साबित करती है कि सही चिकित्सा और सही मार्गदर्शन से कोई भी बीमारी ठीक हो सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में न केवल आधुनिक चिकित्सा पद्धति का समावेश है, बल्कि यहाँ मरीजों की समस्याओं को गहराई से समझकर उनका संपूर्ण इलाज किया जाता है। यदि आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी एक बेहतरीन विकल्प हो सकता है।

acute pancreatitis ka ilaaj
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: एक मरीज की जीवन बदलने वाली कहानी
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस: एक गंभीर समस्या
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में तीव्र सूजन हो जाती है। जब यह समस्या उत्पन्न होती है, तो मरीज को शुरुआत में इसकी जानकारी नहीं होती, लेकिन दर्द इतना असहनीय होता है कि उसे तुरंत अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की आवश्यकता पड़ती है। इस स्थिति का मुख्य कारण अनुचित जीवनशैली, जंक फूड, शराब का सेवन, ऑटोइम्यून बीमारियां, कुछ रसायन और विकिरण हो सकते हैं। यदि समय रहते सही इलाज नहीं किया गया, तो यह स्थिति क्रॉनिक पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस में बदल सकती है।
अमन बाजपेई की प्रेरणादायक यात्रा
मैं, अमन बाजपेई, पिछले 1.5 वर्षों से एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का मरीज था। यह समय मेरे लिए बेहद कठिन था। मैं बहुत परेशान था, खाना खाने तक के लिए तरस गया था। पिछले 7-8 महीनों में मैंने रोटी तक नहीं खाई, केवल खिचड़ी और फल खाकर गुजारा कर रहा था। बार-बार मुझे इस बीमारी के हमले झेलने पड़ रहे थे। हर 5-10 दिनों में दवा लेनी पड़ती थी, लेकिन कोई लाभ नहीं हो रहा था।
इस बीमारी के इलाज में मैंने 6-7 लाख रुपये खर्च कर दिए। दिल्ली और झांसी समेत कई बड़े अस्पतालों में इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई राहत नहीं मिली। मेरा वजन 95 किलो से घटकर 55 किलो हो गया और मैं बहुत कमजोर हो गया था। तभी मुझे सोशल मीडिया के माध्यम से ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के बारे में पता चला।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: उम्मीद की एक नई किरण
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी वह जगह है जहां कम खर्च में उत्कृष्ट इलाज संभव है। मैंने आज तक किसी भी डॉक्टर या अस्पताल में इतना अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं देखा। डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा सर ने मुझे एक नई जिंदगी दी। पहले मुझे लगा था कि मैं शायद कभी ठीक नहीं हो पाऊंगा, लेकिन आज मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ हूं।
मैं सभी मरीजों को यही सलाह दूंगा कि वे पैसे की बर्बादी न करें और सही इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जाएं। यह भारत में एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा अस्पताल है। मेरे लिए डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा किसी देवता से कम नहीं हैं।
वैज्ञानिक रूप से प्रमाणित उपचार पद्धति
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के विशेषज्ञों ने शोध आधारित एक विशेष उपचार पद्धति विकसित की है, जिससे न केवल लक्षणों में सुधार होता है बल्कि बीमारी को जड़ से ठीक किया जाता है। हजारों मरीज इस उपचार का लाभ ले रहे हैं और उनकी मेडिकल रिपोर्ट में भी उल्लेखनीय सुधार देखा गया है।
यदि आप भी इस बीमारी से जूझ रहे हैं और सही इलाज की तलाश कर रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। यह न केवल बीमारी को बढ़ने से रोकता है बल्कि इसे जड़ से ठीक भी करता है।

urticaria ka ilaaj
