japanese encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis : Causes, symptoms, prevention and treatment
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that directly affects the brain and is transmitted by mosquito bites. It is caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), a flavivirus related to dengue, yellow fever and West Nile viruses.

1) Causes and transmission of Japanese encephalitis?
The primary mode of transmission of JE is through the bite of infected Culex mosquitoes, particularly Culex tritaeniorhynchus. Such mosquitoes breed in rice fields, ponds. The virus persists in a transmission cycle between mosquitoes, pigs and marsh birds.
Humans and other animals, such as horses, are accidental hosts, meaning they do not contribute to the spread of the virus once they are infected.
Japanese encephalitis occurs mostly in areas with warm, humid climates, where mosquito populations thrive. The risk of infection is highest during the monsoon and post-monsoon seasons, when mosquito breeding peaks. Although most infections are asymptomatic or mild, in some cases, the virus can cause serious neurological complications.

2) Symptoms and complications of Japanese encephalitis?
People infected with JEV do not develop symptoms. However, in cases where the virus progresses, symptoms usually appear 5-15 days after infection. As the disease progresses, more severe neurological symptoms may develop, such as
- Stiff neck
- Seizures
- Coma
Severe cases may result in permanent neurological damage, cognitive impairment, or even death. The mortality rate in symptomatic cases is around 20-30%, and up to 50% of survivors experience long-term complications such as memory loss, difficulty speaking, and muscle weakness.
Diagnosis of JE involves laboratory tests to detect the presence of JEV in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid. The most common diagnostic method is the detection of JEV-specific IgM antibodies through (ELISA).
There is no specific antiviral treatment for JE, making prevention important. Preventive measures include vaccination, mosquito control, and personal protective measures. Such as,
-1. Vaccination
Severe cases may result in permanent neurological damage, cognitive impairment, or even death. The mortality rate in symptomatic cases is around 20-30%, and up to 50% of survivors experience long-term complications such as memory loss, difficulty speaking, and muscle weakness.
3) What is the prognosis of Japanese encephalitis?
Diagnosis of JE involves laboratory tests to detect the presence of JEV in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid. The most common diagnostic method is the detection of JEV-specific IgM antibodies through (ELISA).
4) What is the prevention of Japanese encephalitis?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for JE, making prevention important. Preventive measures include vaccination, mosquito control, and personal protective measures. Such as,
-1. Vaccination
The most effective way to prevent JE is vaccination. Several vaccines are available, including inactivated and live-attenuated vaccines.
-2. Mosquito control
Using insecticides and larvicides in mosquito breeding areas
-3. Personal protective measures
How individuals can avoid mosquito bites includes:
- Sleeping under an insecticide-treated mosquito net.
* { Treatment }
There is no antiviral treatment for JE. Proper care includes:
-Hospitalisation is necessary for severe cases
Using insecticides and larvicides in mosquito breeding areas
-3. Personal protective measures
How individuals can avoid mosquito bites includes:
- Sleeping under an insecticide-treated mosquito net.
* { Treatment }
There is no antiviral treatment for JE. Proper care includes:
-Hospitalisation is necessary for severe cases
-Anticonvulsants to control seizures
-Due to the high mortality and complication rates, early medical attention is essential for suspected cases.
Stories

chronic pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियास ठीक करने के उपाय
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस एक बीमारी है जो आपके पैंक्रियास में हो सकती है। पैंक्रियास आपके पेट में एक लंबी ग्रंथि है जो भोजन को पचाने में आपकी मदद करती है। यह आपके रक्त प्रवाह में हार्मोन भी जारी करता है जो आपके शरीर को ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग करने में मदद करता है। यदि आपका पैंक्रियास क्षतिग्रस्त हो गया है, तो पाचन एंजाइम सामान्य रूप से आपकी छोटी आंत में नहीं जा सकते हैं और आपका शरीर ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग नहीं कर सकता है।
पैंक्रियास शरीर का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है जो हार्मोन इंसुलिन का उत्पादन करके रक्त शर्करा को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। यदि इस अंग को नुकसान होता है, तो इससे मानव शरीर में गंभीर समस्याएं हो सकती हैं। ऐसी ही एक समस्या है जब पैंक्रियास में सूजन हो जाती है, जिसे तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस कहा जाता है।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस पैंक्रियास की सूजन है जो लंबे समय तक रह सकती है। इससे पैंक्रियास और अन्य जटिलताओं को स्थायी नुकसान हो सकता है। इस सूजन से निशान ऊतक विकसित हो सकते हैं, जो इंसुलिन उत्पन्न करने वाली कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा सकते हैं। यह पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ वाले लगभग 45 प्रतिशत लोगों में मधुमेह का कारण बन सकता है। भारी शराब का सेवन भी वयस्कों में पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकता है। ऑटोइम्यून और आनुवंशिक रोग, जैसे सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस, कुछ लोगों में पुरानी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकते हैं।
उत्तर भारत में, ऐसे बहुत से लोग हैं जिनके पास पीने के लिए बहुत अधिक है और कभी-कभी एक छोटा सा पत्थर उनके पित्ताशय में फंस सकता है और उनके अग्न्याशय के उद्घाटन को अवरुद्ध कर सकता है। इससे उन्हें अपना खाना पचाने में मुश्किल हो सकती है। 3 हाल ही में एशिया-प्रशांत क्षेत्र के विभिन्न देशों में किए गए एक सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार दक्षिण भारत में पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ की व्यापकता प्रति 100,000 जनसंख्या पर 114-200 मामले हैं।
Chronic Pancreatitis Patient Cured Report
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण ?
-कुछ लोगों को पेट में दर्द होता है जो पीठ तक फैल सकता है। -यह दर्द मतली और उल्टी जैसी चीजों के कारण हो सकता है। -खाने के बाद दर्द और बढ़ सकता है। -कभी-कभी किसी के पेट को छूने पर दर्द महसूस हो सकता है। -व्यक्ति को बुखार और ठंड लगना भी हो सकता है। वे बहुत कमजोर और थका हुआ भी महसूस कर सकते हैं।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण ?
-पित्ताशय की पथरी -शराब
-रक्त में उच्च ट्राइग्लिसराइड का स्तर -रक्त में उच्च कैल्शियम का स्तर
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज कैसे किया जाता है?
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस नेक्रोसिस का उपचार उपचारात्मक है। आप कितने समय तक इस बीमारी से पीड़ित रहेंगे यह काफी हद तक आपकी उपचार योजना पर निर्भर करता है। ब्रह्म अनुसंधान पर आधारित चिकित्सकीय रूप से सिद्ध वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी के इलाज में अत्यधिक प्रभावी हैं। हमारे पास आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करने, सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों, रोग के पाठ्यक्रम का दस्तावेजीकरण करने, रोग के चरण, पूर्वानुमान और जटिलताओं को समझने की क्षमता है, हमारे पास अत्यधिक योग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है। फिर वे आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताएंगे, आपको एक उचित आहार योजना (क्या खाएं और क्या नहीं खाएं), व्यायाम योजना, जीवनशैली योजना और कई अन्य कारक प्रदान करेंगे जो आपके समग्र स्वास्थ्य में सुधार कर सकते हैं। पढ़ाना। व्यवस्थित उपचार रोग ठीक होने तक होम्योपैथिक औषधियों से उपचार करें। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, चाहे वह थोड़े समय के लिए हो या कई सालों से। हम सभी ठीक हो सकते हैं, लेकिन बीमारी के प्रारंभिक चरण में हम तेजी से ठीक हो जाते हैं। पुरानी या देर से आने वाली या लंबे समय तक चलने वाली बीमारियों को ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगता है। समझदार लोग इस बीमारी के लक्षण दिखते ही इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं। इसलिए, यदि आपको कोई असामान्यता नज़र आती है, तो कृपया तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।

