
What is the best treatment for fatty pancreas?
Homeopathy is the most successful treatment for fatty pancreas without surgery. You will see significant benefits right away when you begin treatment for fatty pancreas. Brahm Homeopathy serves a vast number of patients, and their service is excellent. Brahm Homeopathy provides the simplest and safest treatments for fatty pancreas without surgery.

What are symptoms of fatty pancreas?
-Upper abdominal pain. -Upper belly pain extends to the back. -Tightness when touching the abdomen. -Fever. -Rapid pulse. -An upset stomach. -Gastrointestinal distress.

How do you reduce fatty pancreas?
Therapeutically, a healthy diet, weight loss, and exercise are the primary ways to minimize pancreatic fat development.
Is fatty pancreas normal?
Fatty infiltration in the pancreas can induce pancreatitis, diabetes, and may be a risk factor for pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic steatosis is now a common incidental finding on abdominal ultrasonography for a variety of causes, and it presents a new challenge in gastroenterology.
What age do people get fatty pancreas?
Men have a larger pancreatic fat content than women, and the prevalence of NAFPD is highest in those aged 40 to 49 years. Furthermore, the frequency of NAFLD in women is quite low until menopause (27,28).
What is fatty parenchyma of the pancreas?
Fatty pancreas is characterized by fatty tissue infiltrating the parenchyma in a scattered pattern (intralobular fat) or accumulating in the peri-lobular region. This pattern is typically seen surrounding major vessels (interlobular fat).
Does fatty pancreas cause weight gain or loss?
Pancreatitis can develop in persons who are overweight or have excessive levels of fat or cholesterol in their blood. However, once the pancreas becomes inflamed, nausea, vomiting, and malabsorption might result in weight loss rather than gain.
What is a Grade 1 fatty pancreas? | What is a Grade 2 fatty pancreas?
CT scans can classify fatty pancreas into five grades based on their location: Grade 0 (normal appearance without fatty replacement), Grade 1 (fatty infiltration involving less than 25% of a given pancreatic region), Grade 2 (fatty replacement involving 25%-50% of a given pancreatic region), Grade 3 (fatty replacement involving 50%-75% of a given pancreatic region), and Grade 4 (fatty infiltration involving more than 75% of a given pancreatic region). The correlation between fat concentration in the pancreas and attenuation indexes in CT scans shows that unenhanced CT is a non-invasive method for assessing pancreatic fat.
Stories

chronic pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियास ठीक करने के उपाय
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस एक बीमारी है जो आपके पैंक्रियास में हो सकती है। पैंक्रियास आपके पेट में एक लंबी ग्रंथि है जो भोजन को पचाने में आपकी मदद करती है। यह आपके रक्त प्रवाह में हार्मोन भी जारी करता है जो आपके शरीर को ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग करने में मदद करता है। यदि आपका पैंक्रियास क्षतिग्रस्त हो गया है, तो पाचन एंजाइम सामान्य रूप से आपकी छोटी आंत में नहीं जा सकते हैं और आपका शरीर ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग नहीं कर सकता है।
पैंक्रियास शरीर का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है जो हार्मोन इंसुलिन का उत्पादन करके रक्त शर्करा को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। यदि इस अंग को नुकसान होता है, तो इससे मानव शरीर में गंभीर समस्याएं हो सकती हैं। ऐसी ही एक समस्या है जब पैंक्रियास में सूजन हो जाती है, जिसे तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस कहा जाता है।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस पैंक्रियास की सूजन है जो लंबे समय तक रह सकती है। इससे पैंक्रियास और अन्य जटिलताओं को स्थायी नुकसान हो सकता है। इस सूजन से निशान ऊतक विकसित हो सकते हैं, जो इंसुलिन उत्पन्न करने वाली कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा सकते हैं। यह पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ वाले लगभग 45 प्रतिशत लोगों में मधुमेह का कारण बन सकता है। भारी शराब का सेवन भी वयस्कों में पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकता है। ऑटोइम्यून और आनुवंशिक रोग, जैसे सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस, कुछ लोगों में पुरानी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकते हैं।
उत्तर भारत में, ऐसे बहुत से लोग हैं जिनके पास पीने के लिए बहुत अधिक है और कभी-कभी एक छोटा सा पत्थर उनके पित्ताशय में फंस सकता है और उनके अग्न्याशय के उद्घाटन को अवरुद्ध कर सकता है। इससे उन्हें अपना खाना पचाने में मुश्किल हो सकती है। 3 हाल ही में एशिया-प्रशांत क्षेत्र के विभिन्न देशों में किए गए एक सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार दक्षिण भारत में पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ की व्यापकता प्रति 100,000 जनसंख्या पर 114-200 मामले हैं।
Chronic Pancreatitis Patient Cured Report
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण ?
-कुछ लोगों को पेट में दर्द होता है जो पीठ तक फैल सकता है। -यह दर्द मतली और उल्टी जैसी चीजों के कारण हो सकता है। -खाने के बाद दर्द और बढ़ सकता है। -कभी-कभी किसी के पेट को छूने पर दर्द महसूस हो सकता है। -व्यक्ति को बुखार और ठंड लगना भी हो सकता है। वे बहुत कमजोर और थका हुआ भी महसूस कर सकते हैं।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण ?
-पित्ताशय की पथरी -शराब
-रक्त में उच्च ट्राइग्लिसराइड का स्तर -रक्त में उच्च कैल्शियम का स्तर
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज कैसे किया जाता है?
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस नेक्रोसिस का उपचार उपचारात्मक है। आप कितने समय तक इस बीमारी से पीड़ित रहेंगे यह काफी हद तक आपकी उपचार योजना पर निर्भर करता है। ब्रह्म अनुसंधान पर आधारित चिकित्सकीय रूप से सिद्ध वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी के इलाज में अत्यधिक प्रभावी हैं। हमारे पास आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करने, सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों, रोग के पाठ्यक्रम का दस्तावेजीकरण करने, रोग के चरण, पूर्वानुमान और जटिलताओं को समझने की क्षमता है, हमारे पास अत्यधिक योग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है। फिर वे आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताएंगे, आपको एक उचित आहार योजना (क्या खाएं और क्या नहीं खाएं), व्यायाम योजना, जीवनशैली योजना और कई अन्य कारक प्रदान करेंगे जो आपके समग्र स्वास्थ्य में सुधार कर सकते हैं। पढ़ाना। व्यवस्थित उपचार रोग ठीक होने तक होम्योपैथिक औषधियों से उपचार करें। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, चाहे वह थोड़े समय के लिए हो या कई सालों से। हम सभी ठीक हो सकते हैं, लेकिन बीमारी के प्रारंभिक चरण में हम तेजी से ठीक हो जाते हैं। पुरानी या देर से आने वाली या लंबे समय तक चलने वाली बीमारियों को ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगता है। समझदार लोग इस बीमारी के लक्षण दिखते ही इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं। इसलिए, यदि आपको कोई असामान्यता नज़र आती है, तो कृपया तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।

