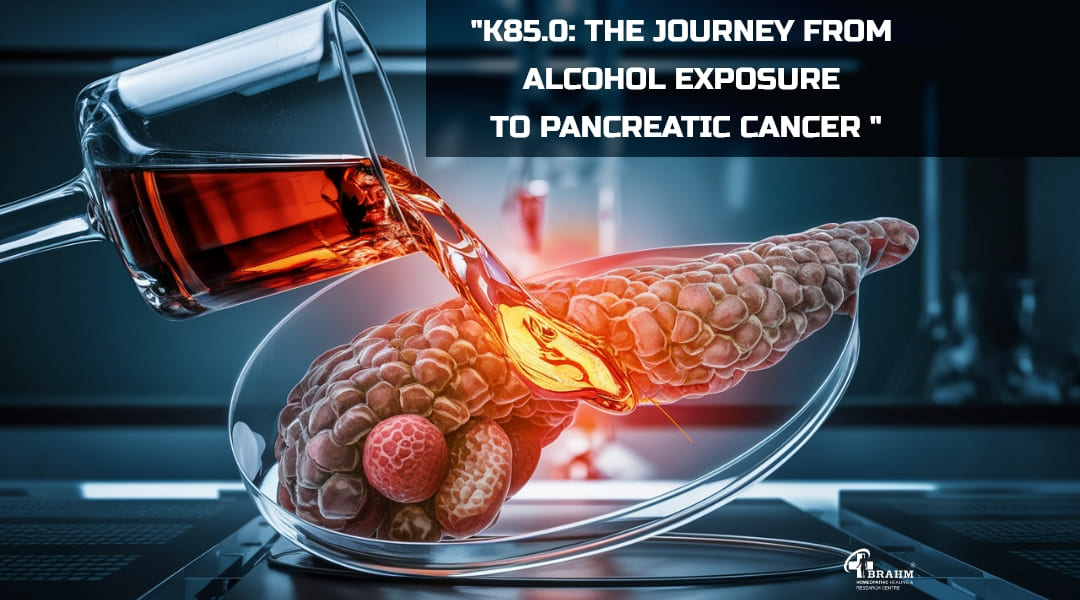
k85.0 classified acute pancreatitis
"K85.0: The Journey from Alcohol Exposure to Pancreatic Cancer "
K85.0, classified as acute pancreatitis, Upon initial exposure to alcohol, the pancreas undergoes acute inflammation, leading to the production of toxic metabolites and the premature activation of digestive enzymes. Over time, this ongoing cycle of inflammation culminates in ductal obstruction and exocrine insufficiency, resulting in persistent pain and further complications. The chronic inflammation associated with repeated episodes of K85.0(Acute Pancreatitis) creates an environment ripe for cellular mutations and dysfunction, significantly increasing the risk of pancreatic cancer. As the damaged tissue struggles to recover, the probability of neoplastic changes escalates, rendering individuals with a history of alcohol-induced acute pancreatitis particularly vulnerable to this aggressive malignancy.

What Contributes to Acute Pancreatitis After Initial Alcohol Exposure?
1. Initial Exposure to Alcohol The journey begins when alcohol enters the body, often through cultural practices of socializing or stress relief. This psychoactive substance rapidly impacts the bloodstream and engulfs the pancreas, a vital organ responsible for both digestion and blood sugar regulation. This introduction is not merely casual; it brings forth a cascade of physiological changes that can set the stage for a tumultuous relationship between alcohol and pancreatic health.
2. Acute Inflammation Onset Upon exposure, the pancreas responds in a reflexive manner, initiating an acute inflammatory reaction. This response is characterized by swelling, redness, and heightened sensitivity in the abdominal area. The enzyme-rich pancreatic tissue becomes infiltrated by immune cells, triggering a localized battle to mitigate damage. This self-protective movement, however, may spiral out of control and manifest through debilitating pain and discomfort.
3. Production of Toxic Metabolites The intricacies of alcohol metabolism lead to the formation of harmful by-products such as acetaldehyde and free radicals. These metabolites infiltrate the pancreatic cells, inducing damage at the cellular and molecular levels. This biochemical warfare creates a toxic milieu within the pancreas, contributing to the destabilization of cellular membranes and protein structures, further amplifying inflammation and cellular distress.
4. Premature Enzyme Activation Rather than being secreted into the intestine in their inactive forms, digestive enzymes like trypsinogen become activated prematurely within the pancreatic tissues. This bizarre turn of events results in autodigestion—the very enzymes meant for fat and nutrient breakdown start to digest the pancreas itself. This intrapancreatic activation sparks a vicious cycle that perpetuates injury and inflammation, highlighting the organ's vulnerability.
5. Oxidative Stress As the inflammatory cascade progresses, the balance between free radicals and antioxidants is disrupted, creating a state of oxidative stress. The pancreas, exposed to excess reactive oxygen species (ROS), faces cellular damage that extends to DNA, lipids, and proteins. This oxidative assault not only exacerbates the initial injury but promotes cell death and the release of pro-inflammatory signals, inflicting further harm.
6. Fibrosis Development In response to sustained injury, the pancreas undergoes a remodelling process marked by fibrosis—the accumulation of scar tissue. This fibrotic transformation is the body’s attempt to heal, yet it paradoxically leads to a reduced functional capacity of the pancreas. The rigid, non-functional collagenous tissue compromises blood supply and enzyme secretion, establishing a lingering state of dysfunction.
7. Ductal Obstruction The continual cycle of inflammation can also lead to ductal injury and obstruction. As inflammatory cells invade the pancreatic ducts, they become narrowed and obstructed, stymying the flow of digestive enzymes. This blockage further perpetuates back-pressure on the pancreas and amplifies inflammation, creating a terrain ripe for complications such as fluid accumulation and infection.
8. Exocrine Insufficiency As pancreatic damage persists, exocrine insufficiency sets in, characterized by an inadequacy in producing digestive enzymes essential for proper food breakdown. Individuals begin to experience malabsorption, leading to nutritional deficiencies and unintentional weight loss. Clinical manifestations may include steatorrhea (fatty stools), reflecting the pancreas's inability to efficiently manage dietary fats.
9. Chronic Inflammation and Pain With the pancreas trapped in a state of persistent inflammation, chronic pancreatitis emerges as a condition marked by recurring bouts of abdominal pain, digestive difficulties, and systemic consequences. The relentless pain becomes a significant aspect of daily life for many, as the ongoing inflammation transforms into a chronic state, characterized by cycles of flare-ups that can leave individuals in a state of anguish and uncertainty.
10. Increased Risk of Pancreatic Cancer The prolonged inflammation and structural changes within the pancreas culminate in an escalated risk for pancreatic cancer. Chronic inflammation is recognized as a precursor for malignancies, fostering an environment conducive to genetic mutations and abnormal cell growth. Over time, the once-vibrant pancreatic tissue degenerates into fertile ground for cancerous development, with individuals facing not just health challenges, but life-threatening complications.

Why should not "surgery" be done for acute pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis is a very critical medical condition in which pancreas becomes inflamed. Yes, many people opt for surgery to treat pancreatitis, especially when the condition is severe or when medical treatment is not effective. But when you first Some people look for homeopathic treatment options when they are aware of this disease. There may be some adverse effects of doing pancreatitis surgery. In most cases, surgery for pancreatitis may have some adverse effects. There is an increased risk of infection after surgery, which may occur in the pancreatic area or other organs. Homeopathy is a holistic system of medicine, which looks at disease not just based on symptoms, but on the overall health status and lifestyle of the individual. is Homeopathic treatment is the best treatment for pancreatitis. Homeopathic treatment has no side effects.