रेणुका बहन श्रीमाली की प्रेरणादायक कहानी: 10 साल की तकलीफ से छुटकारारेणुका बहन श्रीमाली पिछले 10 वर्षों से एक गंभीर समस्या से जूझ रही थीं। उन्हें जब भी कुछ खाने की कोशिश करतीं, उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और अत्यधिक खुजली होने लगती थी। इस समस्या के कारण वे बहुत परेशान थीं और 10 वर्षों तक कुछ भी सही तरीके से नहीं खा पाती थीं। उन्होंने कई जगहों पर इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई भी उपचार कारगर नहीं हुआ।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर से नई उम्मीदआखिरकार, 17 मई 2021 को उन्होंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में अपना ट्रीटमेंट शुरू किया। पहले से निराश हो चुकीं रेणुका बहन के लिए यह एक नई उम्मीद की किरण थी।एक साल में चमत्कारी सुधारट्रीटमेंट शुरू करने के बाद, धीरे-धीरे उनके स्वास्थ्य में सुधार होने लगा। एक साल के भीतर उन्होंने अपने आहार में वे सभी चीजें फिर से शुरू कर दीं, जिन्हें वे पहले नहीं खा पाती थीं। पहले जहाँ कोई भी चीज खाने से उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और खुजली होती थी, वहीं अब वे बिना किसी परेशानी के सामान्य जीवन जी रही हैं।ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर का योगदान
रेणुका बहन का कहना है कि यह इलाज उनके लिए किसी चमत्कार से कम नहीं था। उन्होंने अपनी पुरानी जीवनशैली को फिर से अपनाया और अब वे पूरी तरह से स्वस्थ महसूस कर रही हैं। उनके अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में इलाज का असर तुरंत दिखने लगता है और दवाइयाँ भी पूरी तरह से प्रभावी होती हैं।
अन्य समस्याओं के लिए भी कारगर
इस रिसर्च सेंटर में सिर्फ एलर्जी ही नहीं, बल्कि स्पॉन्डिलाइटिस, पीसीओडी जैसी कई अन्य बीमारियों का भी सफलतापूर्वक इलाज किया जाता है। रेणुका बहन जैसी कई अन्य मरीजों को भी यहाँ से सकारात्मक परिणाम मिले हैं।
रेणुका बहन का संदेश
रेणुका बहन उन सभी लोगों को धन्यवाद देती हैं जिन्होंने उनके इलाज में मदद की। वे यह संदेश देना चाहती हैं कि यदि कोई भी व्यक्ति किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान है और अब तक उसे कोई समाधान नहीं मिला है, तो उन्हें ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में एक बार अवश्य आना चाहिए।
"यहाँ इलाज प्रभावी, सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक तरीके से किया जाता है। मैं इस सेंटर के प्रति आभार व्यक्त करती हूँ, जिसने मुझे 10 साल पुरानी तकलीफ से राहत दिलाई।"
अगर आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं और समाधान की तलाश में हैं, तो इस होम्योपैथिक उपचार को आज़मा सकते हैं।
Departments
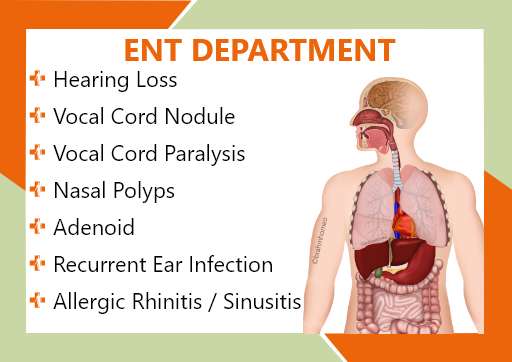
ENT DEPARTMENT
Hearing Loss, Vocal Cord Nodule, Vocal Cord Paralysis, Nasal Polip, Adenoid, Recurrent ear infection, Allergic Rhinitis/Sinusitis

GENERAL MEDICINE
Diabetes
Hypertension
Thyroid Disorders
Cholesterol problem (Dislipimidia)
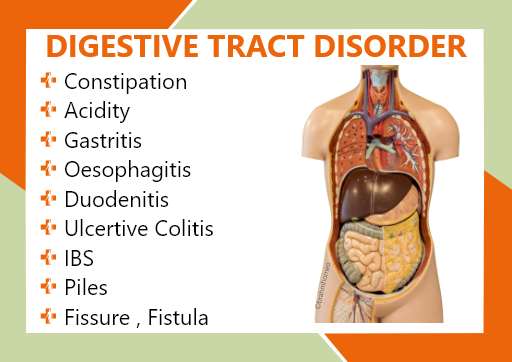
DIGESTIVE TRACT DISORDER
Constipation
Acidity
Gastritis
Oesophagitis
Duodenitis
Ulcertive Colitis
IBS
Piles
Fissure
Fistula
Diseases
malaria treatment in homeopathy
Malaria Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by Plasmodium parasites, which are transmitted by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. It remains a significant global health concern, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. Effective treatment of malaria depends on timely diagnosis, the type of malaria parasite, and the health status of the patient. -This article explores available treatment options, drug resistance challenges, and future developments in malaria treatment.
1. Diagnosis and Immediate Care?
Early diagnosis of malaria is crucial for effective treatment and minimizing complications. Primary diagnostic methods include: -Microscopic tests: Blood smears are examined under a microscope to detect malaria parasites. -Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs): These tests detect malaria antigens and are useful in remote areas lacking laboratory facilities. -Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): This highly sensitive method detects low parasite levels but is mainly used in research settings.