Acute Necrotizing pancreas treatment in hindi
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ ?
आक्रामक अंतःशिरा द्रव पुनर्जीवन, दर्द प्रबंधन, और आंत्र भोजन की जल्द से जल्द संभव शुरुआत उपचार के मुख्य घटक हैं। जबकि उपरोक्त सावधानियों से बाँझ परिगलन में सुधार हो सकता है, संक्रमित परिगलन के लिए अतिरिक्त उपचार की आवश्यकता होती है।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लक्षण ? - बुखार - फूला हुआ पेट - मतली और दस्त तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण ?
- अग्न्याशय में चोट - उच्च रक्त कैल्शियम स्तर और रक्त वसा सांद्रता
ऐसी स्थितियाँ जो अग्न्याशय को प्रभावित करती हैं और आपके परिवार में चलती रहती हैं, उनमें सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस और अन्य आनुवंशिक विकार शामिल हैं जिनके परिणामस्वरूप बार-बार अग्नाशयशोथ होता है|
क्या एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रिएटाइटिस का इलाज होम्योपैथी से संभव है ?
हां, होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनकर एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज संभव है। होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनने से आपको इन दवाओं का कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं होगा और यह समस्या को जड़ से खत्म कर देता है, इसीलिए आपको अपने एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के इलाज के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार का ही चयन करना चाहिए।
आप तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ से कैसे छुटकारा पा सकते हैं ?
शुरुआती चरण में सर्वोत्तम उपचार चुनने से आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस से छुटकारा मिल जाएगा। होम्योपैथिक उपचार का चयन करके, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे विश्वसनीय उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करता है। एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार सबसे अच्छा इलाज है। जैसे ही आप एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक करने के लिए अपना उपचार शुरू करेंगे, आपको निश्चित परिणाम मिलेंगे।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार से तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ का इलाज संभव है। आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, इसका उपचार योजना पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ता है। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कब से अपनी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, या तो हाल ही में या कई वर्षों से - हमारे पास सब कुछ ठीक है, लेकिन बीमारी के शुरुआती चरण में, आप तेजी से ठीक हो जाएंगे। पुरानी स्थितियों के लिए या बाद के चरण में या कई वर्षों की पीड़ा के मामले में, इसे ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगेगा। बुद्धिमान व्यक्ति हमेशा इस बीमारी के किसी भी लक्षण को देखते ही तुरंत इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं, इसलिए जैसे ही आपमें कोई असामान्यता दिखे तो तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एवं रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
ब्रह्म अनुसंधान आधारित, चिकित्सकीय रूप से प्रमाणित, वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी को ठीक करने में बहुत प्रभावी है। हमारे पास सुयोग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है जो आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करती है, रोग की प्रगति के साथ-साथ सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों को रिकॉर्ड करती है, इसकी प्रगति के चरणों, पूर्वानुमान और इसकी जटिलताओं को समझती है। उसके बाद वे आपको आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताते हैं, आपको उचित आहार चार्ट [क्या खाएं या क्या न खाएं], व्यायाम योजना, जीवन शैली योजना प्रदान करते हैं और कई अन्य कारकों के बारे में मार्गदर्शन करते हैं जो व्यवस्थित प्रबंधन के साथ आपकी सामान्य स्वास्थ्य स्थिति में सुधार कर सकते हैं। जब तक यह ठीक न हो जाए तब तक होम्योपैथिक दवाओं से अपनी बीमारी का इलाज करें।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लिए आहार ?
कुपोषण और पोषण संबंधी कमियों को रोकने के लिए, सामान्य रक्त शर्करा के स्तर को बनाए रखने और मधुमेह, गुर्दे की समस्याओं और पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ से जुड़ी अन्य स्थितियों को रोकने या बेहतर ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए, अग्नाशयशोथ की तीव्र घटना से बचना महत्वपूर्ण है।
यदि आप एक स्वस्थ आहार योजना की तलाश में हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। हमारे विशेषज्ञ आपकी व्यक्तिगत आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप एक योजना बनाने में आपकी सहायता कर सकते हैं

Pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ?
जब पैंक्रियाटाइटिसमें सूजन और संक्रमण हो जाता है तो इससे पैंक्रिअटिटिस नामक रोग हो जाता है। पैंक्रियास एक लंबा, चपटा अंग है जो पेट के पीछे पेट के शीर्ष पर छिपा होता है। पैंक्रिअटिटिस उत्तेजनाओं और हार्मोन का उत्पादन करके पाचन में मदद करता है जो आपके शरीर में ग्लूकोज के प्रसंस्करण को विनियमित करने में मदद करते हैं।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण:
-पेट के ऊपरी भाग में दर्द होना। -बेकार वजन घटाना. -पेट का ख़राब होना.
-शरीर का असामान्य रूप से उच्च तापमान। -पेट को छूने पर दर्द होना। -तेज़ दिल की धड़कन. -हाइपरटोनिक निर्जलीकरण.
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण:
-पित्ताशय में पथरी. -भारी शराब का सेवन.
-भारी खुराक वाली दवाएँ। -हार्मोन का असंतुलन. -रक्त में वसा जो ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स का कारण बनता है। -आनुवंशिकता की स्थितियाँ. -पेट में सूजन ।
क्या होम्योपैथी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक कर सकती है?
हाँ, होम्योपैथीपैंक्रियाटाइटिसको ठीक कर सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको पैंक्रिअटिटिस के लिए सबसे भरोसेमंद उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करती है।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा उपचार क्या है?
यदि पैंक्रियाज अच्छी तरह से काम नहीं कर रहा है तो होम्योपैथिक उपचार वास्तव में बेहतर होने में मदद करने का एक अच्छा तरीका है। जब आप उपचार शुरू करते हैं, तो आप जल्दी परिणाम देखेंगे। बहुत सारे लोग इस इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जा रहे हैं और वे वास्तव में अच्छा कर रहे हैं। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपके पैंक्रियाज के को बेहतर बनाने में मदद करने के लिए आपको सबसे तेज़ और सुरक्षित तरीका प्रदान करना सुनिश्चित करती है।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
बीमार होने पर लोगों को बेहतर महसूस कराने में मदद करने के लिए हमारे पास एक विशेष तरीका है। हमारे पास वास्तव में स्मार्ट डॉक्टर हैं जो ध्यान से देखते हैं और नोट करते हैं कि बीमारी व्यक्ति को कैसे प्रभावित कर रही है। फिर, वे सलाह देते हैं कि क्या खाना चाहिए, व्यायाम करना चाहिए और स्वस्थ जीवन कैसे जीना चाहिए। वे व्यक्ति को ठीक होने में मदद करने के लिए विशेष दवा भी देते हैं। यह तरीका कारगर साबित हुआ है!
Tips