EFFECTS OF HOMEOPATHY CURE "WITHOUT SURGERY"
How Homeopathy works: Effects on the patient's body Initial Phase: Identification and First Aid Identification of symptoms: Treatment begins with understanding the symptoms of the disease and identifying the appropriate homeopathic medicine for treatment. It helps in understanding symptoms, pain, and digestive problems.
Initial relief: After taking the drug, the patient may experience mild relief in the first few days, such as reduction in pain and improvement in appetite.
Moderate Phase: Improvement in symptoms Reduction in inflammation: With consistent homeopathic doses, inflammation begins to decrease, thereby improving the general health of the patient.
Improvement in Digestion: Digestion is improved so that the patient can easily digest food and can take normal food.
Final Stage: Long-Term Improvement Energy and Vitality: The patient experiences energy and vitality in his body, leading to an increase in income and physical activity.
Stability in Health: Recurrence of disease is low. Homeopathy helps in maintaining health for a long time and protects the patient from health problems.
Homeopathy is a way of natural medicine that uses only non sideffect substances to stimulate the body's self-healing processes. If you are considering homeopathy for any condition, it is important to consult a qualified homeopath or healthcare professional who can provide personalized recommendations. Chronic inflammation of the pancreas is a disease. Homeopathy can cure chronic pancreatitis without surgery. While pancreatitis is most commonly treated through homeopathic treatment, some cases – particularly simple appendicitis – can be managed without immediate surgical intervention. Homeopathy can solve the risk of pancreatitis with its effective medicine and therapy. Homeopathy is the best way to control your disease through natural and organic treatment options. If you experience symptoms of acute pancreatitis, you should consult your healthcare provider and seek treatment for pancreatitis as soon as possible. Homeopathy prescribes some pain-relieving treatment to its patient.
Stories

chronic pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियास ठीक करने के उपाय
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस एक बीमारी है जो आपके पैंक्रियास में हो सकती है। पैंक्रियास आपके पेट में एक लंबी ग्रंथि है जो भोजन को पचाने में आपकी मदद करती है। यह आपके रक्त प्रवाह में हार्मोन भी जारी करता है जो आपके शरीर को ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग करने में मदद करता है। यदि आपका पैंक्रियास क्षतिग्रस्त हो गया है, तो पाचन एंजाइम सामान्य रूप से आपकी छोटी आंत में नहीं जा सकते हैं और आपका शरीर ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग नहीं कर सकता है।
पैंक्रियास शरीर का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है जो हार्मोन इंसुलिन का उत्पादन करके रक्त शर्करा को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। यदि इस अंग को नुकसान होता है, तो इससे मानव शरीर में गंभीर समस्याएं हो सकती हैं। ऐसी ही एक समस्या है जब पैंक्रियास में सूजन हो जाती है, जिसे तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस कहा जाता है।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस पैंक्रियास की सूजन है जो लंबे समय तक रह सकती है। इससे पैंक्रियास और अन्य जटिलताओं को स्थायी नुकसान हो सकता है। इस सूजन से निशान ऊतक विकसित हो सकते हैं, जो इंसुलिन उत्पन्न करने वाली कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा सकते हैं। यह पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ वाले लगभग 45 प्रतिशत लोगों में मधुमेह का कारण बन सकता है। भारी शराब का सेवन भी वयस्कों में पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकता है। ऑटोइम्यून और आनुवंशिक रोग, जैसे सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस, कुछ लोगों में पुरानी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकते हैं।
उत्तर भारत में, ऐसे बहुत से लोग हैं जिनके पास पीने के लिए बहुत अधिक है और कभी-कभी एक छोटा सा पत्थर उनके पित्ताशय में फंस सकता है और उनके अग्न्याशय के उद्घाटन को अवरुद्ध कर सकता है। इससे उन्हें अपना खाना पचाने में मुश्किल हो सकती है। 3 हाल ही में एशिया-प्रशांत क्षेत्र के विभिन्न देशों में किए गए एक सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार दक्षिण भारत में पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ की व्यापकता प्रति 100,000 जनसंख्या पर 114-200 मामले हैं।
Chronic Pancreatitis Patient Cured Report
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण ?
-कुछ लोगों को पेट में दर्द होता है जो पीठ तक फैल सकता है। -यह दर्द मतली और उल्टी जैसी चीजों के कारण हो सकता है। -खाने के बाद दर्द और बढ़ सकता है। -कभी-कभी किसी के पेट को छूने पर दर्द महसूस हो सकता है। -व्यक्ति को बुखार और ठंड लगना भी हो सकता है। वे बहुत कमजोर और थका हुआ भी महसूस कर सकते हैं।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण ?
-पित्ताशय की पथरी -शराब
-रक्त में उच्च ट्राइग्लिसराइड का स्तर -रक्त में उच्च कैल्शियम का स्तर
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज कैसे किया जाता है?
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस नेक्रोसिस का उपचार उपचारात्मक है। आप कितने समय तक इस बीमारी से पीड़ित रहेंगे यह काफी हद तक आपकी उपचार योजना पर निर्भर करता है। ब्रह्म अनुसंधान पर आधारित चिकित्सकीय रूप से सिद्ध वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी के इलाज में अत्यधिक प्रभावी हैं। हमारे पास आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करने, सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों, रोग के पाठ्यक्रम का दस्तावेजीकरण करने, रोग के चरण, पूर्वानुमान और जटिलताओं को समझने की क्षमता है, हमारे पास अत्यधिक योग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है। फिर वे आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताएंगे, आपको एक उचित आहार योजना (क्या खाएं और क्या नहीं खाएं), व्यायाम योजना, जीवनशैली योजना और कई अन्य कारक प्रदान करेंगे जो आपके समग्र स्वास्थ्य में सुधार कर सकते हैं। पढ़ाना। व्यवस्थित उपचार रोग ठीक होने तक होम्योपैथिक औषधियों से उपचार करें। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, चाहे वह थोड़े समय के लिए हो या कई सालों से। हम सभी ठीक हो सकते हैं, लेकिन बीमारी के प्रारंभिक चरण में हम तेजी से ठीक हो जाते हैं। पुरानी या देर से आने वाली या लंबे समय तक चलने वाली बीमारियों को ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगता है। समझदार लोग इस बीमारी के लक्षण दिखते ही इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं। इसलिए, यदि आपको कोई असामान्यता नज़र आती है, तो कृपया तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।