Once diagnosed, treatment should be started immediately to prevent serious complications such as cerebral malaria, organ failure or death.
First-line treatment options
The treatment regimen depends on the malaria species involved, the severity of the infection and possible drug resistance. The WHO recommends artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) as first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria.
1) Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT)
ACTs combine fast-acting artemisinin derivatives with long-acting partner drugs to increase efficacy and prevent resistance. Common ACTs include: -Artemether-lumefantrine (Coartem): A widely used ACT that provides high cure rates.
-Artesunate-amodiaquine: Effective against Plasmodium falciparum, the most deadly malaria parasite.
-Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine: Provides long-term protection and is used in areas with high transmission.
Chloroquine for P. vivax and P. ovale
For infections caused by Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale, chloroquine remains the drug of choice, except in areas where resistance has emerged. In such cases, alternative drugs such as ACT or quinine can be used.
2) Treatment of severe malaria?
Severe malaria is a medical emergency requiring hospitalization. Intravenous or intramuscular artesunate is preferred for severe cases. Patients receiving artesunate should subsequently transition to a full course of ACT to completely clear the parasite. If artesunate is not available, intravenous quinine can be used, although it has more side effects.
Supportive care
Cases of severe malaria may require additional supportive treatment, such as:
-Fluid replacement: to prevent dehydration and maintain blood pressure.
-Blood transfusion: in cases of severe anemia due to malaria. -Anticonvulsants: for patients experiencing seizures due to cerebral malaria. -Oxygen therapy: to manage respiratory distress.
3) Challenges in malaria treatment?
-Access to medicines In many malaria-endemic areas, access to quality medicines is limited due to economic constraints, weak healthcare infrastructure, and counterfeit medicines. Strengthening health systems and ensuring availability of ACT are critical for effective control of malaria.
4) Prevention and future treatments
While treatment is essential, prevention remains the most effective strategy against malaria. Preventive measures include: - Insecticide treated mosquito nets (ITNs): Reduces mosquito bites and malaria infection.
- Indoor residual spraying (IRS): Kills mosquitoes resting indoors. - Antimalarial prophylaxis: Used for travellers or people living in high-risk areas.
Vaccine development
Recent advances have led to the development of malaria vaccines, which provide protection against malaria, especially in young children,

latex allergy treatment in homeopathy
Latex Allergy Treatment: Causes, Symptoms and Management
Latex allergy is a hypersensitive immune reaction to natural rubber latex, commonly found in medical gloves, balloons, rubber bands and various other products. This allergy can range from mild skin irritation to severe anaphylactic reactions. It is important for individuals affected by this condition to understand the causes, symptoms and available treatment options.
1. What Causes Latex Allergy?
Latex is derived from the sap of the rubber tree and contains proteins that can trigger an allergic reaction in susceptible individuals. The allergy develops when the immune system mistakenly identifies these proteins as harmful substances, leading to an immune response.
-Individuals at higher risk of developing a latex allergy include: -Healthcare workers and individuals who frequently use latex gloves -People having multiple surgeries or medical procedures -People who have a history of allergies, such as hay fever or asthma -People who work in the rubber industry -Repeated exposure to latex increases the likelihood of developing an allergy over time.
2. What are the symptoms of latex allergy?
Latex allergy symptoms vary depending on the level of sensitivity and the type of exposure. Common symptoms include: 1. Mild symptoms: -Itching or rash - Scaly or cracked skin 2. Moderate symptoms: -Runny or stuffy nose -Itchy, watery eyes
3. Severe symptoms (anaphylaxis): -Difficulty breathing -Swelling of throat
-Fast heartbeat -Drop in blood pressure
-Loss of consciousness
3 How is latex allergy diagnosed?
Diagnosis of latex allergy typically includes:
-Medical history review: A doctor will assess symptoms and exposure to latex products. -Skin prick test: A small amount of latex protein is placed on the skin to check for an allergic reaction. -Blood test: Measures the presence of latex-specific antibodies in the bloodstream. -Patch testing: This determines whether delayed hypersensitivity reactions occur when exposed to latex.
4 Treatment and Management
1. Avoidance
The way to reduce latex allergy is to avoid exposure. Using latex-free gloves, bandages, and medical supplies -Choosing synthetic rubber or vinyl alternatives
-Avoiding latex balloons and rubber-based household items 2. Medications n cases where exposure occurs, medications can help reduce symptoms:
-Antihistamines: Help relieve mild allergic reactions such as itching, rashes, and sneezing.
-Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and skin reactions.
3. Desensitization therapy Currently, there is no therapy for latex allergy. Some research is underway to develop immunotherapy options, but avoidance is the best solution.
5. What precautions should be taken to prevent latex allergy?
If you are prone to latex allergy, take the following precautions: -Limit exposure to latex-containing products
-Use powder-free latex gloves with low protein levels if unavoidable -Be aware of cross-reactivity with certain foods such as bananas, avocados, kiwi and chestnuts
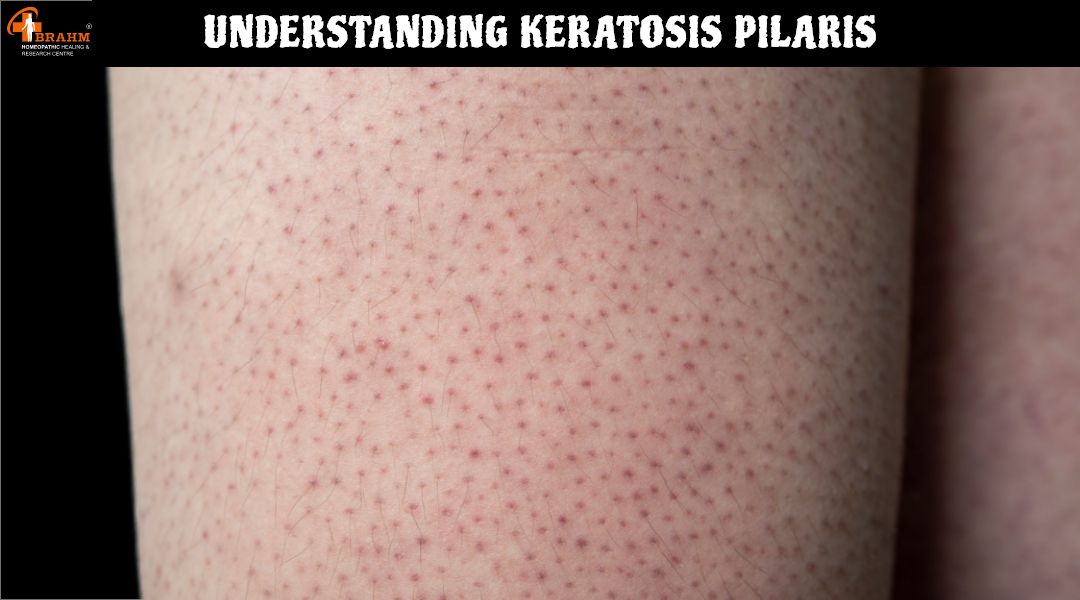
keratosis pilaris treatment in homeopathy
Understanding Keratosis Pilaris: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment?
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is a common, harmless skin condition that manifests as small, rough bumps on the skin, often resembling goosebumps or sandpaper. It is frequently referred to as "chicken skin" and is most commonly found on the upper arms, thighs, cheeks, and buttocks. Though it is not a serious medical condition, it can be a cosmetic concern for many individuals. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help manage and minimize its appearance.
1.Causes of Keratosis Pilaris?
Keratosis pilaris occurs due to the buildup of keratin, a protein that protects the skin from infections and harmful substances. This excess keratin clogs hair follicles, leading to the characteristic bumps. The exact cause of keratin buildup is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to the development of KP, including:
1)Genetics – KP often runs in families, indicating a strong hereditary component. 2)Dry Skin – People with dry skin are more prone to developing KP, as dryness exacerbates the rough texture. 3)Underlying Skin Conditions – Individuals with conditions such as eczema (atopic dermatitis) are at a higher risk.
4)Seasonal Changes – KP often worsens in colder months when the air is drier and improves in warmer, humid conditions.
5)Hormonal Fluctuations – Changes in hormones, such as during puberty or pregnancy, may influence KP severity.
2. Symptoms of Keratosis Pilaris?
The primary symptom of KP is the presence of small, rough, flesh-colored, red, or brown bumps on the skin. Other associated symptoms include: -Mild itching or irritation, though KP is usually not painful. -Dry, rough patches of skin in affected areas.
-Worsening of the condition in dry or cold weather. -A sandpaper-like texture to the skin. -KP does not cause any serious health problems but may lead to self-consciousness or discomfort about skin appearance.
3)Treatment and Management of Keratosis Pilaris?