sarir ke liye vitamin or unke labh
हमारे शरीर के लिए सभी विटामिन और उनके लाभ
विटामिन हमारे शरीर के लिए आवश्यक पोषक तत्व हैं, जो शरीर के विभिन्न कार्यों को सुचारू रूप से चलाने में मदद करते हैं। ये सूक्ष्म पोषक तत्व होते हैं, लेकिन शरीर में इनकी भूमिका बहुत महत्वपूर्ण होती है। विटामिन की कमी से कई स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ हो सकती हैं, इसलिए संतुलित आहार लेना जरूरी है।
विटामिन कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
-विटामिन दो प्रकार के होते हैं: -1. वसा में घुलनशील विटामिन (Fat-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में वसा में संग्रहित होते हैं और जरूरत पड़ने पर उपयोग किए जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन A, D, E और K आते हैं।
-2. जल में घुलनशील विटामिन (Water-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में जमा नहीं होते और मूत्र के माध्यम से बाहर निकल जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन C और सभी B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन आते हैं।
विटामिन और उनके लाभ
1. विटामिन A (रेटिनॉल, बीटा-कैरोटीन)
भूमिका:
आँखों की रोशनी को बनाए रखता है।
त्वचा और इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है।
हड्डियों और दांतों के विकास में सहायक है।
स्रोत:
गाजर पालकआम, शकरकंद, डेयरी उत्पाद, अंडे, मछली का तेल।
कमी के प्रभाव:
रतौंधी (नाइट ब्लाइंडनेस)
त्वचा में रूखापन
रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी
---
2. विटामिन B-कॉम्प्लेक्स (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12)
B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र और रक्त निर्माण में मदद करते हैं। B1 (थायमिन)
भूमिका: ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र के कार्यों में सहायक।
स्रोत: साबुत अनाज, बीन्स, सूरजमुखी के बीज, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: कमजोरी, भूख न लगना, तंत्रिका तंत्र की समस्या।
B2 (राइबोफ्लेविन)
भूमिका: त्वचा, आँखों और ऊर्जा उत्पादन के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: दूध, दही, अंडे, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: होंठों में दरारें, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B3 (नियासिन)
भूमिका: कोलेस्ट्रॉल को नियंत्रित करता है और पाचन में सहायक होता है।
स्रोत: मूंगफली, मशरूम, टमाटर, चिकन, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा रोग, मानसिक कमजोरी। B5 (पैंटोथेनिक एसिड)
भूमिका: हार्मोन उत्पादन और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: मशरूम, एवोकाडो, दूध, ब्रोकली।
कमी के प्रभाव: थकान, सिरदर्द।
B6 (पाइरिडोक्सिन)
भूमिका: तंत्रिका तंत्र और प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को मजबूत करता है।
स्रोत: केला, चिकन, सोयाबीन, आलू।
कमी के प्रभाव: अवसाद, त्वचा रोग।
B7 (बायोटिन)
भूमिका: बालों और त्वचा के स्वास्थ्य को बनाए रखता है।
स्रोत: अंडे, मूंगफली, फूलगोभी।
कमी के प्रभाव: बाल झड़ना, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B9 (फोलिक एसिड)
भूमिका: डीएनए निर्माण और गर्भावस्था में जरूरी।
स्रोत: दालें, हरी सब्जियाँ, बीन्स। कमी के प्रभाव: एनीमिया, जन्म दोष।
B12 (कोबालामिन)
भूमिका: लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं और तंत्रिका तंत्र के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: मांस, अंडे, डेयरी उत्पाद। कमी के प्रभाव: स्मरण शक्ति की कमजोरी, एनीमिया।
---
3. विटामिन C (एस्कॉर्बिक एसिड)
भूमिका: इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है, त्वचा को चमकदार बनाता है, और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: संतरा, नींबू, स्ट्रॉबेरी, टमाटर, हरी मिर्च।
कमी के प्रभाव: स्कर्वी, मसूड़ों से खून आना, रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी।
---
4. विटामिन D (कोलेकल्सीफेरोल)
भूमिका: हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाता है और कैल्शियम के अवशोषण में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: सूर्य का प्रकाश, मछली, अंडे, दूध।
कमी के प्रभाव: हड्डियों में कमजोरी, रिकेट्स।
---
5. विटामिन E (टोकोफेरॉल)
भूमिका: एंटीऑक्सीडेंट के रूप में कार्य करता है और त्वचा तथा बालों के लिए लाभदायक है। स्रोत: बादाम, सूरजमुखी के बीज, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा की समस्याएँ, कमजोरी।
---
6. विटामिन K (फायलोक्विनोन)
भूमिका: रक्त को थक्का जमाने (ब्लड क्लॉटिंग) में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: पालक, ब्रोकोली, हरी सब्जियाँ।
कमी के प्रभाव: चोट लगने पर खून न रुकना। ---
निष्कर्ष
शरीर को सभी विटामिनों की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि सभी अंग सही से काम कर सकें। इनके लिए संतुलित आहार लेना बहुत जरूरी है। यदि विटामिन की कमी हो, तो डॉक्टर से परामर्श लेकर सप्लीमेंट्स भी लिए जा सकते हैं। लेकिन, प्राकृतिक स्रोतों से विटामिन प्राप्त करना हमेशा सबसे अच्छा होता है।
-आपके शरीर की जरूरतों के अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक सेंटर में भी विटामिन डेफिशिएंसी का होम्योपैथिक उपचार उपलब्ध है। यदि आपको कोई लक्षण महसूस हो रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक से संपर्क करें और स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर बनाएँ।