Acute Necrotizing pancreas treatment in hindi
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ ?
आक्रामक अंतःशिरा द्रव पुनर्जीवन, दर्द प्रबंधन, और आंत्र भोजन की जल्द से जल्द संभव शुरुआत उपचार के मुख्य घटक हैं। जबकि उपरोक्त सावधानियों से बाँझ परिगलन में सुधार हो सकता है, संक्रमित परिगलन के लिए अतिरिक्त उपचार की आवश्यकता होती है।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लक्षण ? - बुखार - फूला हुआ पेट - मतली और दस्त तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण ?
- अग्न्याशय में चोट - उच्च रक्त कैल्शियम स्तर और रक्त वसा सांद्रता
ऐसी स्थितियाँ जो अग्न्याशय को प्रभावित करती हैं और आपके परिवार में चलती रहती हैं, उनमें सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस और अन्य आनुवंशिक विकार शामिल हैं जिनके परिणामस्वरूप बार-बार अग्नाशयशोथ होता है|
क्या एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रिएटाइटिस का इलाज होम्योपैथी से संभव है ?
हां, होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनकर एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज संभव है। होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनने से आपको इन दवाओं का कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं होगा और यह समस्या को जड़ से खत्म कर देता है, इसीलिए आपको अपने एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के इलाज के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार का ही चयन करना चाहिए।
आप तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ से कैसे छुटकारा पा सकते हैं ?
शुरुआती चरण में सर्वोत्तम उपचार चुनने से आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस से छुटकारा मिल जाएगा। होम्योपैथिक उपचार का चयन करके, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे विश्वसनीय उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करता है। एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार सबसे अच्छा इलाज है। जैसे ही आप एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक करने के लिए अपना उपचार शुरू करेंगे, आपको निश्चित परिणाम मिलेंगे।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार से तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ का इलाज संभव है। आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, इसका उपचार योजना पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ता है। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कब से अपनी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, या तो हाल ही में या कई वर्षों से - हमारे पास सब कुछ ठीक है, लेकिन बीमारी के शुरुआती चरण में, आप तेजी से ठीक हो जाएंगे। पुरानी स्थितियों के लिए या बाद के चरण में या कई वर्षों की पीड़ा के मामले में, इसे ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगेगा। बुद्धिमान व्यक्ति हमेशा इस बीमारी के किसी भी लक्षण को देखते ही तुरंत इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं, इसलिए जैसे ही आपमें कोई असामान्यता दिखे तो तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एवं रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
ब्रह्म अनुसंधान आधारित, चिकित्सकीय रूप से प्रमाणित, वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी को ठीक करने में बहुत प्रभावी है। हमारे पास सुयोग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है जो आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करती है, रोग की प्रगति के साथ-साथ सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों को रिकॉर्ड करती है, इसकी प्रगति के चरणों, पूर्वानुमान और इसकी जटिलताओं को समझती है। उसके बाद वे आपको आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताते हैं, आपको उचित आहार चार्ट [क्या खाएं या क्या न खाएं], व्यायाम योजना, जीवन शैली योजना प्रदान करते हैं और कई अन्य कारकों के बारे में मार्गदर्शन करते हैं जो व्यवस्थित प्रबंधन के साथ आपकी सामान्य स्वास्थ्य स्थिति में सुधार कर सकते हैं। जब तक यह ठीक न हो जाए तब तक होम्योपैथिक दवाओं से अपनी बीमारी का इलाज करें।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लिए आहार ?
कुपोषण और पोषण संबंधी कमियों को रोकने के लिए, सामान्य रक्त शर्करा के स्तर को बनाए रखने और मधुमेह, गुर्दे की समस्याओं और पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ से जुड़ी अन्य स्थितियों को रोकने या बेहतर ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए, अग्नाशयशोथ की तीव्र घटना से बचना महत्वपूर्ण है।
यदि आप एक स्वस्थ आहार योजना की तलाश में हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। हमारे विशेषज्ञ आपकी व्यक्तिगत आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप एक योजना बनाने में आपकी सहायता कर सकते हैं

Pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ?
जब पैंक्रियाटाइटिसमें सूजन और संक्रमण हो जाता है तो इससे पैंक्रिअटिटिस नामक रोग हो जाता है। पैंक्रियास एक लंबा, चपटा अंग है जो पेट के पीछे पेट के शीर्ष पर छिपा होता है। पैंक्रिअटिटिस उत्तेजनाओं और हार्मोन का उत्पादन करके पाचन में मदद करता है जो आपके शरीर में ग्लूकोज के प्रसंस्करण को विनियमित करने में मदद करते हैं।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण:
-पेट के ऊपरी भाग में दर्द होना। -बेकार वजन घटाना. -पेट का ख़राब होना.
-शरीर का असामान्य रूप से उच्च तापमान। -पेट को छूने पर दर्द होना। -तेज़ दिल की धड़कन. -हाइपरटोनिक निर्जलीकरण.
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण:
-पित्ताशय में पथरी. -भारी शराब का सेवन.
-भारी खुराक वाली दवाएँ। -हार्मोन का असंतुलन. -रक्त में वसा जो ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स का कारण बनता है। -आनुवंशिकता की स्थितियाँ. -पेट में सूजन ।
क्या होम्योपैथी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक कर सकती है?
हाँ, होम्योपैथीपैंक्रियाटाइटिसको ठीक कर सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको पैंक्रिअटिटिस के लिए सबसे भरोसेमंद उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करती है।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा उपचार क्या है?
यदि पैंक्रियाज अच्छी तरह से काम नहीं कर रहा है तो होम्योपैथिक उपचार वास्तव में बेहतर होने में मदद करने का एक अच्छा तरीका है। जब आप उपचार शुरू करते हैं, तो आप जल्दी परिणाम देखेंगे। बहुत सारे लोग इस इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जा रहे हैं और वे वास्तव में अच्छा कर रहे हैं। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपके पैंक्रियाज के को बेहतर बनाने में मदद करने के लिए आपको सबसे तेज़ और सुरक्षित तरीका प्रदान करना सुनिश्चित करती है।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
बीमार होने पर लोगों को बेहतर महसूस कराने में मदद करने के लिए हमारे पास एक विशेष तरीका है। हमारे पास वास्तव में स्मार्ट डॉक्टर हैं जो ध्यान से देखते हैं और नोट करते हैं कि बीमारी व्यक्ति को कैसे प्रभावित कर रही है। फिर, वे सलाह देते हैं कि क्या खाना चाहिए, व्यायाम करना चाहिए और स्वस्थ जीवन कैसे जीना चाहिए। वे व्यक्ति को ठीक होने में मदद करने के लिए विशेष दवा भी देते हैं। यह तरीका कारगर साबित हुआ है!
Tips