Acute Necrotizing pancreas treatment in hindi
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ ?
आक्रामक अंतःशिरा द्रव पुनर्जीवन, दर्द प्रबंधन, और आंत्र भोजन की जल्द से जल्द संभव शुरुआत उपचार के मुख्य घटक हैं। जबकि उपरोक्त सावधानियों से बाँझ परिगलन में सुधार हो सकता है, संक्रमित परिगलन के लिए अतिरिक्त उपचार की आवश्यकता होती है।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लक्षण ? - बुखार - फूला हुआ पेट - मतली और दस्त तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण ?
- अग्न्याशय में चोट - उच्च रक्त कैल्शियम स्तर और रक्त वसा सांद्रता
ऐसी स्थितियाँ जो अग्न्याशय को प्रभावित करती हैं और आपके परिवार में चलती रहती हैं, उनमें सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस और अन्य आनुवंशिक विकार शामिल हैं जिनके परिणामस्वरूप बार-बार अग्नाशयशोथ होता है|
क्या एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रिएटाइटिस का इलाज होम्योपैथी से संभव है ?
हां, होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनकर एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज संभव है। होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनने से आपको इन दवाओं का कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं होगा और यह समस्या को जड़ से खत्म कर देता है, इसीलिए आपको अपने एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के इलाज के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार का ही चयन करना चाहिए।
आप तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ से कैसे छुटकारा पा सकते हैं ?
शुरुआती चरण में सर्वोत्तम उपचार चुनने से आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस से छुटकारा मिल जाएगा। होम्योपैथिक उपचार का चयन करके, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे विश्वसनीय उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करता है। एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार सबसे अच्छा इलाज है। जैसे ही आप एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक करने के लिए अपना उपचार शुरू करेंगे, आपको निश्चित परिणाम मिलेंगे।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार से तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ का इलाज संभव है। आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, इसका उपचार योजना पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ता है। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कब से अपनी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, या तो हाल ही में या कई वर्षों से - हमारे पास सब कुछ ठीक है, लेकिन बीमारी के शुरुआती चरण में, आप तेजी से ठीक हो जाएंगे। पुरानी स्थितियों के लिए या बाद के चरण में या कई वर्षों की पीड़ा के मामले में, इसे ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगेगा। बुद्धिमान व्यक्ति हमेशा इस बीमारी के किसी भी लक्षण को देखते ही तुरंत इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं, इसलिए जैसे ही आपमें कोई असामान्यता दिखे तो तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एवं रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
ब्रह्म अनुसंधान आधारित, चिकित्सकीय रूप से प्रमाणित, वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी को ठीक करने में बहुत प्रभावी है। हमारे पास सुयोग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है जो आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करती है, रोग की प्रगति के साथ-साथ सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों को रिकॉर्ड करती है, इसकी प्रगति के चरणों, पूर्वानुमान और इसकी जटिलताओं को समझती है। उसके बाद वे आपको आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताते हैं, आपको उचित आहार चार्ट [क्या खाएं या क्या न खाएं], व्यायाम योजना, जीवन शैली योजना प्रदान करते हैं और कई अन्य कारकों के बारे में मार्गदर्शन करते हैं जो व्यवस्थित प्रबंधन के साथ आपकी सामान्य स्वास्थ्य स्थिति में सुधार कर सकते हैं। जब तक यह ठीक न हो जाए तब तक होम्योपैथिक दवाओं से अपनी बीमारी का इलाज करें।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लिए आहार ?
कुपोषण और पोषण संबंधी कमियों को रोकने के लिए, सामान्य रक्त शर्करा के स्तर को बनाए रखने और मधुमेह, गुर्दे की समस्याओं और पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ से जुड़ी अन्य स्थितियों को रोकने या बेहतर ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए, अग्नाशयशोथ की तीव्र घटना से बचना महत्वपूर्ण है।
यदि आप एक स्वस्थ आहार योजना की तलाश में हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। हमारे विशेषज्ञ आपकी व्यक्तिगत आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप एक योजना बनाने में आपकी सहायता कर सकते हैं

Pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ?
जब पैंक्रियाटाइटिसमें सूजन और संक्रमण हो जाता है तो इससे पैंक्रिअटिटिस नामक रोग हो जाता है। पैंक्रियास एक लंबा, चपटा अंग है जो पेट के पीछे पेट के शीर्ष पर छिपा होता है। पैंक्रिअटिटिस उत्तेजनाओं और हार्मोन का उत्पादन करके पाचन में मदद करता है जो आपके शरीर में ग्लूकोज के प्रसंस्करण को विनियमित करने में मदद करते हैं।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण:
-पेट के ऊपरी भाग में दर्द होना। -बेकार वजन घटाना. -पेट का ख़राब होना.
-शरीर का असामान्य रूप से उच्च तापमान। -पेट को छूने पर दर्द होना। -तेज़ दिल की धड़कन. -हाइपरटोनिक निर्जलीकरण.
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण:
-पित्ताशय में पथरी. -भारी शराब का सेवन.
-भारी खुराक वाली दवाएँ। -हार्मोन का असंतुलन. -रक्त में वसा जो ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स का कारण बनता है। -आनुवंशिकता की स्थितियाँ. -पेट में सूजन ।
क्या होम्योपैथी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक कर सकती है?
हाँ, होम्योपैथीपैंक्रियाटाइटिसको ठीक कर सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको पैंक्रिअटिटिस के लिए सबसे भरोसेमंद उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करती है।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा उपचार क्या है?
यदि पैंक्रियाज अच्छी तरह से काम नहीं कर रहा है तो होम्योपैथिक उपचार वास्तव में बेहतर होने में मदद करने का एक अच्छा तरीका है। जब आप उपचार शुरू करते हैं, तो आप जल्दी परिणाम देखेंगे। बहुत सारे लोग इस इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जा रहे हैं और वे वास्तव में अच्छा कर रहे हैं। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपके पैंक्रियाज के को बेहतर बनाने में मदद करने के लिए आपको सबसे तेज़ और सुरक्षित तरीका प्रदान करना सुनिश्चित करती है।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
बीमार होने पर लोगों को बेहतर महसूस कराने में मदद करने के लिए हमारे पास एक विशेष तरीका है। हमारे पास वास्तव में स्मार्ट डॉक्टर हैं जो ध्यान से देखते हैं और नोट करते हैं कि बीमारी व्यक्ति को कैसे प्रभावित कर रही है। फिर, वे सलाह देते हैं कि क्या खाना चाहिए, व्यायाम करना चाहिए और स्वस्थ जीवन कैसे जीना चाहिए। वे व्यक्ति को ठीक होने में मदद करने के लिए विशेष दवा भी देते हैं। यह तरीका कारगर साबित हुआ है!
Tips

dehydration treatment in homeopathy
1. Dehydration treatment
When the body loses more fluid than it takes in, it causes an imbalance in electrolytes and fluids needed for normal body function. This can be due to excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, or not drinking enough water.
While severe dehydration requires medical attention, mild to moderate dehydration can often be treated effectively at home without the use of drugs or medication. Natural remedies and lifestyle changes can help restore hydration and balance in a safe and gentle way.
1. Replenish water
The most important step in treating dehydration is to drink water. Clean water is the best way to rehydrate the body. Drink water slowly and in small sips rather than drinking large amounts at once, especially if nausea occurs. -Drinking small amounts at regular intervals allows the body to absorb fluids more effectively.
2. Consume natural electrolytes
When we sweat due to illness, we also lose essential electrolytes like sodium, potassium and magnesium. Without these, just drinking water is not enough. You can make an electrolyte drink at home by mixing the following:
- 1 liter of clean water - 6 teaspoons of sugar
- 1/2 teaspoon of salt This solution helps a lot in balancing electrolytes and can be more effective than plain water.
- Coconut water is a natural alternative as it has a good balance of sodium, potassium and other electrolytes.
3. Eat hydrating foods
Some foods are high in water and can help restore hydration naturally. For example,
watermelon, cucumber, oranges, lettuce - Some foods in your diet can provide both fluids and essential nutrients.
4. Avoid dehydrating substances
- Coffee, energy drinks
- Alcohol
- Salty snacks
These can worsen fluid loss. Sticking to water and natural fluids is the best option until hydration is restored.
5. Rest
If the dehydration is caused by heat or strenuous physical activity, resting in a cool, shady area is a must. - Avoiding excessive sweating or exertion helps the body recover more easily. - Using a fan, cool cloth or taking a warm bath also helps regulate body temperature
6. Monitor symptoms
It is important to monitor your condition. Signs of dehydration include: - Increased urine with a light color
- Decreased thirst
If symptoms persist or worsen - such as dizziness, very dark urine, it is important to seek medical help immediately.
Final Thoughts
Dehydration can often be treated effectively without medication or drugs, especially when it's caught early.
-While natural remedies are helpful, it's important to see a doctor if symptoms become severe or don't respond to home remedies

hamare sarir ke liye sabji ke labh
सब्जियाँ हमारे आहार का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा हैं। इनमें कई प्रकार के विटामिन, खनिज, एंटीऑक्सीडेंट और फाइबर होते हैं, जो शरीर को स्वस्थ बनाए रखते हैं। सब्जियों का सेवन न केवल रोगों से बचाव करता है बल्कि संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य को भी बनाए रखता है।
सब्जियों के प्रकार और उनके लाभ
1. हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ (Leafy Green Vegetables)
हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ पोषण से भरपूर होती हैं और शरीर को कई तरह के आवश्यक तत्व प्रदान करती हैं।
-1. पालक (Spinach) लाभ: आयरन, कैल्शियम और फाइबर से भरपूर। हड्डियों और मांसपेशियों को मजबूत बनाता है। एनीमिया और कब्ज से बचाव करता है।
2. सरसों के पत्ते (Mustard Greens)
-लाभ: -हड्डियों के लिए फायदेमंद। -इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है। -त्वचा और बालों को स्वस्थ रखता है।
3. मेथी (Fenugreek Leaves)
-लाभ: -डायबिटीज को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। -पाचन को सुधारता है और भूख बढ़ाता है।
4. धनिया और पुदीना (Coriander & Mint Leaves)
-लाभ: -पाचन को सुधारते हैं। -विषाक्त पदार्थों को बाहर निकालते हैं। -त्वचा को चमकदार बनाते हैं।
2. जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ (Root Vegetables)
जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ फाइबर और आवश्यक खनिजों से भरपूर होती हैं।
5. गाजर (Carrot)