best 5 winter food to keep you warm and strong
1.Root Vegetables
Ingredients: Carrots, Beets, and Sweet Potatoes are rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Nutrients:
Carrots: High in beta-carotene (vitamin A), fiber, and potassium. Beets: Contain folate, manganese, and antioxidants. Sweet Potatoes: Rich in vitamins A, C, and B6, as well as fiber and manganese.
Benefits: Vitamin A supports eye health and enhances immunity, while fiber aids digestion.Folate plays a key role in red blood cell formation and helps maintain brain health. Beets also have anti-inflammatory properties that can improve cardiovascular function.Sweet potatioes also packed with antioxidants, they protect against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Their high fiber content promotes digestive health and stabilizes blood sugar levels.
2. Citrus Fruits
Ingredients: Oranges, grapefruits, and lemons provide a refreshing addition to winter diets. Nutrients: All three are excellent sources of vitamin C, flavonoids, and fiber.
Benefits: Vitamin C strengthens the immune system, helping the body fend off winter colds and infections. Flavonoids have antioxidant properties that combat inflammation and support heart health. The fiber content aids in digestion, enhancing gut health, which is crucial during the winter months when digestive issues can be more prevalent.
3. Nuts and Seeds
Ingredients: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds are nutrient-packed options for winter snacks. Nutrients:
Almonds: Main source of vitamin E, magnesium, and healthy fats. Walnuts: High in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins.
Chia Seeds: Loaded with fiber, protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential minerals such as calcium and iron. Benefits:
Vitamin E acts as a potent antioxidant, promoting skin health and maintaining immune function. Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function, which can be especially important during colder months when exercises might decrease.Walnuts are Rich in omega-3s, they support brain health and it also help to alleviate symptoms like depression, which can be exacerbated in winter. Their antioxidant content contributes to heart health.Chia Seed is also Known to maintain hydration and provide long-lasting energy, benefiting those who may engage in winter sports or outdoor activities. Their fiber can also promote gut health, helping to alleviate any tendency towards constipation during winter.
4. Whole Grains
Ingredients: Quinoa, oats, and brown rice are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates.
Nutrients:
Quinoa: Contains complete protein, fiber, magnesium, and iron.
Oats: High in beta-glucan fiber, vitamins B1 and B5, and manganese. Brown Rice: Rich in fiber, B vitamins, and essential minerals.
Benefits:
Quinoa is a complete protein, it supports muscle health and provides sustained energy throughout the day. Its iron content helps in the formation of red blood cells, especially important during winter.You should obtained beta-glucan in oats aids in cholesterol reduction, supporting heart health, while their fiber content keeps one feeling full and satisfied, promoting weight management.Unlike white rice, Brown Rice provides more fiber and nutrients, stabilizing blood sugar levels, which is crucial during winter when metabolism may slow.
5. Spices and Herbs
Ingredients:The main spices and Herbs like Ginger, turmeric, cinnamon, and garlic.
Nutrients: Antioxidants: Combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Anti-inflammatory compounds: Reduce inflammation and pain.
Vitamins and Minerals: Many spices offer small amounts of essential vitamins and minerals.
Benefits:
Ginger and garlic boost the immune system and can help reduce symptoms of cold and flu.Turmeric has powerful anti-inflammatory properties, ideal for joint health during cold months.Enhance flavor of foods without added calories, making dishes more enjoyable. Homeopathic treatment stands as a beacon of holistic healing, emphasizing the body’s innate capacity to restore balance and health. Under the expert guidance of a dedicated homeopath, patients receive personalized remedies tailored to their unique symptoms and underlying causes, rather than merely treating superficial manifestations. This philosophy fosters a profound understanding of individual health, where the doctor and patient collaborate closely to explore not only the physical ailments but also emotional and mental well-being. By utilizing highly diluted natural substances that trigger the body’s self-healing processes, homeopathy aims to stimulate vitality and resilience, paving the way for sustainable health and preventing future ailments. This gentle yet effective approach not only alleviates symptoms but also empowers individuals to achieve optimal well-being and harmony in their lives.