There is no permanent cure for keratosis pilaris, but various treatments can help improve the skin’s texture and appearance. The key to managing KP is consistent skincare, including:
1. Exfoliation
-Chemical exfoliants – Products containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs), or urea can help break down keratin buildup. -Physical exfoliants – Using mild scrubs, loofahs, or exfoliating gloves can help smooth the skin. However, excessive scrubbing can irritate the skin.
2. Moisturization
Keeping the skin hydrated is crucial in reducing KP symptoms. Effective moisturizers include: -Thick creams and lotions :– Products with ingredients like ceramides, lactic acid, glycerin, or shea butter help retain moisture. -Urea-based creams : – These can help soften the rough skin texture. 3. Topical Treatments Certain medicated creams can improve KP, including:
-Retinoids – Derived from Vitamin A, retinoids like help speed up cell turnover and prevent clogged follicles. -Salicylic Acid – A beta-hydroxy acid that penetrates pores and reduces keratin buildup.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments -Use Gentle Cleansers – Harsh soaps can strip the skin of natural oils, exacerbating dryness. -Avoid Hot Showers – Hot water can further dry out the skin; lukewarm showers are recommended. -Wear Loose Clothing – Tight clothing may cause friction and irritation, making KP more noticeable.
Videos

homeopathy me cancer ka upchaar
होम्योपैथी में कैंसर का उपचार: एक समग्र दृष्टिकोण
कैंसर एक जटिल और घातक बीमारी है, जो असामान्य कोशिका वृद्धि के कारण होती है। आधुनिक चिकित्सा में कैंसर के उपचार के लिए सर्जरी, कीमोथेरेपी और रेडिएशन थेरेपी जैसे विकल्प उपलब्ध हैं। लेकिन कई लोग होम्योपैथी की ओर भी रुख कर रहे हैं, जो एक समग्र और प्राकृतिक उपचार पद्धति मानी जाती है।
1) होम्योपैथी की अवधारणा?
होम्योपैथी एक वैकल्पिक चिकित्सा प्रणाली है, जो 'समरूपता के सिद्धांत' (Law of Similars) पर आधारित है। यह मान्यता रखती है कि जो पदार्थ स्वस्थ व्यक्ति में किसी विशेष बीमारी के लक्षण उत्पन्न कर सकता है, वही पदार्थ अत्यंत पतली मात्रा में लेकर रोगी के शरीर में उसकी प्राकृतिक उपचार प्रक्रिया को सक्रिय कर सकता है।
2) कैंसर में होम्योपैथी कैसे काम करती है?
होम्योपैथी कैंसर को केवल एक शारीरिक समस्या के रूप में नहीं देखती, बल्कि इसे मानसिक, भावनात्मक और शारीरिक असंतुलन का परिणाम मानती है। यह उपचार प्रक्रिया को चार प्रमुख तरीकों से प्रभावी बनाती है:
* रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता को बढ़ाना * - होम्योपैथी शरीर की प्राकृतिक प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को मजबूत करने में सहायता करती है, जिससे कैंसर कोशिकाओं के प्रसार को धीमा किया जा सकता है।
* लक्षणों में सुधार
-कैंसर के कारण उत्पन्न दर्द, सूजन, थकान और मानसिक तनाव को कम करने में होम्योपैथिक दवाएँ प्रभावी हो सकती हैं। * अवरुद्ध ऊर्जा प्रवाह को संतुलित करना
-होम्योपैथी शरीर के भीतर ऊर्जा प्रवाह को संतुलित करने का प्रयास करती है, जिससे शरीर की स्व-उपचार प्रणाली सक्रिय हो जाती है। * कीमोथेरेपी और रेडिएशन के दुष्प्रभावों को कम करना -होम्योपैथिक दवाएँ कीमोथेरेपी और रेडिएशन थेरेपी के दुष्प्रभावों जैसे मतली, उल्टी, बाल झड़ना और कमजोरी को कम करने में सहायक हो सकती हैं।
3)होम्योपैथी और समग्र उपचार?
होम्योपैथी कैंसर के लक्षणों का इलाज करने तक ही सीमित नहीं रहती, बल्कि यह हमारे पूरे शरीर को अच्छा बनाने पर ध्यान देती है। इसके तहत मरीज के जीवनशैली, खानपान और मानसिक स्थिति रोगी के उपचार में तेजी लाई जाती है
सावधानियां और सीमाएं
होम्योपैथी कई तरह के बीमारी या रोगों में लाभकारी है, लेकिन कैंसर जैसी स्थिति में इसे मुख्य चिकित्सा के रूप में अपनाने से पहले एक बार अनुभवी डॉक्टर की सलाह लेनी चाहिए। कई बार कैंसर उन्नत अवस्था में होता है, जहां तत्काल सर्जरी या अन्य उपचार आवश्यक हो सकते हैं।
4) क्या होम्योपैथी कैंसर का पूर्ण इलाज कर सकती है?