dehydration treatment in homeopathy
1. Dehydration treatment
When the body loses more fluid than it takes in, it causes an imbalance in electrolytes and fluids needed for normal body function. This can be due to excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, or not drinking enough water.
While severe dehydration requires medical attention, mild to moderate dehydration can often be treated effectively at home without the use of drugs or medication. Natural remedies and lifestyle changes can help restore hydration and balance in a safe and gentle way.
1. Replenish water
The most important step in treating dehydration is to drink water. Clean water is the best way to rehydrate the body. Drink water slowly and in small sips rather than drinking large amounts at once, especially if nausea occurs. -Drinking small amounts at regular intervals allows the body to absorb fluids more effectively.
2. Consume natural electrolytes
When we sweat due to illness, we also lose essential electrolytes like sodium, potassium and magnesium. Without these, just drinking water is not enough. You can make an electrolyte drink at home by mixing the following:
- 1 liter of clean water - 6 teaspoons of sugar
- 1/2 teaspoon of salt This solution helps a lot in balancing electrolytes and can be more effective than plain water.
- Coconut water is a natural alternative as it has a good balance of sodium, potassium and other electrolytes.
3. Eat hydrating foods
Some foods are high in water and can help restore hydration naturally. For example,
watermelon, cucumber, oranges, lettuce - Some foods in your diet can provide both fluids and essential nutrients.
4. Avoid dehydrating substances
- Coffee, energy drinks
- Alcohol
- Salty snacks
These can worsen fluid loss. Sticking to water and natural fluids is the best option until hydration is restored.
5. Rest
If the dehydration is caused by heat or strenuous physical activity, resting in a cool, shady area is a must. - Avoiding excessive sweating or exertion helps the body recover more easily. - Using a fan, cool cloth or taking a warm bath also helps regulate body temperature
6. Monitor symptoms
It is important to monitor your condition. Signs of dehydration include: - Increased urine with a light color
- Decreased thirst
If symptoms persist or worsen - such as dizziness, very dark urine, it is important to seek medical help immediately.
Final Thoughts
Dehydration can often be treated effectively without medication or drugs, especially when it's caught early.
-While natural remedies are helpful, it's important to see a doctor if symptoms become severe or don't respond to home remedies

hamare sarir ke liye sabji ke labh
सब्जियाँ हमारे आहार का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा हैं। इनमें कई प्रकार के विटामिन, खनिज, एंटीऑक्सीडेंट और फाइबर होते हैं, जो शरीर को स्वस्थ बनाए रखते हैं। सब्जियों का सेवन न केवल रोगों से बचाव करता है बल्कि संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य को भी बनाए रखता है।
सब्जियों के प्रकार और उनके लाभ
1. हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ (Leafy Green Vegetables)
हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ पोषण से भरपूर होती हैं और शरीर को कई तरह के आवश्यक तत्व प्रदान करती हैं।
-1. पालक (Spinach) लाभ: आयरन, कैल्शियम और फाइबर से भरपूर। हड्डियों और मांसपेशियों को मजबूत बनाता है। एनीमिया और कब्ज से बचाव करता है।
2. सरसों के पत्ते (Mustard Greens)
-लाभ: -हड्डियों के लिए फायदेमंद। -इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है। -त्वचा और बालों को स्वस्थ रखता है।
3. मेथी (Fenugreek Leaves)
-लाभ: -डायबिटीज को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। -पाचन को सुधारता है और भूख बढ़ाता है।
4. धनिया और पुदीना (Coriander & Mint Leaves)
-लाभ: -पाचन को सुधारते हैं। -विषाक्त पदार्थों को बाहर निकालते हैं। -त्वचा को चमकदार बनाते हैं।
2. जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ (Root Vegetables)
जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ फाइबर और आवश्यक खनिजों से भरपूर होती हैं।
5. गाजर (Carrot)