10 benfits of makhna
Top 10 Benefits of Makhana in your daily life!
1.Rich in Nutrients 2.High in Antioxidants 3.Good for Heart Health 4.Boosts Kidney Health
5.Aids Digestion
6.Supports Weight Loss 7.Rich Source of Calcium
8.Supports Skin Health 9.Enhances Immunity
10.Helps Regulate Blood Pressure Makhana, also known as fox nuts or lotus seeds, is a nutrient-dense superfood that has been celebrated in traditional medicine for its extensive health benefits. Its incorporation into a regular diet is highly recommended due to its rich nutrient profile and the multitude of health advantages it offers. Below are some key benefits of makhana, emphasizing how it can boost your immunity and overall health.
1. Rich in Nutrients
Makhana is a powerhouse of essential nutrients, including proteins, carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. Being low in calories yet high in nutrients, it serves as an ideal snack for those aiming to maintain a balanced diet without excess calories.
2. High in Antioxidants
Makhana is rich in antioxidants that combat oxidative stress in the body caused by free radicals. This helps protect cells from damage and reduces the risk of chronic diseases, thereby supporting overall health and longevity.
3. Good for Heart Health
The presence of heart-healthy compounds within makhana helps in managing cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Its low sodium content ensures that blood pressure is kept in check, promoting a healthier heart.
4. Boosts Kidney Health
Makhana has been used in Ayurveda as a remedy for kidney-related issues like blood flow.Its natural diuretic properties aid in flushing out toxins and preventing kidney stones, making it a beneficial addition for those concerned about renal health.
5. Aids Digestion
Rich in dietary fiber, makhana aids in the proper functioning of the digestive system. It helps prevent constipation and promotes gut health, leading to improved nutrient absorption and overall digestive wellness.
6. Supports Weight Loss
Makhana, a low-calorie and high-fiber food, is an excellent option for individuals seeking to manage their weight. The fiber content promotes satiety, reducing cravings and overall calorie intake, thus supporting weight loss efforts.
7. Rich Source of Calcium
Makhana is an excellent source of calcium, which is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Calcium also plays a critical role in muscle function, nerve signaling, and hormonal secretion, promoting overall health.
8. Supports Skin Health
The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties of makhana can lead to improved skin health. They help in reducing acne and blemishes, while the nutrients in makhana promote a youthful glow and hydration.
9. Enhances Immunity
Makhana plays a significant role in boosting immunity due to its rich nutrient content. Antioxidants, along with vitamins and minerals found in makhana, enhance the body's immune response, helping fight off infections and diseases more effectively.
10. Helps Regulate Blood Pressure
Makhana's rich potassium content contributes to regulating blood pressure levels. Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body, reducing tension in blood vessel walls and supporting cardiovascular health.
Why Makhana is Recommended for Regular Diet ?
Given its extensive array of health benefits, makhana stands out as an ideal food to be included in a regular diet. Its low-caloric count, rich nutrient profile, and potent antioxidant properties make it a fantastic snack or ingredient in meals. Regular consumption of makhana can not only lead to improved immunity and heart health but can also support digestion, enhance skin wellness, and aid in weight management. Integrating makhana into your dietary routine is a simple and effective way to boost overall health and well-being, making it a worthwhile addition to your daily nutrition plan.
Benefits of Consuming 30 to 50 Grams of Makhana Daily!
Immune Support: This portion provides a sufficient amount of antioxidants and essential nutrients to help enhance immune function.
Heart Health: Regular consumption in this range can help manage cholesterol levels and support cardiovascular health.
Aids Digestion: The fiber content in this quantity can assist in digestion and prevent constipation.
Weight Management: Eating this moderate serving can promote satiety, aiding in weight control without contributing to excessive caloric intake.
Bone Health: With its significant calcium content, this daily serving can contribute positively to bone health. At Brahmhomeopathy Healing and Research Center, we emphasize the importance of nutrition in promoting holistic well-being. Integrating makhana (fox nuts) into your daily diet is a powerful step towards enhancing your health. Rich in essential nutrients, antioxidants, and dietary fiber, makhana offers a multitude of benefits, including improved immune function, heart health, and digestive support. Its low-calorie profile makes it an ideal choice for weight management while being a rich source of calcium, promoting bone strength.By incorporating makhana into your regular meals—whether as a wholesome snack, a crunchy addition to salads, or as an ingredient in nutritious dishes—you can experience significant positive impacts on your overall health.
Testimonials

body weakness treatment
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से 10 महीने में चमत्कारी इलाज: एक मरीज की कहानी
आज के समय में जब लोग तरह-तरह की बीमारियों से जूझ रहे हैं, तब होम्योपैथी चिकित्सा कई मरीजों के लिए आशा की किरण बन रही है। ऐसी ही एक प्रेरणादायक कहानी है एक मरीज की, जिसने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के माध्यम से 10 महीने में अपनी बीमारी से निजात पाई।
शुरुआत में थी थकान और शरीर में भारीपन
मरीज ने बताया, "मुझे कई दिनों से शरीर में थकान, भारीपन और बेचैनी महसूस हो रही थी। यह परेशानी धीरे-धीरे इतनी बढ़ गई कि रोजमर्रा के काम भी कठिन लगने लगे। मेरी माँ पहले से ही ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी क्लीनिक में इलाज करा रही थीं। उन्होंने बताया कि उन्हें वेरीकोज वेन्स की समस्या थी और यहाँ के इलाज से उन्हें बहुत लाभ हुआ था। उनकी सलाह पर मैं भी यहाँ आया।"
होम्योपैथी इलाज का असर मात्र एक सप्ताह में
मरीज के अनुसार, "जब मैंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा से परामर्श लिया और उनकी सलाह के अनुसार दवाएं लेना शुरू किया, तो सिर्फ एक हफ्ते के भीतर ही मुझे सुधार महसूस होने लगा। मेरी थकान कम हो गई, शरीर की ऊर्जा बढ़ने लगी और पहले की तुलना में मैं ज्यादा सक्रिय महसूस करने लगा।"
लगातार 10 महीने तक किया उपचार, मिली पूरी राहत
मरीज ने लगातार 10 महीने तक ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाएं लीं और सभी निर्देशों का पालन किया। उन्होंने कहा, "लगभग 15 दिनों के अंदर ही मेरी स्थिति में काफी सुधार हुआ और अब 10 महीने बाद मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ महसूस कर रहा हूँ। यह सब डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा और ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाओं की वजह से संभव हुआ।"
होम्योपैथी: सभी बीमारियों के लिए वरदान
मरीज ने आगे कहा, "इस क्लिनिक का माहौल बहुत अच्छा है और इलाज का तरीका बेहद प्रभावी है। यहाँ की दवाएँ बहुत असरदार हैं और मुझे इनके इस्तेमाल से कोई साइड इफेक्ट भी नहीं हुआ। यह सच में होम्योपैथी का सबसे बेहतरीन केंद्र है। मैं सभी मरीजों से अनुरोध करूंगा कि अगर वे किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान हैं, तो एक बार ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी का इलाज जरूर लें। यह एक बीमार मरीजों के लिए किसी स्वर्ग से कम नहीं है।"
निष्कर्ष
इस मरीज की कहानी यह साबित करती है कि सही चिकित्सा और सही मार्गदर्शन से कोई भी बीमारी ठीक हो सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में न केवल आधुनिक चिकित्सा पद्धति का समावेश है, बल्कि यहाँ मरीजों की समस्याओं को गहराई से समझकर उनका संपूर्ण इलाज किया जाता है। यदि आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी एक बेहतरीन विकल्प हो सकता है।