होम्योपैथी कैंसर का पूर्ण इलाज कर सकती है या नहीं, इस पर चिकित्सा जगत में मतभेद हैं। हालांकि, यह निश्चित रूप से कैंसर रोगियों की जीवन गुणवत्ता को सुधार सकती है और लक्षणों को कम करने में मदद कर सकती है। यह उन मरीजों के लिए विशेष रूप से उपयोगी हो सकती है, जो पारंपरिक उपचार के साथ-साथ एक समग्र और कम हानिकारक उपचार की तलाश में हैं।
निष्कर्ष
होम्योपैथी एक प्राकृतिक और व्यक्तिगत चिकित्सा प्रणाली है, जो कैंसर के लक्षणों को कम करने और शरीर की प्राकृतिक उपचार प्रणाली को सक्रिय करने में सहायक हो सकती है। हालाँकि, कैंसर जैसी गंभीर बीमारी में पारंपरिक चिकित्सा के साथ होम्योपैथी को सहायक चिकित्सा के रूप में अपनाना अधिक सुरक्षित और प्रभावी हो सकता है। रोगी को हमेशा एक योग्य चिकित्सक से परामर्श करके ही होम्योपैथिक उपचार अपनाना चाहिए।

dr pradeep kushwaha youtube faq section
Q1.मेरा अपेंडिक्स 6.7 एमएम का है क्या करना चाहिए दवाई से ठीक नहीं हो सकता है क्या?
अपेंडिक्स का सेक्शन है वहां पर इन्होंने यह क्वेश्चन पूछा है देखिए अपेंडिसाइटिस मतलब जो अपेंडिक्स है उसमें इन्फ्लेमेशन होना बार-बार जिन केसेस में इंफ्लेमेटरी चेंस आता है मेडिसिन से थोड़ा सेट हो जाता है फिर आ जाता है उस केस में या फिर बहुत ज्यादा इंफ्लेमेशन आ गया है उस केस में इसे निकाल देने की सलाह दी जाती है और ज्यादातर लोग निकाल भी देते हैं लेकिन होम्योपैथिक मेडिसिन से अपेंडिसाइटिस के केसेस को विदाउट सर्जरी भी ठीक किया जा सकता है बहुत ही वेल एक्सपीरियंस डॉक्टर के अंडर में आप अपना ट्रीटमेंट ले सकते हैं जब इंफ्लेमेशन 6.7 एएम का इसे रिवर्स किया जा सकता है होम्योपैथिक मेडिसिन से 7 8 9 एमएम तक के केसेस को हम देखते हैं कि बहुत अच्छे से मेडिसिन से क्योर किया जा सकता है और सर्जरी की जरूरत नहीं पड़ती है लेकिन अपेंडिसाइटिस के केसेस थोड़े सेंसिटिव केस होते हैं आप सोच समझ के अपना इलाज शुरू करिए एक्सपीरियंस डॉक्टर के अंडर में क्योंकि जब यह साइज बढ़ता है तो इसका जो मैनेजमेंट रहता है पूरा दो या तीन दिन का ही गेम रहता है अगर आपने तीन दिन में केस को सेटल कर दिया तब तो आप बाहर आ जाएंगे लेकिन अगर सेटल नहीं होता है डिजीज बढ़ते जाती है तो आप फर्द कॉम्प्लिकेशन में पड़ सकते हैं इसलिए एक्सपीरियंस डॉक्टर जिसने ऑलरेडी इस तरह के केसेस को कई बार ठीक किया है उसके अंडर में अगर आप होम्योपैथिक ट्रीटमेंट लेते हो तो डेफिनेटली इसे विदाउट सर्जरी क्योर किया जा सकता है थैंक यू
Q2.ये एक क्वेश्चन है क्या ऑटोइम्यून पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ठीक हो सकता है होम्योपैथी से ?