sarir ke liye vitamin or unke labh
हमारे शरीर के लिए सभी विटामिन और उनके लाभ
विटामिन हमारे शरीर के लिए आवश्यक पोषक तत्व हैं, जो शरीर के विभिन्न कार्यों को सुचारू रूप से चलाने में मदद करते हैं। ये सूक्ष्म पोषक तत्व होते हैं, लेकिन शरीर में इनकी भूमिका बहुत महत्वपूर्ण होती है। विटामिन की कमी से कई स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ हो सकती हैं, इसलिए संतुलित आहार लेना जरूरी है।
विटामिन कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
-विटामिन दो प्रकार के होते हैं: -1. वसा में घुलनशील विटामिन (Fat-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में वसा में संग्रहित होते हैं और जरूरत पड़ने पर उपयोग किए जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन A, D, E और K आते हैं।
-2. जल में घुलनशील विटामिन (Water-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में जमा नहीं होते और मूत्र के माध्यम से बाहर निकल जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन C और सभी B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन आते हैं।
विटामिन और उनके लाभ
1. विटामिन A (रेटिनॉल, बीटा-कैरोटीन)
भूमिका:
आँखों की रोशनी को बनाए रखता है।
त्वचा और इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है।
हड्डियों और दांतों के विकास में सहायक है।
स्रोत:
गाजर पालकआम, शकरकंद, डेयरी उत्पाद, अंडे, मछली का तेल।
कमी के प्रभाव:
रतौंधी (नाइट ब्लाइंडनेस)
त्वचा में रूखापन
रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी
---
2. विटामिन B-कॉम्प्लेक्स (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12)
B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र और रक्त निर्माण में मदद करते हैं। B1 (थायमिन)
भूमिका: ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र के कार्यों में सहायक।
स्रोत: साबुत अनाज, बीन्स, सूरजमुखी के बीज, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: कमजोरी, भूख न लगना, तंत्रिका तंत्र की समस्या।
B2 (राइबोफ्लेविन)
भूमिका: त्वचा, आँखों और ऊर्जा उत्पादन के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: दूध, दही, अंडे, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: होंठों में दरारें, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B3 (नियासिन)
भूमिका: कोलेस्ट्रॉल को नियंत्रित करता है और पाचन में सहायक होता है।
स्रोत: मूंगफली, मशरूम, टमाटर, चिकन, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा रोग, मानसिक कमजोरी। B5 (पैंटोथेनिक एसिड)
भूमिका: हार्मोन उत्पादन और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: मशरूम, एवोकाडो, दूध, ब्रोकली।
कमी के प्रभाव: थकान, सिरदर्द।
B6 (पाइरिडोक्सिन)
भूमिका: तंत्रिका तंत्र और प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को मजबूत करता है।
स्रोत: केला, चिकन, सोयाबीन, आलू।
कमी के प्रभाव: अवसाद, त्वचा रोग।
B7 (बायोटिन)
भूमिका: बालों और त्वचा के स्वास्थ्य को बनाए रखता है।
स्रोत: अंडे, मूंगफली, फूलगोभी।
कमी के प्रभाव: बाल झड़ना, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B9 (फोलिक एसिड)
भूमिका: डीएनए निर्माण और गर्भावस्था में जरूरी।
स्रोत: दालें, हरी सब्जियाँ, बीन्स। कमी के प्रभाव: एनीमिया, जन्म दोष।
B12 (कोबालामिन)
भूमिका: लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं और तंत्रिका तंत्र के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: मांस, अंडे, डेयरी उत्पाद। कमी के प्रभाव: स्मरण शक्ति की कमजोरी, एनीमिया।
---
3. विटामिन C (एस्कॉर्बिक एसिड)
भूमिका: इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है, त्वचा को चमकदार बनाता है, और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: संतरा, नींबू, स्ट्रॉबेरी, टमाटर, हरी मिर्च।
कमी के प्रभाव: स्कर्वी, मसूड़ों से खून आना, रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी।
---
4. विटामिन D (कोलेकल्सीफेरोल)
भूमिका: हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाता है और कैल्शियम के अवशोषण में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: सूर्य का प्रकाश, मछली, अंडे, दूध।
कमी के प्रभाव: हड्डियों में कमजोरी, रिकेट्स।
---
5. विटामिन E (टोकोफेरॉल)
भूमिका: एंटीऑक्सीडेंट के रूप में कार्य करता है और त्वचा तथा बालों के लिए लाभदायक है। स्रोत: बादाम, सूरजमुखी के बीज, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा की समस्याएँ, कमजोरी।
---
6. विटामिन K (फायलोक्विनोन)
भूमिका: रक्त को थक्का जमाने (ब्लड क्लॉटिंग) में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: पालक, ब्रोकोली, हरी सब्जियाँ।
कमी के प्रभाव: चोट लगने पर खून न रुकना। ---
निष्कर्ष
शरीर को सभी विटामिनों की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि सभी अंग सही से काम कर सकें। इनके लिए संतुलित आहार लेना बहुत जरूरी है। यदि विटामिन की कमी हो, तो डॉक्टर से परामर्श लेकर सप्लीमेंट्स भी लिए जा सकते हैं। लेकिन, प्राकृतिक स्रोतों से विटामिन प्राप्त करना हमेशा सबसे अच्छा होता है।
-आपके शरीर की जरूरतों के अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक सेंटर में भी विटामिन डेफिशिएंसी का होम्योपैथिक उपचार उपलब्ध है। यदि आपको कोई लक्षण महसूस हो रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक से संपर्क करें और स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर बनाएँ।
Testimonials

body weakness treatment
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से 10 महीने में चमत्कारी इलाज: एक मरीज की कहानी
आज के समय में जब लोग तरह-तरह की बीमारियों से जूझ रहे हैं, तब होम्योपैथी चिकित्सा कई मरीजों के लिए आशा की किरण बन रही है। ऐसी ही एक प्रेरणादायक कहानी है एक मरीज की, जिसने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के माध्यम से 10 महीने में अपनी बीमारी से निजात पाई।
शुरुआत में थी थकान और शरीर में भारीपन
मरीज ने बताया, "मुझे कई दिनों से शरीर में थकान, भारीपन और बेचैनी महसूस हो रही थी। यह परेशानी धीरे-धीरे इतनी बढ़ गई कि रोजमर्रा के काम भी कठिन लगने लगे। मेरी माँ पहले से ही ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी क्लीनिक में इलाज करा रही थीं। उन्होंने बताया कि उन्हें वेरीकोज वेन्स की समस्या थी और यहाँ के इलाज से उन्हें बहुत लाभ हुआ था। उनकी सलाह पर मैं भी यहाँ आया।"
होम्योपैथी इलाज का असर मात्र एक सप्ताह में
मरीज के अनुसार, "जब मैंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा से परामर्श लिया और उनकी सलाह के अनुसार दवाएं लेना शुरू किया, तो सिर्फ एक हफ्ते के भीतर ही मुझे सुधार महसूस होने लगा। मेरी थकान कम हो गई, शरीर की ऊर्जा बढ़ने लगी और पहले की तुलना में मैं ज्यादा सक्रिय महसूस करने लगा।"
लगातार 10 महीने तक किया उपचार, मिली पूरी राहत
मरीज ने लगातार 10 महीने तक ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाएं लीं और सभी निर्देशों का पालन किया। उन्होंने कहा, "लगभग 15 दिनों के अंदर ही मेरी स्थिति में काफी सुधार हुआ और अब 10 महीने बाद मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ महसूस कर रहा हूँ। यह सब डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा और ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाओं की वजह से संभव हुआ।"
होम्योपैथी: सभी बीमारियों के लिए वरदान
मरीज ने आगे कहा, "इस क्लिनिक का माहौल बहुत अच्छा है और इलाज का तरीका बेहद प्रभावी है। यहाँ की दवाएँ बहुत असरदार हैं और मुझे इनके इस्तेमाल से कोई साइड इफेक्ट भी नहीं हुआ। यह सच में होम्योपैथी का सबसे बेहतरीन केंद्र है। मैं सभी मरीजों से अनुरोध करूंगा कि अगर वे किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान हैं, तो एक बार ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी का इलाज जरूर लें। यह एक बीमार मरीजों के लिए किसी स्वर्ग से कम नहीं है।"
निष्कर्ष
इस मरीज की कहानी यह साबित करती है कि सही चिकित्सा और सही मार्गदर्शन से कोई भी बीमारी ठीक हो सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में न केवल आधुनिक चिकित्सा पद्धति का समावेश है, बल्कि यहाँ मरीजों की समस्याओं को गहराई से समझकर उनका संपूर्ण इलाज किया जाता है। यदि आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी एक बेहतरीन विकल्प हो सकता है।