acute pancreatitis ka ilaaj
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: एक मरीज की जीवन बदलने वाली कहानी
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस: एक गंभीर समस्या
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में तीव्र सूजन हो जाती है। जब यह समस्या उत्पन्न होती है, तो मरीज को शुरुआत में इसकी जानकारी नहीं होती, लेकिन दर्द इतना असहनीय होता है कि उसे तुरंत अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की आवश्यकता पड़ती है। इस स्थिति का मुख्य कारण अनुचित जीवनशैली, जंक फूड, शराब का सेवन, ऑटोइम्यून बीमारियां, कुछ रसायन और विकिरण हो सकते हैं। यदि समय रहते सही इलाज नहीं किया गया, तो यह स्थिति क्रॉनिक पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस में बदल सकती है।
अमन बाजपेई की प्रेरणादायक यात्रा
मैं, अमन बाजपेई, पिछले 1.5 वर्षों से एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का मरीज था। यह समय मेरे लिए बेहद कठिन था। मैं बहुत परेशान था, खाना खाने तक के लिए तरस गया था। पिछले 7-8 महीनों में मैंने रोटी तक नहीं खाई, केवल खिचड़ी और फल खाकर गुजारा कर रहा था। बार-बार मुझे इस बीमारी के हमले झेलने पड़ रहे थे। हर 5-10 दिनों में दवा लेनी पड़ती थी, लेकिन कोई लाभ नहीं हो रहा था।
इस बीमारी के इलाज में मैंने 6-7 लाख रुपये खर्च कर दिए। दिल्ली और झांसी समेत कई बड़े अस्पतालों में इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई राहत नहीं मिली। मेरा वजन 95 किलो से घटकर 55 किलो हो गया और मैं बहुत कमजोर हो गया था। तभी मुझे सोशल मीडिया के माध्यम से ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के बारे में पता चला।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: उम्मीद की एक नई किरण
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी वह जगह है जहां कम खर्च में उत्कृष्ट इलाज संभव है। मैंने आज तक किसी भी डॉक्टर या अस्पताल में इतना अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं देखा। डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा सर ने मुझे एक नई जिंदगी दी। पहले मुझे लगा था कि मैं शायद कभी ठीक नहीं हो पाऊंगा, लेकिन आज मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ हूं।
मैं सभी मरीजों को यही सलाह दूंगा कि वे पैसे की बर्बादी न करें और सही इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जाएं। यह भारत में एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा अस्पताल है। मेरे लिए डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा किसी देवता से कम नहीं हैं।
वैज्ञानिक रूप से प्रमाणित उपचार पद्धति
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के विशेषज्ञों ने शोध आधारित एक विशेष उपचार पद्धति विकसित की है, जिससे न केवल लक्षणों में सुधार होता है बल्कि बीमारी को जड़ से ठीक किया जाता है। हजारों मरीज इस उपचार का लाभ ले रहे हैं और उनकी मेडिकल रिपोर्ट में भी उल्लेखनीय सुधार देखा गया है।
यदि आप भी इस बीमारी से जूझ रहे हैं और सही इलाज की तलाश कर रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। यह न केवल बीमारी को बढ़ने से रोकता है बल्कि इसे जड़ से ठीक भी करता है।

urticaria ka ilaaj
रेणुका बहन श्रीमाली की प्रेरणादायक कहानी: 10 साल की तकलीफ से छुटकारारेणुका बहन श्रीमाली पिछले 10 वर्षों से एक गंभीर समस्या से जूझ रही थीं। उन्हें जब भी कुछ खाने की कोशिश करतीं, उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और अत्यधिक खुजली होने लगती थी। इस समस्या के कारण वे बहुत परेशान थीं और 10 वर्षों तक कुछ भी सही तरीके से नहीं खा पाती थीं। उन्होंने कई जगहों पर इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई भी उपचार कारगर नहीं हुआ।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर से नई उम्मीदआखिरकार, 17 मई 2021 को उन्होंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में अपना ट्रीटमेंट शुरू किया। पहले से निराश हो चुकीं रेणुका बहन के लिए यह एक नई उम्मीद की किरण थी।एक साल में चमत्कारी सुधारट्रीटमेंट शुरू करने के बाद, धीरे-धीरे उनके स्वास्थ्य में सुधार होने लगा। एक साल के भीतर उन्होंने अपने आहार में वे सभी चीजें फिर से शुरू कर दीं, जिन्हें वे पहले नहीं खा पाती थीं। पहले जहाँ कोई भी चीज खाने से उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और खुजली होती थी, वहीं अब वे बिना किसी परेशानी के सामान्य जीवन जी रही हैं।ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर का योगदान
रेणुका बहन का कहना है कि यह इलाज उनके लिए किसी चमत्कार से कम नहीं था। उन्होंने अपनी पुरानी जीवनशैली को फिर से अपनाया और अब वे पूरी तरह से स्वस्थ महसूस कर रही हैं। उनके अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में इलाज का असर तुरंत दिखने लगता है और दवाइयाँ भी पूरी तरह से प्रभावी होती हैं।
अन्य समस्याओं के लिए भी कारगर
इस रिसर्च सेंटर में सिर्फ एलर्जी ही नहीं, बल्कि स्पॉन्डिलाइटिस, पीसीओडी जैसी कई अन्य बीमारियों का भी सफलतापूर्वक इलाज किया जाता है। रेणुका बहन जैसी कई अन्य मरीजों को भी यहाँ से सकारात्मक परिणाम मिले हैं।
रेणुका बहन का संदेश
रेणुका बहन उन सभी लोगों को धन्यवाद देती हैं जिन्होंने उनके इलाज में मदद की। वे यह संदेश देना चाहती हैं कि यदि कोई भी व्यक्ति किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान है और अब तक उसे कोई समाधान नहीं मिला है, तो उन्हें ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में एक बार अवश्य आना चाहिए।
"यहाँ इलाज प्रभावी, सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक तरीके से किया जाता है। मैं इस सेंटर के प्रति आभार व्यक्त करती हूँ, जिसने मुझे 10 साल पुरानी तकलीफ से राहत दिलाई।"
अगर आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं और समाधान की तलाश में हैं, तो इस होम्योपैथिक उपचार को आज़मा सकते हैं।
Departments
ENT DEPARTMENT
Hearing Loss, Vocal Cord Nodule, Vocal Cord Paralysis, Nasal Polip, Adenoid, Recurrent ear infection, Allergic Rhinitis/Sinusitis