सो हमारे अंदर ऑलरेडी हंड्रेड्स ऑफ पेशेंट है जो ऑटोइम्यून पैंक्रियाटाइटिस से ग्रसित है और ब्रम होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर का ट्रीटमेंट ले रहे हैं आप जब अपने रिपोर्ट्स को देखेंगे उसमें एक रिपोर्ट होता है आईजीजी फ का यह रिपोर्ट उन ग्रुप के लोगों के लिए कराया जाता है देखने के लिए क्या वह ऑटोइम्यून पॉजिटिव पेशेंट तो नहीं है जिस किसी केस में य आईजीजी फ एलिवेटेड उनको ऑटोइम्यून पनक टाइटिस है सो जब इनके केस को अच्छे से समझा जाता है और उसके बाद उनकी जो मेडिसिन प्लान की जाती है मेडिसिन के साथ प्रॉपर डाट लाइफस्टाइल और यह बहुत ही इंपॉर्टेंट है कि ऑटो इम्यून डिजीज में आपका मेंटल हेल्थ अच्छा रहे क्योंकि स्ट्रेस भी एक इंपॉर्टेंट फैक्टर होता है जो इसको ट्रिगर करता रहता है तो अगर आप इसको समझते हैं और उसको मैनेज करते हैं उसको मैनेज करने के लिए हम प्रॉपर उनको गाइड करते हैं क्या-क्या स्टेप्स ध्यान रखने हैं और जब यह सारी ची चीजों को लेकर चला जाता है तो एक राइट होम्योपैथिक मेडिसिन डेफिनेटली आपको इस कंडीशन से बाहर निकाल देती है कितने ही पेशेंट है जिनको हमने ऑलरेडी ट्रीट किया है और उनका आईजी g4 का लेवल भी नॉर्मल लाया है अलोंग विद दैट उनकी जो पैथोलॉजिकल चेंजेज है वो रिपोर्ट वाइज भी नॉर्मल है और हेल्थ वाइज भी पेशेंट को किसी का किसी तरह का पेन या तकलीफ नहीं है सो अगर इसका मैं आपको आंसर करूं तो डेफिनेटली ऑटोइम्यून पनकटा इटिस को होम्योपैथिक मेडिसिन से क्योर करना पॉसिबल है थैंक यू
मयंक खराड़ी जी का एक कमेंट है यू आर राइट मेरा भी हाल तुम्हारे जैसा था भाई बट प्रदीप सर से जुड़ने के बाद उनकी ट्रीटमेंट से बिल्कुल ठीक और नॉर्मल लाइफ जी रहा हूं इनकी वजह से य नंबर वन डॉक्टर ऑल इंडिया में यही कहूंगा
मैं यह है सो मैं उन्हें दिल से थैंक यू कहना चाहूंगा मैं खराड़ी जी भी बहुत अच्छे से बहुत डिसिप्लिन वे में इन्होंने ट्रीटमेंट को फॉलो किया है और इनका केस एक्यूट नेक्रोलाइसिस का था और इस केस में पहले इनको मल्टीपल पॉकेट्स थे और ट्रीटमेंट के बाद से सारे पॉकेट रिजॉल्व हो गए इनके साइन एंड सिंटमोबाइल उसे शेयर किया थैंक यू
Q3.ओवेरियन सिस्ट के इस वीडियो में एक क्वेश्चन है मुझे कुछ भी दर्द नहीं होता मैं एक नॉर्मल हूं रिलेशन टाइम में भी दर्द नहीं होता पीरियड भी टाइम से आता है फिर मुझे सिंपल सिस्ट हो गया नेचुरली कंसीव कर सकती हो ?
सो हर तरह से नॉर्मल है लेकिन आप देख रहे हैं कि ओवरी में एक सिंपल सिस्ट हुआ है सिस्ट का साइज अगर नॉर्मल है मान लीजिए 3 बा 3 सेंटीमीटर का यहां पे आपने साइज नहीं लिखा है अगर साइज लिखे होते तो मैं आपको और अच्छे से गाइड करता बट मैं एक आपको मेरे एंड से एक अजमन बता दे रहा हूं कि यदि 3 बा 3 सेंटीमीटर या 3/4 सेंटीमीटर है या इस रेंज के आसपास का सिंपल सिस्ट रह रहा है और आपका क्वेश्चन है कि नेचुरली प्रेगनेंसी रह सकती है तो बिल्कुल रह सकती है नेचुरली प्रेगनेंसी रहेगी वो भी पॉसिबल है और इस सिस्ट के साथ प्रेगनेंसी कंटिन्यू आप करते हैं किसी अच्छे गायनेकोलॉजिस्ट डॉक्टर के गाइडेंस में तो डेफिनेटली प्रेगनेंसी भी सेफ रहेगी और किसी तरह का प्रॉब्लम नहीं होगा लेकिन सिस्ट बड़े साइज का है और विद प्रेगनेंसी है तो आपको अपने गायनेकोलॉजिस्ट से सलाह लेना चाहिए और उसके मार्गदर्शन में आगे बढ़ना चाहिए थैंक यू

homeopathy medicine kaise kaam karti hai?