acute pancreatitis ka ilaaj
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: एक मरीज की जीवन बदलने वाली कहानी
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस: एक गंभीर समस्या
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में तीव्र सूजन हो जाती है। जब यह समस्या उत्पन्न होती है, तो मरीज को शुरुआत में इसकी जानकारी नहीं होती, लेकिन दर्द इतना असहनीय होता है कि उसे तुरंत अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की आवश्यकता पड़ती है। इस स्थिति का मुख्य कारण अनुचित जीवनशैली, जंक फूड, शराब का सेवन, ऑटोइम्यून बीमारियां, कुछ रसायन और विकिरण हो सकते हैं। यदि समय रहते सही इलाज नहीं किया गया, तो यह स्थिति क्रॉनिक पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस में बदल सकती है।
अमन बाजपेई की प्रेरणादायक यात्रा
मैं, अमन बाजपेई, पिछले 1.5 वर्षों से एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का मरीज था। यह समय मेरे लिए बेहद कठिन था। मैं बहुत परेशान था, खाना खाने तक के लिए तरस गया था। पिछले 7-8 महीनों में मैंने रोटी तक नहीं खाई, केवल खिचड़ी और फल खाकर गुजारा कर रहा था। बार-बार मुझे इस बीमारी के हमले झेलने पड़ रहे थे। हर 5-10 दिनों में दवा लेनी पड़ती थी, लेकिन कोई लाभ नहीं हो रहा था।
इस बीमारी के इलाज में मैंने 6-7 लाख रुपये खर्च कर दिए। दिल्ली और झांसी समेत कई बड़े अस्पतालों में इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई राहत नहीं मिली। मेरा वजन 95 किलो से घटकर 55 किलो हो गया और मैं बहुत कमजोर हो गया था। तभी मुझे सोशल मीडिया के माध्यम से ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के बारे में पता चला।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: उम्मीद की एक नई किरण
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी वह जगह है जहां कम खर्च में उत्कृष्ट इलाज संभव है। मैंने आज तक किसी भी डॉक्टर या अस्पताल में इतना अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं देखा। डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा सर ने मुझे एक नई जिंदगी दी। पहले मुझे लगा था कि मैं शायद कभी ठीक नहीं हो पाऊंगा, लेकिन आज मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ हूं।
मैं सभी मरीजों को यही सलाह दूंगा कि वे पैसे की बर्बादी न करें और सही इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जाएं। यह भारत में एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा अस्पताल है। मेरे लिए डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा किसी देवता से कम नहीं हैं।
वैज्ञानिक रूप से प्रमाणित उपचार पद्धति
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के विशेषज्ञों ने शोध आधारित एक विशेष उपचार पद्धति विकसित की है, जिससे न केवल लक्षणों में सुधार होता है बल्कि बीमारी को जड़ से ठीक किया जाता है। हजारों मरीज इस उपचार का लाभ ले रहे हैं और उनकी मेडिकल रिपोर्ट में भी उल्लेखनीय सुधार देखा गया है।
यदि आप भी इस बीमारी से जूझ रहे हैं और सही इलाज की तलाश कर रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। यह न केवल बीमारी को बढ़ने से रोकता है बल्कि इसे जड़ से ठीक भी करता है।

urticaria ka ilaaj
रेणुका बहन श्रीमाली की प्रेरणादायक कहानी: 10 साल की तकलीफ से छुटकारारेणुका बहन श्रीमाली पिछले 10 वर्षों से एक गंभीर समस्या से जूझ रही थीं। उन्हें जब भी कुछ खाने की कोशिश करतीं, उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और अत्यधिक खुजली होने लगती थी। इस समस्या के कारण वे बहुत परेशान थीं और 10 वर्षों तक कुछ भी सही तरीके से नहीं खा पाती थीं। उन्होंने कई जगहों पर इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई भी उपचार कारगर नहीं हुआ।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर से नई उम्मीदआखिरकार, 17 मई 2021 को उन्होंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में अपना ट्रीटमेंट शुरू किया। पहले से निराश हो चुकीं रेणुका बहन के लिए यह एक नई उम्मीद की किरण थी।एक साल में चमत्कारी सुधारट्रीटमेंट शुरू करने के बाद, धीरे-धीरे उनके स्वास्थ्य में सुधार होने लगा। एक साल के भीतर उन्होंने अपने आहार में वे सभी चीजें फिर से शुरू कर दीं, जिन्हें वे पहले नहीं खा पाती थीं। पहले जहाँ कोई भी चीज खाने से उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और खुजली होती थी, वहीं अब वे बिना किसी परेशानी के सामान्य जीवन जी रही हैं।ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर का योगदान
रेणुका बहन का कहना है कि यह इलाज उनके लिए किसी चमत्कार से कम नहीं था। उन्होंने अपनी पुरानी जीवनशैली को फिर से अपनाया और अब वे पूरी तरह से स्वस्थ महसूस कर रही हैं। उनके अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में इलाज का असर तुरंत दिखने लगता है और दवाइयाँ भी पूरी तरह से प्रभावी होती हैं।
अन्य समस्याओं के लिए भी कारगर
इस रिसर्च सेंटर में सिर्फ एलर्जी ही नहीं, बल्कि स्पॉन्डिलाइटिस, पीसीओडी जैसी कई अन्य बीमारियों का भी सफलतापूर्वक इलाज किया जाता है। रेणुका बहन जैसी कई अन्य मरीजों को भी यहाँ से सकारात्मक परिणाम मिले हैं।
रेणुका बहन का संदेश
रेणुका बहन उन सभी लोगों को धन्यवाद देती हैं जिन्होंने उनके इलाज में मदद की। वे यह संदेश देना चाहती हैं कि यदि कोई भी व्यक्ति किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान है और अब तक उसे कोई समाधान नहीं मिला है, तो उन्हें ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में एक बार अवश्य आना चाहिए।
"यहाँ इलाज प्रभावी, सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक तरीके से किया जाता है। मैं इस सेंटर के प्रति आभार व्यक्त करती हूँ, जिसने मुझे 10 साल पुरानी तकलीफ से राहत दिलाई।"
अगर आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं और समाधान की तलाश में हैं, तो इस होम्योपैथिक उपचार को आज़मा सकते हैं।
Departments
ENT DEPARTMENT
Hearing Loss, Vocal Cord Nodule, Vocal Cord Paralysis, Nasal Polip, Adenoid, Recurrent ear infection, Allergic Rhinitis/Sinusitis