GENERAL MEDICINE
Diabetes
Hypertension
Thyroid Disorders
Cholesterol problem (Dislipimidia)
DIGESTIVE TRACT DISORDER
Constipation
Acidity
Gastritis
Oesophagitis
Duodenitis
Ulcertive Colitis
IBS
Piles
Fissure
Fistula
Diseases
crohn's rog kya hai
क्रोहन रोग किस हिस्से को प्रभावित करता हैक्रोहन रोग एक पुरानी सूजन संबंधी आंत्र रोग (IBD) है, जो पाचन तंत्र की सूजन का कारण बनता है। यह किसी भी हिस्से को प्रभावित कर सकता है, लेकिन आमतौर पर छोटी आंत और बड़ी आंत के अंतिम हिस्से को प्रभावित करता है।
क्रोहन रोग के लक्षण ?-दस्त- पेट में दर्द और ऐंठन
-वजन में कमी
-थकान -मल में खून आना
क्रोहन रोग के कारण: सटीक कारण अज्ञात है, लेकिन आनुवंशिकता, प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली की गड़बड़ी, और पर्यावरणीय कारक इसमें भूमिका निभा सकते हैं।
बिना सर्जरी के उपचार: अहमदाबाद स्थित ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर में क्रोहन रोग का बिना सर्जरी के प्रभावी उपचार उपलब्ध है। यहां अनुभवी चिकित्सकों की टीम उच्च गुणवत्ता वाली दवाओं और अनुसंधान-आधारित तरीकों का उपयोग करती है। केंद्र की विशेषताएं:
-अनुभवी चिकित्सकों की टीम
-उच्च गुणवत्ता वाली दवाएं
-समय की बचत करने वाली प्रबंधन प्रणाली -दवा वितरण सुविधा
-अनुसंधान केंद्र
संपर्क जानकारी:
पता: 8-9-10, गणेश कॉलोनी, निकोल रोड, मन्मोहन पार्क क्रॉस रोड के पास, जनता नगर, ओढव, अहमदाबाद, गुजरात 382415 वेबसाइट: www.brahmhomeo.com क्रोहन रोग के उपचार के लिए, आप ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर से संपर्क कर सकते हैं, जहां बिना सर्जरी के प्रभावी होम्योपैथिक उपचार उपलब्ध है।
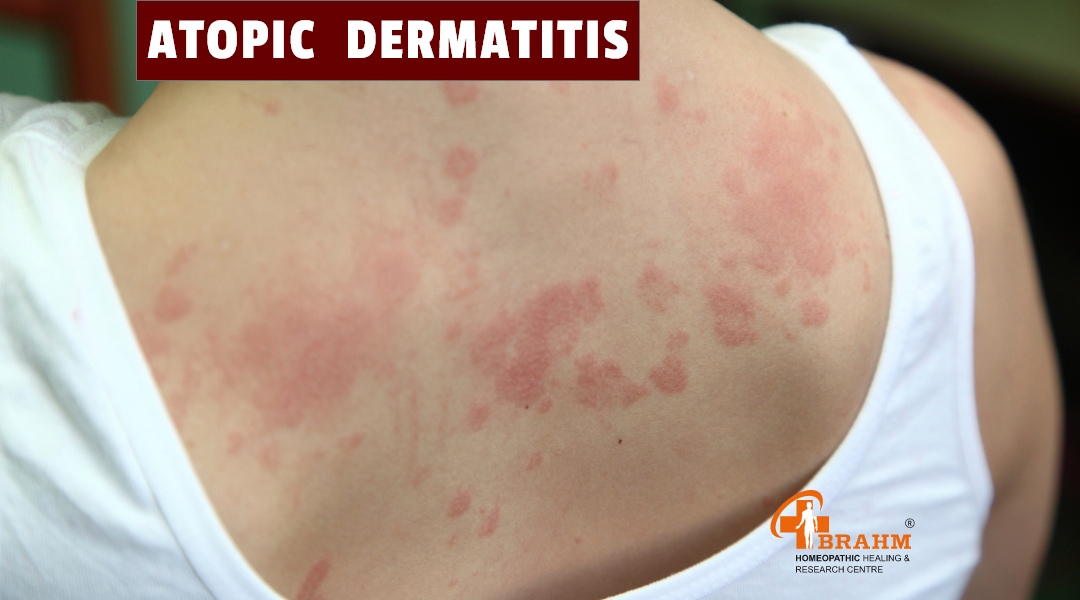
atopic dermatitis treatment in homeopathy
Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
-Atopic dermatitis is also known as eczema. It is a skin disease in which the skin is itchy, swollen, red, dry, and flaky. -It is common in children, but this disease can occur in people of any age. -It mostly starts in childhood, and many people recover from it by adulthood.
2. Which parts are affected by eczema?
In children, eczema can mostly affect the face, head, hands, and feet. Whereas in older children, eczema can only affect the inner part of the elbow and the back of the knees. There is a lot of itching when this disease occurs.
3. What tests do doctors do to detect eczema?
To diagnose eczema, the doctor asks for some tests, which can be as follows,
- Blood test
- Patch test
- Skin biopsy
4) What are the symptoms of atopic dermatitis?
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis are: - Itchy, red rash
- Patches on the skin
- Blisters that ooze and form crusts - Higher risk of skin infections
5) What are the risk factors for atopic dermatitis?
- Genetics
- Hormone changes - Dietary factors: food allergies

autism treatment in homeopathic
Autism symptoms,cause,treatment
Autism is a lifelong condition and there is no permanent cure for it. If proper care and treatment is taken, the quality of life of people with autism can be improved.
2) What is the main cause of autism?
-It is not yet known what causes autism ASD.
-This disorder is very complex and no two people with autism can be exactly alike, so there are many causes of autism.
- Interaction between genes and environment: Exposure to infections or chemicals in the environment can cause autism in a person who is susceptible due to genetics.
3) How long can autism last?
-Autism can start in a child before the age of 3 and it can last throughout his life. * Symptoms of autism Typically, a child with autism shows several signs, including: - Unexplainable tantrums - Unusual attachments - Unusual actions such as flapping hands - Fear of certain sounds - Not looking directly at any person or object
Videos