sarir ke liye vitamin or unke labh
हमारे शरीर के लिए सभी विटामिन और उनके लाभ
विटामिन हमारे शरीर के लिए आवश्यक पोषक तत्व हैं, जो शरीर के विभिन्न कार्यों को सुचारू रूप से चलाने में मदद करते हैं। ये सूक्ष्म पोषक तत्व होते हैं, लेकिन शरीर में इनकी भूमिका बहुत महत्वपूर्ण होती है। विटामिन की कमी से कई स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ हो सकती हैं, इसलिए संतुलित आहार लेना जरूरी है।
विटामिन कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
-विटामिन दो प्रकार के होते हैं: -1. वसा में घुलनशील विटामिन (Fat-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में वसा में संग्रहित होते हैं और जरूरत पड़ने पर उपयोग किए जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन A, D, E और K आते हैं।
-2. जल में घुलनशील विटामिन (Water-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में जमा नहीं होते और मूत्र के माध्यम से बाहर निकल जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन C और सभी B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन आते हैं।
विटामिन और उनके लाभ
1. विटामिन A (रेटिनॉल, बीटा-कैरोटीन)
भूमिका:
आँखों की रोशनी को बनाए रखता है।
त्वचा और इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है।
हड्डियों और दांतों के विकास में सहायक है।
स्रोत:
गाजर पालकआम, शकरकंद, डेयरी उत्पाद, अंडे, मछली का तेल।
कमी के प्रभाव:
रतौंधी (नाइट ब्लाइंडनेस)
त्वचा में रूखापन
रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी
---
2. विटामिन B-कॉम्प्लेक्स (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12)
B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र और रक्त निर्माण में मदद करते हैं। B1 (थायमिन)
भूमिका: ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र के कार्यों में सहायक।
स्रोत: साबुत अनाज, बीन्स, सूरजमुखी के बीज, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: कमजोरी, भूख न लगना, तंत्रिका तंत्र की समस्या।
B2 (राइबोफ्लेविन)
भूमिका: त्वचा, आँखों और ऊर्जा उत्पादन के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: दूध, दही, अंडे, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: होंठों में दरारें, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B3 (नियासिन)
भूमिका: कोलेस्ट्रॉल को नियंत्रित करता है और पाचन में सहायक होता है।
स्रोत: मूंगफली, मशरूम, टमाटर, चिकन, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा रोग, मानसिक कमजोरी। B5 (पैंटोथेनिक एसिड)
भूमिका: हार्मोन उत्पादन और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: मशरूम, एवोकाडो, दूध, ब्रोकली।
कमी के प्रभाव: थकान, सिरदर्द।
B6 (पाइरिडोक्सिन)
भूमिका: तंत्रिका तंत्र और प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को मजबूत करता है।
स्रोत: केला, चिकन, सोयाबीन, आलू।
कमी के प्रभाव: अवसाद, त्वचा रोग।
B7 (बायोटिन)
भूमिका: बालों और त्वचा के स्वास्थ्य को बनाए रखता है।
स्रोत: अंडे, मूंगफली, फूलगोभी।
कमी के प्रभाव: बाल झड़ना, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B9 (फोलिक एसिड)
भूमिका: डीएनए निर्माण और गर्भावस्था में जरूरी।
स्रोत: दालें, हरी सब्जियाँ, बीन्स। कमी के प्रभाव: एनीमिया, जन्म दोष।
B12 (कोबालामिन)
भूमिका: लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं और तंत्रिका तंत्र के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: मांस, अंडे, डेयरी उत्पाद। कमी के प्रभाव: स्मरण शक्ति की कमजोरी, एनीमिया।
---
3. विटामिन C (एस्कॉर्बिक एसिड)
भूमिका: इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है, त्वचा को चमकदार बनाता है, और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: संतरा, नींबू, स्ट्रॉबेरी, टमाटर, हरी मिर्च।
कमी के प्रभाव: स्कर्वी, मसूड़ों से खून आना, रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी।
---
4. विटामिन D (कोलेकल्सीफेरोल)
भूमिका: हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाता है और कैल्शियम के अवशोषण में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: सूर्य का प्रकाश, मछली, अंडे, दूध।
कमी के प्रभाव: हड्डियों में कमजोरी, रिकेट्स।
---
5. विटामिन E (टोकोफेरॉल)
भूमिका: एंटीऑक्सीडेंट के रूप में कार्य करता है और त्वचा तथा बालों के लिए लाभदायक है। स्रोत: बादाम, सूरजमुखी के बीज, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा की समस्याएँ, कमजोरी।
---
6. विटामिन K (फायलोक्विनोन)
भूमिका: रक्त को थक्का जमाने (ब्लड क्लॉटिंग) में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: पालक, ब्रोकोली, हरी सब्जियाँ।
कमी के प्रभाव: चोट लगने पर खून न रुकना। ---
निष्कर्ष
शरीर को सभी विटामिनों की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि सभी अंग सही से काम कर सकें। इनके लिए संतुलित आहार लेना बहुत जरूरी है। यदि विटामिन की कमी हो, तो डॉक्टर से परामर्श लेकर सप्लीमेंट्स भी लिए जा सकते हैं। लेकिन, प्राकृतिक स्रोतों से विटामिन प्राप्त करना हमेशा सबसे अच्छा होता है।
-आपके शरीर की जरूरतों के अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक सेंटर में भी विटामिन डेफिशिएंसी का होम्योपैथिक उपचार उपलब्ध है। यदि आपको कोई लक्षण महसूस हो रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक से संपर्क करें और स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर बनाएँ।
Testimonials

body weakness treatment
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से 10 महीने में चमत्कारी इलाज: एक मरीज की कहानी
आज के समय में जब लोग तरह-तरह की बीमारियों से जूझ रहे हैं, तब होम्योपैथी चिकित्सा कई मरीजों के लिए आशा की किरण बन रही है। ऐसी ही एक प्रेरणादायक कहानी है एक मरीज की, जिसने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के माध्यम से 10 महीने में अपनी बीमारी से निजात पाई।
शुरुआत में थी थकान और शरीर में भारीपन
मरीज ने बताया, "मुझे कई दिनों से शरीर में थकान, भारीपन और बेचैनी महसूस हो रही थी। यह परेशानी धीरे-धीरे इतनी बढ़ गई कि रोजमर्रा के काम भी कठिन लगने लगे। मेरी माँ पहले से ही ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी क्लीनिक में इलाज करा रही थीं। उन्होंने बताया कि उन्हें वेरीकोज वेन्स की समस्या थी और यहाँ के इलाज से उन्हें बहुत लाभ हुआ था। उनकी सलाह पर मैं भी यहाँ आया।"
होम्योपैथी इलाज का असर मात्र एक सप्ताह में
मरीज के अनुसार, "जब मैंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा से परामर्श लिया और उनकी सलाह के अनुसार दवाएं लेना शुरू किया, तो सिर्फ एक हफ्ते के भीतर ही मुझे सुधार महसूस होने लगा। मेरी थकान कम हो गई, शरीर की ऊर्जा बढ़ने लगी और पहले की तुलना में मैं ज्यादा सक्रिय महसूस करने लगा।"
लगातार 10 महीने तक किया उपचार, मिली पूरी राहत
मरीज ने लगातार 10 महीने तक ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाएं लीं और सभी निर्देशों का पालन किया। उन्होंने कहा, "लगभग 15 दिनों के अंदर ही मेरी स्थिति में काफी सुधार हुआ और अब 10 महीने बाद मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ महसूस कर रहा हूँ। यह सब डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा और ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाओं की वजह से संभव हुआ।"
होम्योपैथी: सभी बीमारियों के लिए वरदान
मरीज ने आगे कहा, "इस क्लिनिक का माहौल बहुत अच्छा है और इलाज का तरीका बेहद प्रभावी है। यहाँ की दवाएँ बहुत असरदार हैं और मुझे इनके इस्तेमाल से कोई साइड इफेक्ट भी नहीं हुआ। यह सच में होम्योपैथी का सबसे बेहतरीन केंद्र है। मैं सभी मरीजों से अनुरोध करूंगा कि अगर वे किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान हैं, तो एक बार ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी का इलाज जरूर लें। यह एक बीमार मरीजों के लिए किसी स्वर्ग से कम नहीं है।"
निष्कर्ष
इस मरीज की कहानी यह साबित करती है कि सही चिकित्सा और सही मार्गदर्शन से कोई भी बीमारी ठीक हो सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में न केवल आधुनिक चिकित्सा पद्धति का समावेश है, बल्कि यहाँ मरीजों की समस्याओं को गहराई से समझकर उनका संपूर्ण इलाज किया जाता है। यदि आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी एक बेहतरीन विकल्प हो सकता है।