GENERAL MEDICINE
Diabetes
Hypertension
Thyroid Disorders
Cholesterol problem (Dislipimidia)
DIGESTIVE TRACT DISORDER
Constipation
Acidity
Gastritis
Oesophagitis
Duodenitis
Ulcertive Colitis
IBS
Piles
Fissure
Fistula
Diseases
liver cancer kya hai?
१) लीवर कैंसर क्या है?
लीवर हमारे शरीर का सबसे बड़ा भाग है। जो की , भोजन को पचाने में ,और शरीर से विषाक्त पदार्थों को बाहर निकालता है। - लीवर कैंसर जिसे हेपेटिक कैंसर के नाम से भी जाना जाता है,
-यह बीमारी जब होती है जब प्राकृतिक कोशिका वृद्धि प्रक्रिया बाधित होने लग जाती है, जिससे लीवर में अनियंत्रित ट्यूमर बनता है।
इन कैंसर कोशिकाओं में शरीर के भागो में फैलने की क्षमता होती है।
२) लिवर कैंसर होने के क्या-क्या लक्षण हो सकते है ?
लिवर कैंसर के लक्षण निचे बताये गए अनुसार हो सकते है ,जैसे की ,
- पेट के ऊपरी-दाएँ भाग में दर्द का होना- त्वचा और आँखों का पीला हो जाना -मतली या उल्टी
-वजन का कम होना -थकान लगना या कमज़ोरी -आसानी से चोट लगना या खून बहना
३) लिवर कैंसर के क्या कारण हो सकते है?
लिवर कैंसर कारण निचे बताये गए है ,जो की इस प्रकार से है , - शराब का ज्यादा सेवन : ज्यादा शराब पीने से लिवर में सिरोसिस होता है, जो लीवर कैंसर का कारक है
-सिरोसिस : लीवर की गंभीर बीमारी है जिसमें लीवर के ऊतक क को नुक्सान हो जाते हैं और ऊतक में निशान पड़ जाते हैं.
- वंशानुगत रोग : कुछ पारिवारिक इतिहास के कारण से ये रोग होने के कारण है -ज्यादा वसा : अधिक चर्बी वाले फैटी लिवर और गैर-अल्कोहल फैटी लिवर रोग भी लीवर कैंसर जोखिम को बढ़ा सकते हैं. - मधुमेह : लीवर कैंसर के खतरे को बढ़ा सकता है.- कुछ दवाएं और संक्रमण भी लीवर कैंसर का कारण बन सकते हैं.
४) लिवर कैंसर के जोखिम कारक क्या है?
1. लिंग
ये बीमारी महिलाओं की तुलना में पुरुषों में ज्यादा देखने को मिलती है
2. आयु
60 वर्ष से अधिक आयु के लोगों में देखे जाते हैं, खासकर 80 से 95 वर्ष की आयु के लोगों में लिवर कैंसर होता है 3. पारिवारिक इतिहास
यदि किसी व्यक्ति के परिवार में इस बीमारी का इतिहास है, तो उसे यह बीमारी होने का अधिक जोखिम होता है
4) जीवनशैली विकल्प
- मोटापा
- शराब का अत्यधिक सेवन - धूम्रपान
5) हानिकारक रसायनों
हानिकारक रसायनों के संपर्क में आना

joint pain treatment in homeopathy
1) Joint Pain Treatment?
Millions of people around the world suffer from joint pain, which ranges from mild discomfort to debilitating pain that can interfere with daily activities.
- It can affect any joint in the body, but the most commonly affected areas are the knees, shoulders, and hands.
2) What can cause joint pain?
Joint pain can occur due to many reasons, such as, - Arthritis: It is one of the most common causes of joint pain. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease, has two main types.
- Injury: Sprains, strains, or fractures can cause both acute and chronic joint pain. - Gout: A form of arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid, which can cause sudden, severe pain and swelling.
- Infection: Viral or bacterial infections can also cause inflammation in the joints.
3) What are the symptoms of joint pain?
Symptoms of joint pain can be as follows,
-Pain: Sharp and dull pain in the joints that increases during rest or activity.
-Stiffness: Stiffness in the joints even after sitting for a long time.
-Swelling: Inflammation around the joints or swelling in the legs.
-Redness: Redness of the skin around the joints.
-Fatigue: Feeling weak due to joint pain.
4) What are the measures to prevent joint pain?
Measures to prevent joint pain are as follows, - Consuming a healthy diet rich in calcium and minerals. -Spending time in the morning sun can also be good for vitamin D.
-Regular exercise also helps maintain strength and mobility in the joints.
-Avoid sudden, jerky and twisting movements of the joints, even when lifting heavy objects.
5) What do doctors do to diagnose joint pain?
Diagnosing joint pain involves a combination of a physical examination, a review of medical history, and possibly laboratory or imaging tests.
Here is a more detailed description of the diagnostic process:
- 1. Physical examination:
Doctors perform a physical examination to check for swelling, redness, and tenderness. They may also look at the range of motion and stability of the joint.
- 2. Imaging tests:
- X-rays: X-rays are used to check where the problem is, around or in the bone.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound can look at soft tissues and identify fluid in the joint.
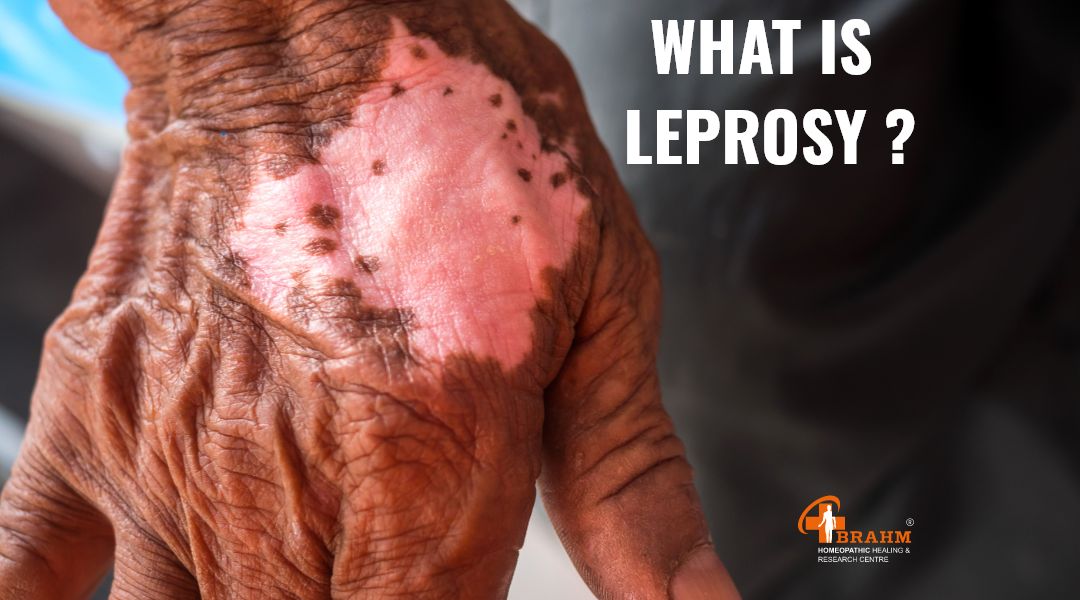
leprosy treatment in homeopathy
1) What is leprosy?Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease that affects the skin, nervous system, eyes and respiratory tract. There was no cure for this disease years ago. It was also referred to as a socially stigmatized disease. Modern day medicine has a cure for this disease .- Medicines are the primary treatment of this disease, but its overall treatment does not consist of only medicines. The patient is taken care of in terms of physical, mental and physical condition.2) What are the symptoms of leprosy?
The signs and symptoms of leprosy can be like this,
* Change in skin * It can be skin discoloration Red spots on skin are wounds Skin gets too thick dry and hardened Lumps of skin get too developed Ulcers form on soles of feet.
- Discoloration of the skin - Wounds on the skin are usually red spots
- Skin becomes thick, dry and hard - Excessive development of lumps on the skin - Formation of ulcers on the soles of the feet
3) What are the causes of leprosy?
The causes of leprosy are as follows, –The Mycobacterium leprae bacteria is the extreme cause of leprosy. - Infection : It is transmitted when an individual comes in contact with an infected man. Most of the time it is transmitted when little particles come out of the nose and mouth of an infected person.
- – Weak immune system – A few patients have a reduced immune system which makes them more vulnerable to leprosy. - Genetic predisposition – It can be genetic, making them more prone to infection.
4) What are the risk factors exist for leprosy?
Risk factors (for leprosy) may include: - Close contact: Long-term contact with an infected individual increases the risk of contracting the disease.-Age: Older individuals are at greater risk for developing leprosy[. It is mostly witnessed in the age group of 5 to 15 years portal. -- Hereditary Factor : Some individuals can become infected due to genetic defects
- Through animals : This disease is also transmitted to human through some animals
Videos