१. होम्योपैथी मेडिसिन कैसे काम करती है?
होम्योपैथी एक वैकल्पिक चिकित्सा प्रणाली है जो "समरूपता के सिद्धांत" (Law of Similars) पर आधारित है। इस सिद्धांत के अनुसार, जो पदार्थ स्वस्थ व्यक्ति में किसी विशेष रोग के लक्षण उत्पन्न करता है, वही पदार्थ बहुत ही सूक्ष्म मात्रा में लेकर रोगी में उन लक्षणों का उपचार कर सकता है। यह चिकित्सा प्रणाली 18वीं शताब्दी में जर्मन चिकित्सक सैमुएल हैनीमैन द्वारा विकसित की गई थी।
२. होम्योपैथी का सिद्धांत और कार्यप्रणाली?
(1)समरूपता का नियम (Law of Similars)
इस सिद्धांत के अनुसार, "जो चीज बीमारी उत्पन्न कर सकती है, वही उसे ठीक भी कर सकती है।" -उदाहरण के लिए, क्विनाइन (Cinchona Bark) मलेरिया जैसी बीमारी के लक्षण पैदा करता है, इसलिए होम्योपैथी में इसे मलेरिया के उपचार के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाता है।
(२) अत्यधिक पतला (Ultra Dilution) और शक्ति प्रदान करना (Potentization)
होम्योपैथिक दवाओं को प्राकृतिक स्रोतों (पौधे, खनिज, पशु उत्पाद) से तैयार किया जाता है और उन्हें बार-बार पतला (dilute) किया जाता है।
- इस प्रक्रिया को "पोटेंशिएशन" कहा जाता है, जिससे दवा में मूल पदार्थ के अणु नगण्य रह जाते हैं, लेकिन उसकी ऊर्जा या कंपन शरीर को प्रभावित करता है।
(३) शरीर की आत्म-उपचार शक्ति (Self-Healing Power) को बढ़ावा होम्योपैथी शरीर की प्राकृतिक रोग-प्रतिरोधक क्षमता (immunity) को बढ़ाकर उसे खुद से ठीक करने में मदद करती है।
यह सिर्फ लक्षणों को दबाने के बजाय बीमारी के मूल कारण को ठीक करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करती है।३.होम्योपैथी के कार्य करने का तरीका ?
- ऊर्जा स्तर पर कार्य करती है
होम्योपैथिक दवाएं अत्यधिक पतली होती हैं, वे शरीर की ऊर्जा प्रणाली को संतुलित करने का काम करती हैं। यह जैव-ऊर्जा (Vital Force) को उत्तेजित करके शरीर को खुद से ठीक करने के लिए प्रेरित करती हैं। - कोशिकाओं और अंगों पर प्रभाव जब होम्योपैथिक दवा शरीर में जाती है, तो यह कोशिकाओं के स्तर पर कार्य करके उनके कार्यों को सामान्य बनाती है। - बिमारी के मूल कारण पर काम
होम्योपैथी सिर्फ बाहरी लक्षणों को ठीक करने के बजाय बीमारी की जड़ तक पहुंचकर उसे ठीक करने का कार्य करती है। यह मानसिक, शारीरिक और भावनात्मक स्तर पर कार्य करके समग्र स्वास्थ्य को सुधारने में मदद करती है।
४.होम्योपैथिक उपचार के फायदे?
-सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक – इसमें केमिकल्स नहीं होते, इसलिए यह शरीर के लिए सुरक्षित है।
-बच्चों और बुजुर्गों के लिए उपयुक्त – होम्योपैथी दवाएं सभी आयु वर्ग के लोगों के लिए सुरक्षित हैं। -पुरानी और जटिल बीमारियों में प्रभावी – एलर्जी, अस्थमा, त्वचा रोग, माइग्रेन, और आर्थराइटिस जैसी बीमारियों में लाभकारी होती हैं। -मानसिक स्वास्थ्य पर प्रभाव – तनाव, चिंता, डिप्रेशन जैसी मानसिक समस्याओं में भी असरदार होती है।
५ .क्या होम्योपैथी वैज्ञानिक रूप से सिद्ध है?
होम्योपैथी पर कई शोध हुए हैं, लेकिन वैज्ञानिक समुदाय में इसे लेकर मिश्रित राय है। कुछ अध्ययन होम्योपैथी को प्रभावी मानते हैं, जबकि कुछ इसे प्लेसिबो प्रभाव (Placebo Effect) मानते हैं। हालांकि, दुनियाभर में लाखों लोग इसे अपनाते हैं और इसका लाभ अनुभव कर चुके हैं।