acute pancreatitis ka ilaaj
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: एक मरीज की जीवन बदलने वाली कहानी
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस: एक गंभीर समस्या
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में तीव्र सूजन हो जाती है। जब यह समस्या उत्पन्न होती है, तो मरीज को शुरुआत में इसकी जानकारी नहीं होती, लेकिन दर्द इतना असहनीय होता है कि उसे तुरंत अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की आवश्यकता पड़ती है। इस स्थिति का मुख्य कारण अनुचित जीवनशैली, जंक फूड, शराब का सेवन, ऑटोइम्यून बीमारियां, कुछ रसायन और विकिरण हो सकते हैं। यदि समय रहते सही इलाज नहीं किया गया, तो यह स्थिति क्रॉनिक पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस में बदल सकती है।
अमन बाजपेई की प्रेरणादायक यात्रा
मैं, अमन बाजपेई, पिछले 1.5 वर्षों से एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का मरीज था। यह समय मेरे लिए बेहद कठिन था। मैं बहुत परेशान था, खाना खाने तक के लिए तरस गया था। पिछले 7-8 महीनों में मैंने रोटी तक नहीं खाई, केवल खिचड़ी और फल खाकर गुजारा कर रहा था। बार-बार मुझे इस बीमारी के हमले झेलने पड़ रहे थे। हर 5-10 दिनों में दवा लेनी पड़ती थी, लेकिन कोई लाभ नहीं हो रहा था।
इस बीमारी के इलाज में मैंने 6-7 लाख रुपये खर्च कर दिए। दिल्ली और झांसी समेत कई बड़े अस्पतालों में इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई राहत नहीं मिली। मेरा वजन 95 किलो से घटकर 55 किलो हो गया और मैं बहुत कमजोर हो गया था। तभी मुझे सोशल मीडिया के माध्यम से ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के बारे में पता चला।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: उम्मीद की एक नई किरण
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी वह जगह है जहां कम खर्च में उत्कृष्ट इलाज संभव है। मैंने आज तक किसी भी डॉक्टर या अस्पताल में इतना अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं देखा। डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा सर ने मुझे एक नई जिंदगी दी। पहले मुझे लगा था कि मैं शायद कभी ठीक नहीं हो पाऊंगा, लेकिन आज मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ हूं।
मैं सभी मरीजों को यही सलाह दूंगा कि वे पैसे की बर्बादी न करें और सही इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जाएं। यह भारत में एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा अस्पताल है। मेरे लिए डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा किसी देवता से कम नहीं हैं।
वैज्ञानिक रूप से प्रमाणित उपचार पद्धति
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के विशेषज्ञों ने शोध आधारित एक विशेष उपचार पद्धति विकसित की है, जिससे न केवल लक्षणों में सुधार होता है बल्कि बीमारी को जड़ से ठीक किया जाता है। हजारों मरीज इस उपचार का लाभ ले रहे हैं और उनकी मेडिकल रिपोर्ट में भी उल्लेखनीय सुधार देखा गया है।
यदि आप भी इस बीमारी से जूझ रहे हैं और सही इलाज की तलाश कर रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। यह न केवल बीमारी को बढ़ने से रोकता है बल्कि इसे जड़ से ठीक भी करता है।

urticaria ka ilaaj
रेणुका बहन श्रीमाली की प्रेरणादायक कहानी: 10 साल की तकलीफ से छुटकारारेणुका बहन श्रीमाली पिछले 10 वर्षों से एक गंभीर समस्या से जूझ रही थीं। उन्हें जब भी कुछ खाने की कोशिश करतीं, उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और अत्यधिक खुजली होने लगती थी। इस समस्या के कारण वे बहुत परेशान थीं और 10 वर्षों तक कुछ भी सही तरीके से नहीं खा पाती थीं। उन्होंने कई जगहों पर इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई भी उपचार कारगर नहीं हुआ।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर से नई उम्मीदआखिरकार, 17 मई 2021 को उन्होंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में अपना ट्रीटमेंट शुरू किया। पहले से निराश हो चुकीं रेणुका बहन के लिए यह एक नई उम्मीद की किरण थी।एक साल में चमत्कारी सुधारट्रीटमेंट शुरू करने के बाद, धीरे-धीरे उनके स्वास्थ्य में सुधार होने लगा। एक साल के भीतर उन्होंने अपने आहार में वे सभी चीजें फिर से शुरू कर दीं, जिन्हें वे पहले नहीं खा पाती थीं। पहले जहाँ कोई भी चीज खाने से उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और खुजली होती थी, वहीं अब वे बिना किसी परेशानी के सामान्य जीवन जी रही हैं।ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर का योगदान
रेणुका बहन का कहना है कि यह इलाज उनके लिए किसी चमत्कार से कम नहीं था। उन्होंने अपनी पुरानी जीवनशैली को फिर से अपनाया और अब वे पूरी तरह से स्वस्थ महसूस कर रही हैं। उनके अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में इलाज का असर तुरंत दिखने लगता है और दवाइयाँ भी पूरी तरह से प्रभावी होती हैं।
अन्य समस्याओं के लिए भी कारगर
इस रिसर्च सेंटर में सिर्फ एलर्जी ही नहीं, बल्कि स्पॉन्डिलाइटिस, पीसीओडी जैसी कई अन्य बीमारियों का भी सफलतापूर्वक इलाज किया जाता है। रेणुका बहन जैसी कई अन्य मरीजों को भी यहाँ से सकारात्मक परिणाम मिले हैं।
रेणुका बहन का संदेश
रेणुका बहन उन सभी लोगों को धन्यवाद देती हैं जिन्होंने उनके इलाज में मदद की। वे यह संदेश देना चाहती हैं कि यदि कोई भी व्यक्ति किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान है और अब तक उसे कोई समाधान नहीं मिला है, तो उन्हें ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में एक बार अवश्य आना चाहिए।
"यहाँ इलाज प्रभावी, सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक तरीके से किया जाता है। मैं इस सेंटर के प्रति आभार व्यक्त करती हूँ, जिसने मुझे 10 साल पुरानी तकलीफ से राहत दिलाई।"
अगर आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं और समाधान की तलाश में हैं, तो इस होम्योपैथिक उपचार को आज़मा सकते हैं।
Departments
ENT DEPARTMENT
Hearing Loss, Vocal Cord Nodule, Vocal Cord Paralysis, Nasal Polip, Adenoid, Recurrent ear infection, Allergic Rhinitis/Sinusitis