gut health kyu jaruri hai
१)आंतों का स्वास्थ्य (Gut Health) क्यों ज़रूरी है?
आज की तेज़ रफ़्तार ज़िंदगी में हम अकसर अपने शारीरिक स्वास्थ्य को लेकर सतर्क तो रहते हैं, लेकिन एक चीज़ को नज़रअंदाज़ कर देते हैं — वह है हमारी आंतों का स्वास्थ्य। आधुनिक विज्ञान ने सिद्ध कर दिया है कि हमारी आंतें सिर्फ खाना पचाने का काम ही नहीं करतीं, बल्कि हमारे संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य का आधार होती हैं। एक स्वस्थ गट (gut) न केवल पाचन तंत्र को दुरुस्त रखता है, बल्कि मानसिक स्वास्थ्य, इम्यून सिस्टम, त्वचा, और यहाँ तक कि हमारे मूड को भी प्रभावित करता है।
२)आंतों का स्वास्थ्य क्या होता है?
हमारे पेट में लाखों-करोड़ों सूक्ष्मजीव (bacteria, fungi, viruses) रहते हैं जिन्हें सामूहिक रूप से गट माइक्रोबायोम कहा जाता है। ये सूक्ष्मजीव हमारी आंतों के भीतर रहते हैं और पाचन, पोषण अवशोषण, विषैले तत्वों को बाहर निकालने, और रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता को बनाए रखने में मदद करते हैं। जब ये सभी सूक्ष्मजीव संतुलित रहते हैं, तो हमारी आंतें स्वस्थ रहती हैं। लेकिन जब इनका संतुलन बिगड़ता है, तब कई बीमारियों का खतरा बढ़ जाता है।
३)आंतों का स्वास्थ्य क्यों ज़रूरी है?
1. बेहतर पाचन के लिए:
सबसे पहले और ज़रूरी भूमिका होती है खाने के पाचन में। एक स्वस्थ गट खाने को सही तरह से तोड़ता है और पोषक तत्वों को अवशोषित करने में मदद करता है। अगर गट हेल्दी नहीं है, तो अपच, गैस, एसिडिटी, कब्ज़ जैसी समस्याएं आम हो जाती हैं।
2. रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता मजबूत करता है:
क्या आप जानते हैं कि शरीर की 70% इम्यून सिस्टम आंतों से जुड़ी होती है? गट माइक्रोबायोम हानिकारक बैक्टीरिया और वायरस से लड़ने में मदद करता है और शरीर को संक्रमण से बचाता है। यदि आपकी आंतें अस्वस्थ हैं, तो आपको बार-बार सर्दी-जुकाम, संक्रमण, या थकान हो सकती है। 3. मानसिक स्वास्थ्य से गहरा संबंध:
गट को हम “दूसरा मस्तिष्क” के नाम से भी जाना जाता है, क्योंकि सीधा मस्तिष्क से जुड़ा है। गट में सेरोटोनिन नामक एक न्यूरोट्रांसमीटर बनता है जो मूड और भावनाओं को कण्ट्रोल करता है। और गट अच्छा रहेगा तो मूड भी अच्छा रहेगा,
4. त्वचा का स्वास्थ्य सुधारता है:
अगर आपकी आंतें गंदगी और विषैले पदार्थों से भरी हैं, तो इसका असर आपकी त्वचा पर भी पड़ेगा। मुहांसे, एक्जिमा, और त्वचा की एलर्जी जैसे रोगों का कारण गट की गड़बड़ी हो सकती है।
5. वजन को नियंत्रित करता है:
कुछ बैक्टीरिया शरीर में फैट स्टोर करने की प्रक्रिया को नियंत्रित करते हैं। अगर आपकी आंत में गलत बैक्टीरिया ज़्यादा हैं, तो वजन तेज़ी से बढ़ सकता है। एक स्वस्थ गट मेटाबोलिज्म को बढ़ाता है और वजन को संतुलित रखने में मदद करता है।
४)गट हेल्थ को कैसे बेहतर बनाएं?
1. फाइबर युक्त आहार लें:
फल, सब्ज़ियां, साबुत अनाज, और दालों में फाइबर भरपूर होता है जो अच्छे बैक्टीरिया को बढ़ावा देता है। 2. प्रोबायोटिक और प्रीबायोटिक खाएं:
प्रोबायोटिक जैसे दही, छाछ, और अचार में जीवित बैक्टीरिया होते हैं जो गट हेल्थ सुधारते हैं। प्रीबायोटिक फूड्स (जैसे प्याज़, लहसुन, केला) उन बैक्टीरिया को खाने का काम करते हैं। 3. पानी भरपूर पिएं:
हाइड्रेशन बहुत ज़रूरी है। यह पाचन को आसान बनाता है और विषैले तत्वों को बाहर निकालने में मदद करता है। 4. प्रोसेस्ड और शुगर युक्त भोजन से बचें:
जंक फूड और अधिक चीनी गट बैक्टीरिया का संतुलन बिगाड़ सकते हैं। इनसे बचना ही बेहतर है। 5. तनाव को कम करें:
जैसा कि हमने ऊपर देखा, मानसिक तनाव सीधे गट हेल्थ को प्रभावित करता है। योग, मेडिटेशन, और पर्याप्त नींद इसके लिए ज़रूरी हैं।