chronic atrophy or calcification pancreas ka ilaaj
१) क्रोनिक , एट्रोफी , कैल्सिफिकेशन पैंक्रियास का इलाज ?
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियास जटिल स्थिति है ,जिसमें पैंक्रियास में बार-बार सूजन हो जाती है, जिससे एट्रोफी और कैल्सिफिकेशन जैसे गंभीर बीमारी भी होते हैं। इस स्थिति का उपचार संभव है, लेकिन इसके लिए एक व्यापक और मल्टीडिसिप्लिनरी दृष्टिकोण की आवश्यकता होती है। आज का आर्टिकल में हम क्रोनिक, एट्रोफी, और कैल्सिफिकेशन पैंक्रियास के इलाज के अलग -अलग तरीकों पर बात करने वाले है
२) क्रोनिक पैंक्रियास के कारण और लक्षण क्या क्या है?
* क्रोनिक पैंक्रियास के कारण निचे बताये अनुसार हो सकते है ,जैसे की ,
-बहुत ही शराब का सेवन करना -आनुवांशिक कारण -ऑटोइम्यून विकार - ज्यादा ध्रूमपान करना * क्रोनिक पैंक्रियास के लक्षण निचे बताये अनुसार हो सकते है ,जैसे की , - पेट में बहुत ही दर्द का होना - वजन घट जाना- मधुमेह - भूख भी कम लगना
३) एट्रोफी और कैल्सिफिकेशन पैंक्रियास क्या है ?
एट्रोफी का अर्थ है की पैंक्रियास के कोशिका में सिकुड़ना या कार्य करने की शक्ति में कमी आना। इसके परिणाम स्वरूप पैंक्रियास में कैल्शियम जमा होने लग जाता है, जिसे कैल्सिफिकेशन पैंक्रियास कहते है। - यह स्थिति पाचन एंजाइमों और इन्सुलिन के पाचन और ग्लूकोज को कण्ट्रोल पर भी असर करता है।
४ ) पैंक्रियास को अच्छा रखने के लिए क्या क्या उपाय करना चाहिए?
पैंक्रियास को अच्छा बनाये रखने के लिए, कुछ उपाय करना चाहिए जैसे की ,
-डेली ५-८ गिलास पानी पीना चाहिए - संतुलित आहार का उपयोग करना . - डेली कसरत - शराब और सिगरेट से दुरी बनाये रखना - जंक फ़ूड न ही उपयोग करें.

Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency ka ilaaj
१) अग्नाशयी एक्सोक्राइन अपर्याप्तता (Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency - PEI) का इलाजअग्नाशयी एक्सोक्राइन अपर्याप्तता (PEI) एक स्थिति है जिसमें पैंक्रियास एंजाइमों का पर्याप्त उत्पादन या स्त्राव नहीं कर पाता। इसमें भोजन का अच्छे से पाचन नहीं हो पता है जिससे पोषण की कमी, वजन काम होना , और गैस्ट्रोइंटेस्टाइनल समस्याएँ हो सकती हैं। २) अग्नाशयी एक्सोक्राइन अपर्याप्तता का मुख्य कारण क्या है?अग्नाशयी एक्सोक्राइन अपर्याप्तता का मुख्य कारण पैंक्रियास की कार्य क्षमता में कमी होना होता है। इसके प्रमुख कारणों जैसे की ,-Chronic पैंक्रिअटिटिस : पैंक्रियास में लम्बे समय तक सूजन-Cystic फाइब्रोसिस : अनुवांशिक बीमारी -Pancreatic कैंसर : पैंक्रियास की संरचना और कार्य पर असर होना -अल्कोहल का अत्यधिक सेवन ३) अग्नाशयी एक्सोक्राइन अपर्याप्तता का क्या लक्षण है? अग्नाशयी एक्सोक्राइन अपर्याप्तता का लक्षण निचे अनुसार हो सकता है जैसे की ,-वजन कम होना -पेट में दर्द और सूजन का हो जाना -गैस की समस्या- विटामिन की कमी (A, D, E, K)४) अग्नाशयी एक्सोक्राइन अपर्याप्तता का परीक्षणों कैसे होता है ?PEI का परीक्षणों करने के लिए डॉक्टर कुछ जाँच करने को कहते है: जो की निचे अनुसार हो सकता है -Fecal Elastase Test-Steatorrhea Test-सीटी स्कैन -MRI-ब्लड टेस्ट

pancreatitis ka satik ilaaj kya hai
पैंक्रियास का सटीक इलाज
पैंक्रियास, को हम दूसरे अग्नाशय के नाम में भी जानते है, यह शरीर के एक महत्वपूर्ण भागो में से एक है,पाचन और शरीर में इंसुलिन और अन्य पाचक एंजाइमों के उत्पादन के लिए जिम्मेदार होता है।-आज के इस आर्टिकल में हम पैंक्रियास से संबंधित बीमारियों का इलाज कैसे होता है, इसके अलग -अलग पहलुओं पर चर्चा करने वाले है ।
१) पैंक्रियास से संबंधित सामान्य कौन कौन सी बीमारियाँ है?
- यह पैंक्रियास की सूजन से संबंधित बीमारि है। यह २ तरह के हो सकते है एक्यूट या क्रोनिक पैंक्रियास. एक्यूट पैंक्रियाटाइटिस में अचानक दर्द होता है जबकि क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस में धीरे-धीरे और लंबे समय तक दर्द बना रहता है।
- पैंक्रियास कैंसर : पैंक्रियास की कोशिकाओं में उत्पन्न होती है। यह कैंसर अक्सर शुरुआती अवस्था में उपचार नहीं हो पाता, जिससे इसका इलाज और भी जटिल हो जाता है।
डायबिटीज : यह स्थिति खून में ग्लूकोज के स्तर को उच्च कर सकता है।
२) पैंक्रियास को स्वस्थ रखने के लिए, क्या उपाय करना चाहिए?पैंक्रियास को स्वस्थ रखने के लिए, निचे बताये अनुसार उपाय कर सकते है , जैसे की - भरपूर मात्रा में संतुलित आहार का उपयोग - डेली कसरत करना - शराब और सिगरेट से दूर रहना - अधिक मात्रा में पानी पीना - जंक फ़ूड से दूर रहना .
३) पैंक्रियास बिमारियों का पता कैसे लगया जाता है?
पैंक्रियास की बीमारियों का पता लगाने के लिए डॉक्टर कुछ जाँच करने के लिए कहते है जिसमे :
--सीटी स्कैन, -MRCP, - रक्त परीक्षण.