GENERAL MEDICINE
Diabetes
Hypertension
Thyroid Disorders
Cholesterol problem (Dislipimidia)
DIGESTIVE TRACT DISORDER
Constipation
Acidity
Gastritis
Oesophagitis
Duodenitis
Ulcertive Colitis
IBS
Piles
Fissure
Fistula
Diseases
zinc ki kami kyu hoti hai
जिंक की कमी को समझना : कारण, लक्षण और रोकने के उपाय
1) जिंक की कमी क्या है?
जिंक की कमी तब होती है जब शरीर में जिंक की उचित मात्रा नहीं होती है। बहुत कम मात्रा में आवश्यक जिंक 300 से अधिक एंजाइमेटिक प्रतिक्रियाओं में शामिल होता है, जो इसे समग्र स्वास्थ्य के लिए आवश्यक बनाता है।
2) जिंक की कमी के क्या कारण हैं?
-जिंक की कमी निम्नलिखित कारणों से हो सकती है:
* अपर्याप्त आहार सेवन: जिंक युक्त खाद्य पदार्थों जैसे मांस, डेयरी, नट्स और साबुत अनाज में कम आहार जिंक की कमी का कारण बनता है, खासकर शाकाहारियों में
* मैलाबॉस्पशन सिंड्रोम: क्रोहन रोग, सीलिएक रोग और क्रोनिक डायरिया जैसी स्थितियां शरीर की जिंक को अवशोषित करने की क्षमता को खराब कर सकती हैं।
* बढ़ी हुई शारीरिक मांग: गर्भवती और स्तनपान कराने वाली महिलाओं के साथ-साथ बढ़ते बच्चों को जिंक की अधिक आवश्यकता होती है।
* बढ़ी हुई हानि: क्रोनिक किडनी रोग, लीवर रोग, लंबे समय तक दस्त से मूत्र के माध्यम से जिंक की हानि बढ़ सकती है।* शराब: जिंक के अवशोषण में बाधा डालती है और मूत्र में जिंक के उत्सर्जन को बढ़ाती है। * फाइटेट युक्त आहार: साबुत अनाज और फलियों में उच्च मात्रा में पाए जाने वाले फाइटेट जिंक से बंध सकते हैं और इसके अवशोषण को बाधित कर सकते हैं।
3) जिंक की कमी के लक्षण क्या हैं?
जिंक की कमी के कई लक्षण हो सकते हैं, जैसे,
-भूख न लगना: जिंक की कमी से भूख भी कम लगती है। -बच्चों में धीमी वृद्धि और विकास: बच्चों में जिंक की कमी से वृद्धि और विकास में भी कमी आ सकती है।
-बालों का झड़ना: जिंक की कमी से बाल भी झड़ते हैं। -चिड़चिड़ापन: जिंक की कमी से व्यक्ति सुस्त और चिड़चिड़ा महसूस कर सकता है।
-प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली का कमजोर होना: जिंक की कमी से शरीर की प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली कमजोर हो जाती है, जिससे संक्रमण का खतरा भी बढ़ जाता है।
4) जिंक की कमी को रोकने के लिए क्या करना चाहिए?
जिंक की कमी को कम करने का सबसे अच्छा तरीका अपने आहार में जिंक युक्त खाद्य पदार्थों का उपयोग करना है। - मांस: मुर्गी और मछली में जिंक की अच्छी मात्रा होती है। - दालें और फलियां: दालें, बीन्स और फलियां जिंक का अच्छा स्रोत हैं।
- मेवे और बीज: मेवे, बीज और कद्दू के बीजों में जिंक की अच्छी मात्रा होती है। - डेयरी उत्पाद: जिंक पनीर और दूध में पाया जाता है।