oviran cyst or lymph nodes ka ilaaj
१) ओवेरियन सिस्ट और मेसेंटेरिक लिंफ नोड्स का होम्योपैथिक इलाज क्या है ?
आज के वर्तमान समय में बदलते जीवनशैली, चिंता , हार्मोनल का असंतुलन और आहार संबंधी कारणों से महिलाओं में कई प्रकार की शारीरिक समस्याएं देखने को मिलती हैं। - इनमें से दो स्थितियाँ हैं १) ओवेरियन सिस्ट और २) मेसेंटेरिक लिंफ नोड्स
इन दोनों ही समस्याओं का इलाज आमतौर पर एलोपैथिक दवाओं और गंभीर मामलों में (सर्जरी) से भी इलाज किया जाता है, लेकिन बहुत सी महिलाएं अब प्राकृतिक और सुरक्षित और बिना साइड इफेक्ट वाले पद्धति की ओर मुड़ रहे है।
१) ओवेरियन सिस्ट क्या है?
ओवेरियन सिस्ट का अर्थ है की अंडाशय में बनने वाली तरल या ठोस गांठें । - यह सिस्ट नार्मल तौर पर हार्मोनल का असंतुलन होना , (PCOS), चिंता , थाइरॉइड की प्रॉब्लम ** के कारण बन सकती है। अक्सर यह सिस्ट बिना लक्षण के होती है, लेकिन कई बार इनमें दर्द, अनियमित पीरियड्स, और पेट का फूलना, या बांझपन जैसी समस्याएं हो सकती है
२) मेसेंटेरिक लिंफ नोड्स क्या होते हैं?
मेसेंटेरी शरीर का एक अंग है जो की आंतों को पेट की दीवार से जोड़ता है। इसमें लिंफ नोड्स (गांठें) शरीर के इम्यून सिस्टम का भाग होते हैं। जब शरीर में संक्रमण या सूजन होती है, तो लिंफ नोड्स आकार में बढ़ सकते हैं और पेट दर्द, उल्टी, बुखार या बेचैनी जैसे लक्षण देखना की मिलते है
३) होम्योपैथी में इनका इलाज कैसे होता है?
होम्योपैथी ऐसी चिकित्सा प्रणाली है जो की रोग के लक्षणों, मानसिक स्थिति और शारीरिक संरचना को ध्यान में रखकर इलाज करती है। यह न केवल लक्षणों को दूर करती है बल्कि हमारे शरीर को संतुलित करती है ✅ 1. समग्र दृष्टिकोण होम्योपैथी केवल रोग लक्षणों पर नहीं, ये रोग के मूल कारण पर काम करती है।उदाहरण के लिए : ओवेरियन सिस्ट का कारण हार्मोनल असंतुलन है, तो उपचार उस संतुलन को पुनः स्थापित करने पर केंद्रित होता है। यदि बार-बार मेसेंटेरिक लिंफ नोड्स की सूजन होने वाले पेट संक्रमण के कारण है, तो प्रतिरोधक क्षमता को बढ़ाने के लिए उपचार किया जाता है। ✅ 2. जीवनशैली में सुधार करना होम्योपैथिक केवल दवा ही नहीं देते, बल्कि जीवनशैली और आहार में सुधार के लिए भी मार्गदर्शन करते हैं: - नियमित कसरत करना - तनाव पर कण्ट्रोल - हल्का आहार - समय पर नींद का संतुलन बनाये रखना ✅ 3. बिना साइड इफेक्ट के इलाज होम्योपैथिक दवाएं अत्यंत सूक्ष्म मात्रा में दी जाती हैं और इनका कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं होता। यह विशेष रूप से उन महिलाओं के लिए उपयोगी है जो: लंबे समय से किसी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं , पहले से कई एलोपैथिक दवाएं ले रही हैं ✅ 4. बच्चों ,बुजुर्गों के लिए भी सेफ है होम्योपैथी की सबसे बड़ी विशेषता है कि यह सभी उम्र के लोगों के लिए उपयुक्त है — बच्चे, गर्भवती महिलाएं और बुजुर्ग। मेसेंटेरिक लिंफ नोड्स की सूजन जो अक्सर बच्चों में पाई जाती है, उसका भी सहनशील और सुरक्षित उपचार होम्योपैथी में संभव है। ✅ 5. दीर्घकालिक समाधान
होम्योपैथी में रोग के दोबारा होने की संभावना बहुत ही कम रहती है, क्योंकि इसका उद्देश्य शरीर के मूल असंतुलन को ठीक करना है, न कि केवल ऊपरी लक्षणों को कम करना है.निष्कर्ष
ओवेरियन सिस्ट और मेसेंटेरिक लिंफ नोड्स जैसी स्थितियाँ दिखने में आम लग सकती हैं, लेकिन यदि इनका इलाज सतही तौर पर किया जाए तो यह आगे चलकर गंभीर स्वास्थ्य समस्याएं उत्पन्न कर सकती हैं।

homeopathy me acute pancreatitis ka ilaaj?
१)होमियोपैथी में एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज?
पैंक्रियास हमारे शरीर का भाग है जो की आमतौर पर पेट के ऊपरी हिस्से में दर्द और उल्टी के साथ होता है. यह ऐसी स्थिति है जहां अग्न्याशय थोड़े समय के लिए सूज जाता है. एक्यूट पैंक्रियास ये क्रोनिक पैंक्रियास से अलग होता है, जहाँ अग्न्याशय की सूजन कुछ वर्षों तक बनी रहती है और स्थायी क्षति हो सकती है.
२) एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के क्या कारण है ?एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण निचे बताया गया है जो की इस प्रकार से है -एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस में गॉलब्लैडर की पथरी सबसे आम कारण में शामिल है - ज्यादा शराब सेवन का सेवन करना - कुछ दवाएं का बार बार उपयोग करना -खून में चर्बी की मात्रा ज्यादा होना - आनुवंशिक कारण
-ध्रूमपान का सेवन
३) एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कौन से लक्षण है ?
एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण निचे बताया गया है , -पेट के ऊपरी भाग में लगातार दर्द का होना -दर्द पीठ में फैल सकता है -उल्टी और मितली -बुखार - हार्ट का धड़कन तेज होना
४) एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस इलाज के कौन -कौन से चरण है ?
- 1. अस्पताल में एडमिट होना
कुछ मामलों में, पेशेंट को अस्पताल में एडमिट करने की जरुरत होती है, क्योंकि गंभीर स्थिति हो सकती है। यहां मरीज की स्थिति पर निरंतर निगरानी की जाती है। -2. भोजन से परहेज
शुरुआती इलाज में, मरीज को कुछ दिनों तक खाना नहीं दिया जाता है । इससे अग्न्याशय को कुछ हद तक ‘आराम’ मिलता है और वह सूजन से उबरने लगता है। -3. दर्द और सूजन का कण्ट्रोल
एंटीबायोटिक्स – केवल तब जब संक्रमण की पुष्टि हो तब तक दिया जाता हैं -4. मूल कारण का इलाज
गॉलब्लैडर की पथरी : यह कारण हो तो मरीज को ERCP या सर्जरी के माध्यम से पथरी हटाने की जरुरत होती है - अत्यधिक शराब सेवन
- 5. आहार में परिवर्तन
एक बार जब लक्षण कण्ट्रोल में आ जाते हैं, धीरे-धीरे लिक्विड डाइट से ठोस आहार की ओर बढ़ा जाता है। कम फैट वाला और सुपाच्य आहार प्राथमिकता होती है।
५) मरीज की देखभाल और रिकवरी?
-आराम: मरीज को जितना हो सके तो उनको पूरा ही आराम करना जरूरी है। -लंबी अवधि की फॉलो अप : समय -समय से बार-बार पैंक्रियाटाइटिस होने से यह क्रोनिक में न बदल सके इसलिए नियमित जांच जरूरी है।
- डायबिटीज : अग्न्याशय इंसुलिन भी बनाता है, इसकी क्षति से डायबिटीज हो सकता है।