narcolepsy kya hota hai
नार्कोलेप्सी रोग, इसके लक्षण, कारण, और Brahm होम्योपैथी द्वारा इलाज के बारे में लिखा गया है।
१) नार्कोलेप्सी : एक अनदेखी नींद की बीमारी और Brahm होम्योपैथी से इलाज?
नींद हमारे शरीर और मस्तिष्क के लिए उतनी ही जरूरी है जितना खाना और पानी। लेकिन कुछ लोगों के लिए नींद एक सामान्य प्रक्रिया नहीं, बल्कि एक समस्या बन जाती है। ऐसी ही एक बीमारी है
नार्कोलेप्सी (Narcolepsy) — एक न्यूरोलॉजिकल विकार, जो व्यक्ति के सोने और जागने के चक्र को असंतुलित कर देता है।
नार्कोलेप्सी में व्यक्ति को दिनभर अत्यधिक नींद आती है, चाहे वह पर्याप्त नींद ही क्यों न ले रहा हो। यह रोग आम नहीं है, लेकिन जिन लोगों को होता है, उनकी दिनचर्या और जीवनशैली पर इसका गहरा असर पड़ता है।
२) नार्कोलेप्सी के प्रमुख लक्षण?
- दिन में अत्यधिक नींद (Excessive Daytime Sleepiness):
बिना किसी चेतावनी के अचानक नींद आ जाना, चाहे व्यक्ति किसी मीटिंग में हो, गाड़ी चला रहा हो या बात कर रहा हो। -कैटाप्लेक्सी :
भावनात्मक प्रतिक्रिया (जैसे हंसी, गुस्सा या डर) से अचानक मांसपेशियों की शक्ति खो जाना – जैसे अचानक बैठ जाना या बोलना बंद हो जाना।
-स्लीप पैरालिसिस:
नींद के दौरान शरीर का अस्थायी रूप से जड़ हो जाना – व्यक्ति जाग रहा होता है लेकिन हिल नहीं पाता। -हैलुसिनेशन: नींद में या जागने के दौरान डरावने दृश्य या आवाजें महसूस करना। -रात की खराब नींद : दिन में नींद आने के बावजूद, रात में बार-बार नींद टूटना या बेचैनी से सोना।
३) नार्कोलेप्सी के कारण ?
-हाइपोक्रेटिन की कमी : यह एक ब्रेन केमिकल है जो नींद-जागने के चक्र को नियंत्रित करता है। इसकी कमी नार्कोलेप्सी की मुख्य वजह मानी जाती है। -ऑटोइम्यून विकार : शरीर की रोग-प्रतिरोधक प्रणाली गलती से ब्रेन की उन कोशिकाओं पर हमला करती है जो नींद को नियंत्रित करती हैं। -जेनेटिक फैक्टर : कुछ लोगों में यह रोग आनुवंशिक रूप से पाया जाता है। -ब्रेन इंजरी या इंफेक्शन : दुर्लभ मामलों में, मस्तिष्क को नुकसान या किसी संक्रमण के कारण भी यह समस्या उत्पन्न हो सकती है।
४) Brahm होम्योपैथी द्वारा नार्कोलेप्सी का इलाज?
Brahm Homeopathy में नार्कोलेप्सी का इलाज सिर्फ लक्षणों को दबाने तक सीमित नहीं है, बल्कि इसका उद्देश्य शरीर की अंदरूनी गड़बड़ी को ठीक करना है।
इलाज की खास बातें:
व्यक्तिगत केस स्टडी : हर मरीज की मानसिक, शारीरिक और भावनात्मक स्थिति को ध्यान में रखते हुए उपचार किया जाता है।
-कस्टमाइज मेडिसिन : होम्योपैथिक दवाएं व्यक्ति के स्वभाव, लक्षणों और कारणों के आधार पर दी जाती हैं।
-साइड इफेक्ट फ्री : सभी दवाएं प्राकृतिक होती हैं, जिनका कोई नुकसान नहीं होता।
-इम्यून सिस्टम पर काम : अगर समस्या का कारण ऑटोइम्यून है, तो इलाज रोग प्रतिरोधक प्रणाली को संतुलित करने पर केंद्रित होता है।
नोट : दवाएं केवल प्रशिक्षित होम्योपैथिक चिकित्सक की सलाह से लें।
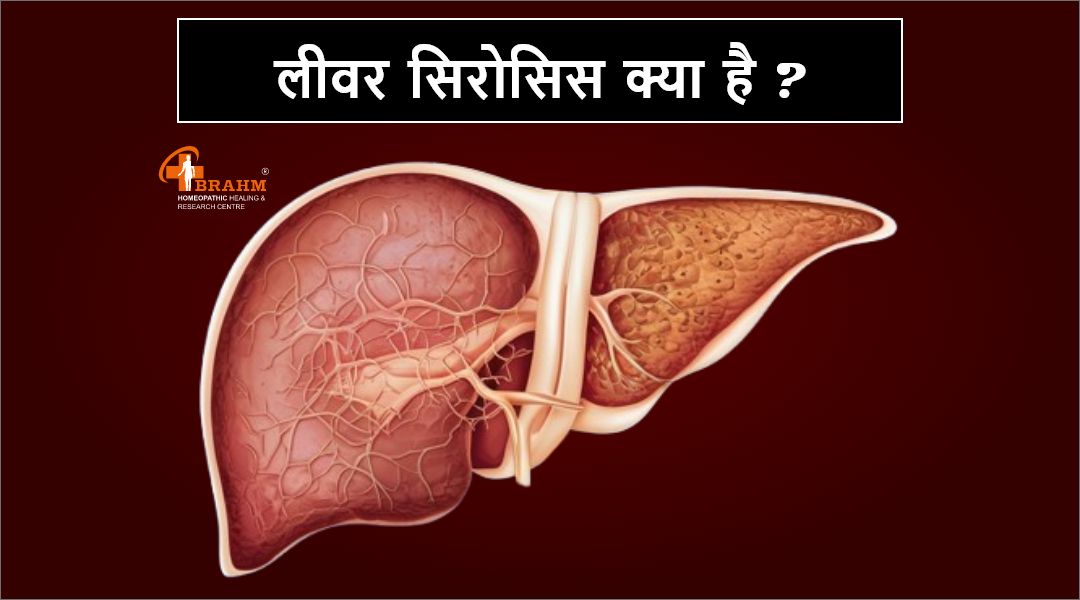
homeopathy me liver cirrhosis ka ilaaj
लीवर सिरोसिस और होम्योपैथिक उपचार : प्राकृतिक इलाज की ओर एक कदम
लीवर (यकृत) हमारे शरीर का एक महत्वपूर्ण अंग है, जो पाचन, विषहरण (डिटॉक्सिफिकेशन), ऊर्जा भंडारण और पोषक तत्वों के मेटाबॉलिज्म में अहम भूमिका निभाता है। लेकिन जब यह अंग धीरे-धीरे खराब होने लगता है, तो एक गंभीर स्थिति उत्पन्न होती है जिसे लीवर सिरोसिस (Liver Cirrhosis) कहा जाता है।
यह लेख लीवर सिरोसिस के कारणों, लक्षणों और विशेष रूप से होम्योपैथिक इलाज पर केंद्रित है, जो इस रोग को प्राकृतिक और सुरक्षित रूप से नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है।
1) लीवर सिरोसिस क्या है?
लीवर सिरोसिस एक दीर्घकालिक (क्रॉनिक) और प्रगतिशील रोग है, जिसमें लीवर की स्वस्थ कोशिकाएं क्षतिग्रस्त होकर फाइब्रोसिस (scarring) में बदल जाती हैं। यह स्कार टिशू रक्त प्रवाह को बाधित करता है और लीवर की कार्यक्षमता को धीरे-धीरे खत्म कर देता है।
सिरोसिस के कारण लीवर अपने आवश्यक कार्य जैसे विषैले पदार्थों को बाहर निकालना, रक्त को साफ करना, पाचन में मदद करना और प्रोटीन बनाना ठीक से नहीं कर पाता।
2) लीवर सिरोसिस के कारण ?
* अत्यधिक शराब सेवन : लंबे समय तक शराब पीने से लीवर कोशिकाएं नष्ट हो जाती हैं और सूजन के साथ स्कारिंग हो जाती है।
* हेपेटाइटिस बी और सी : ये वायरल संक्रमण लीवर की सूजन और क्षति का मुख्य कारण हैं।
* नॉन-अल्कोहॉलिक फैटी लीवर डिज़ीज : मोटापा, मधुमेह और उच्च कोलेस्ट्रॉल के कारण लीवर में चर्बी जमा होती है, जो बाद में सिरोसिस में बदल सकती है।
* आनुवांशिक बीमारियाँ * दवाइयों और रसायनों का अधिक सेवन : कुछ दवाएं या हानिकारक रसायन लीवर पर दीर्घकालिक दुष्प्रभाव डालते हैं।
3) लीवर सिरोसिस के लक्षण ?
सिरोसिस के शुरूआती चरण में कोई विशेष लक्षण नहीं दिखते, लेकिन रोग बढ़ने पर निम्न लक्षण देखे जा सकते हैं: * लगातार थकान और कमजोरी
* वजन कम होना * उल्टी, जी मिचलाना * पेट और टांगों में सूजन * पीलिया * शरीर में खुजली
* मल या उल्टी में खून
4) होम्योपैथी से लीवर सिरोसिस का प्राकृतिक उपचार?
होम्योपैथी एक सम्पूर्ण और प्राकृतिक चिकित्सा पद्धति है, जो शरीर की प्राकृतिक उपचार शक्ति को सक्रिय करती है। यह रोग के मूल कारण को दूर करने और पूरे शरीर को संतुलित करने का कार्य करती है।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार से लाभ
-लीवर की कोशिकाओं का पुनर्निर्माण- सूजन कम करना
- लीवर की कार्यक्षमता को बढ़ाना- थकान, अपच, सूजन जैसे लक्षणों से राहत- बिना किसी साइड इफेक्ट के सुरक्षित इलाज
5) Brahm होम्योपैथी में इलाज की विशेषता?
Brahm Homeopathy में हम हर मरीज की व्यक्तिगत जांच करते हैं — उनकी जीवनशैली, मानसिक स्थिति, भोजन की आदतें, और पारिवारिक इतिहास को समझकर व्यक्तिगत दवा योजना बनाई जाती है।
- विस्तृत केस स्टडी और रोग विश्लेषण - रोग के मूल कारण पर केंद्रित इलाज - कस्टमाइज्ड दवा योजना - डाइट और लाइफस्टाइल में सुधार के सुझाव - नियमित फॉलो-अप और प्रगति पर नजर
निष्कर्ष
लीवर सिरोसिस एक गंभीर लेकिन संभालने योग्य बीमारी है। समय पर सही इलाज और जीवनशैली में बदलाव से इस रोग को बढ़ने से रोका जा सकता है।
होम्योपैथिक इलाज से शरीर को गहराई से संतुलित किया जाता है और रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता को बढ़ाया जाता है। यदि आप एक सुरक्षित, प्राकृतिक और प्रभावी समाधान की तलाश में हैं, तो Brahm Homeopathy से संपर्क करें
Videos

homeopathy me gerd ka ilaaj
१) GERD का क्या इलाज है?
GERD यह पाचन संबंधी की समस्या है, जिसमें अम्लीय पदार्थ भोजन नली में वापस आ जाता है। यह परीस्थिति अक्सर जलन, सीने में दर्द का होना , खट्टा या कड़वा स्वाद, गले में खराश होना , और खांसी जैसी लक्षणों के रूप में होती है। -यदि इसका समय पर सही इलाज न किया जाए, तो यह जठरांत्र संबंधी जटिलताओं जैसे कि (संकीर्णता) का कारण बन सकती है।
-आज का आर्टिकल में हम GERD का प्रभावी उपचार, जीवनशैली में बदलाव, और घरेलू उपायों पर बात करने वाले है
२) GERD होने के क्या कारण हो सकते है ?
GERD के कई कारण हो सकते है ,जैसे की १) वजन बढ़ना : ज्यादा वजन होने से पेट पर दबाव आता है, जिससे LES पर दबाव कम हो जाता है और GERD का खतरा बढ़ जाता है. २) कुछ खाद्य और पेय पदार्थ : तले हुए, मसालेदार खाना , चॉकलेट, कॉफी, शराब, लहसुन ये सब GERD के लक्षणों को ट्रिगर कर सकते हैं. ३) ज्यादा भोजन करना या देर रात को भोजन करना : पेट पर दबाव बढ़ जाने से एसिड रिफ्लक्स हो सकता है.
४) धूम्रपान : धूम्रपान LES को कमजोर कर सकता है और एसिड रिफ्लक्स के जोखिम का खतरा बढ़ा सकता है.
३) GERD होने के क्या लक्षण है?
GERD के कई लक्षण हो सकते है ,जैसे की
- सीने में जलन का होना -मुंह में खट्टा स्वाद का आना -गले में खराश का होना -गले में सूजन
- डकार का आना और पाचन में परेशानी
४) GERD का जीवनशैली में परिवर्तन से क्या होता है ?
-छोटे और बार-बार भोजन करें : दिन में कई बार हल्का-हल्का भोजन खाएं। -तैलीय, मसालेदार, और तीखे भोजन करने से दुरी बनाये रखे. -कैफीन, चॉकलेट, अदरक, और शराब का सेवन कम होना चाहिए. -धूम्रपान से दुरी रखे. -वजन को नियंत्रित रखें
-सोते समय सिर के निचे ऊंचा तकिया रखें.५) GERD के लिए क्या सावधानियां और सुझाव है ?
- ज्यादा मसालेदार भोजन खाने से बचें। -खाने के तुरंत बाद सोना नहीं चाहिए -वजन को नियंत्रित करें। - शराब से दूर रहें।
-तनाव को कम करने केलिए , कसरत करना चाहिए -नियमित रूप से चिकित्सक से जांच कराएं और दवाइयों का सेवन चिकित्सक की सलाह के अनुसार करें।

mastoiditis treatment in hindi
१) मास्टोइडाइटिस का इलाज क्या है?
मास्टोइडाइटिस गंभीर संक्रमण है जो की कान के पीछे स्थित मास्टोइड हड्डी को असर करता है। यह हड्डी छोटे-छोटे वायुवीय कक्षों से बने होते है और इसका सीधा संबंध middle ear से होता है।
जब कान का संक्रमण समय रहते ठीक नहीं होता है तो , यह मास्टोइड हड्डी तक फैल सकता है, जिससे मास्टोइडाइटिस होता है। यह स्थिति बच्चों में होती है, पर कोई भी उम्र ये बीमारी हो सकता है।
२) मास्टोइडाइटिस के लक्षण क्या है?
मास्टोइडाइटिस के लक्षण निचे अनुसार हो सकते है ,जैसे की - कान के पीछे सूजन का होना -लालिमा -तेजी से सिर में दर्द - कान से मवाद का आना -सुनने में कमी -बुखार - कान को छूने पर दर्द का तेजी से होना -गर्दन की अकड़न
३) मास्टोइडाइटिस के होने का कारण क्या है?
मास्टोइडाइटिस होने का कारण इस प्रकार से है , -मध्य कान में संक्रमण : सबसे आम कारण है। पर मध्य कान का संक्रमण सही से इलाज नहीं किया जाये तो संक्रमण मास्टॉयड हड्डी तक फैल सकता है.
-कोलेस्टीटोमा : मध्य कान में असामान्य त्वचा में वृद्धि होती है जो कान के अंदर पानी निकलने में असर डालती है और संक्रमण को बढ़ावा देती है, जिससे मास्टोइडाइटिस हो सकता है. -अन्य संक्रमण : मास्टोइडाइटिस मस्तिष्क के फोड़े या अन्य संक्रमण से भी हो सकता है.४) मास्टोइडाइटिस रोकथाम का उपाय क्या है?
- कान की साफ-सफाई करना और तैराकी के दौरान सावधानी भी जरूरी है। ताकि पानी कान में न जाये .-शांत करने वाले उपकरणों का उपयोग मध्य कान में संक्रमण का खतरा बढ़ा सकता है. -सर्दी और फ्लू से बचना -अपने बच्चे को सभी टीकों लगाना चाहिए खासकर न्यूमोकोकल और फ्लू के टीके. -एलर्जी के कारण से सूजन और बलगम हो सकता है उस से दूर रहना चाहिए

homeopathic me acute pancreas ka kya ilaaj hai?
१) एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का होम्योपैथी में क्या इलाज है?
एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस गंभीर अवस्था है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में सूजन आ जाती है। यह स्थिति अचानक से होती है और पेट के ऊपरी भाग में तेज दर्द, उल्टी, बुखार, और पाचन से संबंधित समस्याओं का कारण भी बनती है। एलोपैथी में इसका इलाज है, लेकिन होम्योपैथी भी एक असरकारक और सुरक्षित विकल्प के रूप में है, विशेष रूप से रोग की प्रारंभिक अवस्था में और रिकवरी के दौरान।
२) एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के क्या कारण हो सकते है ?
एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण निचे बताये गए है , * पित्ताशय की पथरी : एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस में सबसे सामान्य कारण में से एक है। * ज्यादा शराब का सेवन : लंबे समय तक ज्यादा मात्रा में शराब का सेवन करने से अग्न्याशय को असर होता है * कुछ दवाओं का दुष्प्रभाव से भी इसका खतरा ज्यादा होता है *कैल्शियम का उच्च स्तर : खून में कैल्शियम का स्तर ज्यादा बढ़ने से भी एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस हो सकता है. *वंशानुगत : कुछ लोगों के पारिवारिक इतिहास में भी एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस होने चान्सेस होता है.
३)एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कौन से लक्षण दिखाई देते है?
एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण निचे अनुसार हो सकते है ,जैसे की , - पेट के ऊपरी भाग में तेज और स्थायी दर्द का होना - दर्द जो की पीठ तक फैल सकता है -उल्टी और मतली -बुखार -पेट का फूलना - भूख में कमी होना - शरीर में कमजोरी आ जाना
४) होम्योपैथी का सिद्धांत क्या है ?
होम्योपैथी का मुख्य सिद्धांत "समान का समान से उपचार" है। यह सिद्धांत कहता है कि जो पदार्थ किसी स्वस्थ व्यक्ति में किसी रोग जैसे लक्षण उत्पन्न करता है, वही पदार्थ से अत्यंत सूक्ष्म मात्रा में मरीज को देने पर उन लक्षणों को दूर भी कर सकता है। होम्योपैथी यह भी मानता है कि दवा को जितना पतला हो , वह उतना ही अधिक शक्तिशाली होगा। * होम्योपैथी के सिद्धांत * - समानता का नियम : एक पदार्थ जो स्वस्थ मानव को बीमारी के लक्षण पैदा करता है, वही पदार्थ बीमार मरीज को समान लक्षणों का इलाज भी कर सकता है। - न्यूनतम खुराक का नियम :
होम्योपैथी में, दवा को जितना पतला किया जाएगा, वह उतना ही अधिक शक्तिशाली होता है । - प्राणशक्ति का सिद्धांत : होम्योपैथी में, ऐसी शक्ति की कल्पना की जाती है जो की मानव शरीर को सजीव करती है और शरीर के सामंजस्यपूर्ण कामकाज को बनाए रखती है।
५)होम्योपैथिक इलाज की क्या विशेषताएँ है ?
- व्यक्तिगत इलाज : कोई भी मरीज को उसकी बीमारी के लक्षणों के अनुसार ही दवा दी जाती है।
- कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं : होम्योपैथिक दवाएं का सेवन करने से कोई भी दुष्प्रभाव नहीं होता है। -प्रतिरोधक क्षमता बढ़ाना : होम्योपैथिक दवाये शरीर की रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता को मजबूत बनाती है।
